In the world of electronics, there are two main types of transistors: PMOS and NMOS. But what’s the difference between them? In this comprehensive guide, we will answer all of your questions about PMOS and NMOS transistors. We will discuss their characteristics, how they are used in circuits, and tips for using them effectively. So whether you’re a beginner or an experienced engineer, read on to learn everything you need to know about PMOS and NMOS transistors!
MOSFET Transistors in General
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to amplify or switch electronic signals and electrical power. It is composed of semiconductor material with at least three terminals for connection to an external circuit. A voltage or current applied to one pair of the transistor’s terminals changes the current through another pair of terminals. Because the controlled (output) power can be much more than the controlling (input) power, the transistor provides amplification of a signal. Today, some transistors are packaged individually, but many more are found embedded in integrated circuits.
The MOSFET, (short for metal-oxide-semiconductor field-effect transistor) is a type of Field Effect Transistor (FET). MOSFETs are the most common type of FET. The main difference between a MOSFET and other types of FETs is that a MOSFET can be made with very small dimensions. This allows for higher speed operation and lower power consumption. [1]
Uses of MOSFET Transistors
MOSFETs are one of the most important types of transistors used today. They are used in a wide variety of electronic applications, including:
- Computers
- Cell phones
- Televisions
- Digital cameras
- DVD players
MOSFETs are also used in more industrial applications, such as:
- Automotive electronics
- Security systems
- Energy management systems
There are two types of MOSFET transistors: PMOS and NMOS. Let’s take a closer look at each type. [1], [2]
What is a PMOS Transistor?
A PMOS transistor is a field-effect transistor that uses a n-type semiconductor for the substrate, where “n” stands for negative. In contrast, the drain and source of PMOS are constructed of p-type semiconductor. A PMOS transistor can be thought of as an enhancement-mode MOSFET with the source and drain swapped.
The most important thing to know about PMOS transistors is that they are basically the opposite of NMOS transistors. When the low voltage is applied to the gate, it repels the electrons in the body and creates a p-type channel between the source and drain. This conducts current from the source to the drain, allowing current to flow through the transistor. On the contrary, if high voltage is applied to the gate, the transistor will simply not conduct.
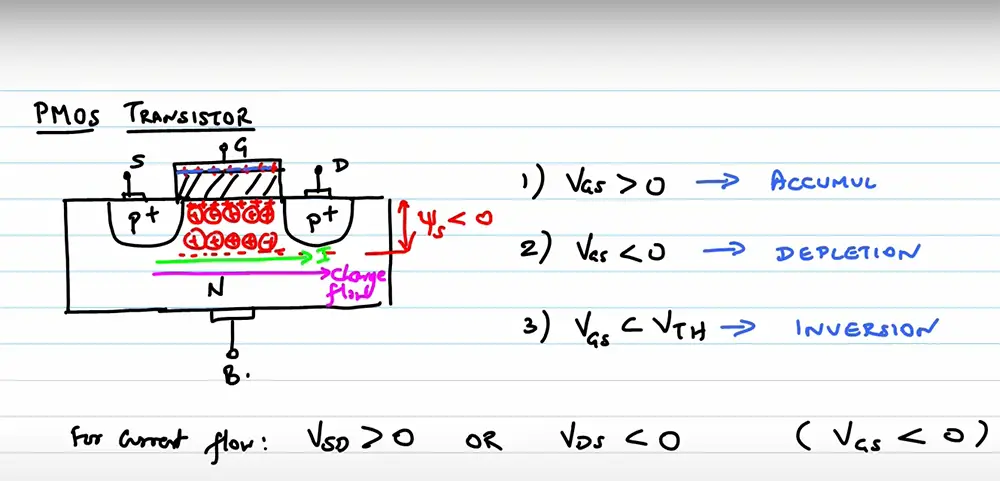
As you might expect, PMOS transistors are used in a variety of electronic devices, including computers, cell phones, and other digital electronics. They are also used in some analog circuits, such as operational amplifiers. [3], [4]
What is an NMOS Transistor?
NMOS transistors are made with a semiconductor material that has been doped with impurities. Contrary to PMOS, NMOS transistors are constructed from the p-type substrate, while the source and drain are made of n-type. The current flow in an NMOS transistor is from the source to the drain, and is controlled by the voltage applied to the gate.
When low voltage is applied to the gate, the transistor is in its cut-off state, meaning that no current flows between the source and drain. In case high voltage is applied however, the transistor is turned “on,” meaning that current can flow between the source and drain.
The reason NMOS transistors are used so often in digital circuits is that they can be made very small. This makes them ideal for use in digital circuits where space is at a premium.
Definition of CMOS Transistors
CMOS transistors are a type of a transistor (FET) that is created using both PMOS and NMOS transistors in its construction. CMOS transistors are used in many different types of electronic devices, including computers, cell phones, and other digital electronics. They are also used in some analog circuits, such as operational amplifiers.
The most interesting thing about CMOS transistors, is that they inherit qualities of both PMOS and NMOS devices. The PMOS transistor is responsible for conducting current when the voltage is low, while the NMOS transistor is responsible for conducting current when the voltage is high.
CMOS transistors are sometimes used in place of NMOS or PMOS transistors because they have better electrical characteristics and can be manufactured more cheaply. [4]
Differences Between PMOS and NMOS Transistors
Now that we’ve looked at each type of MOSFET transistor, let’s compare and contrast them.
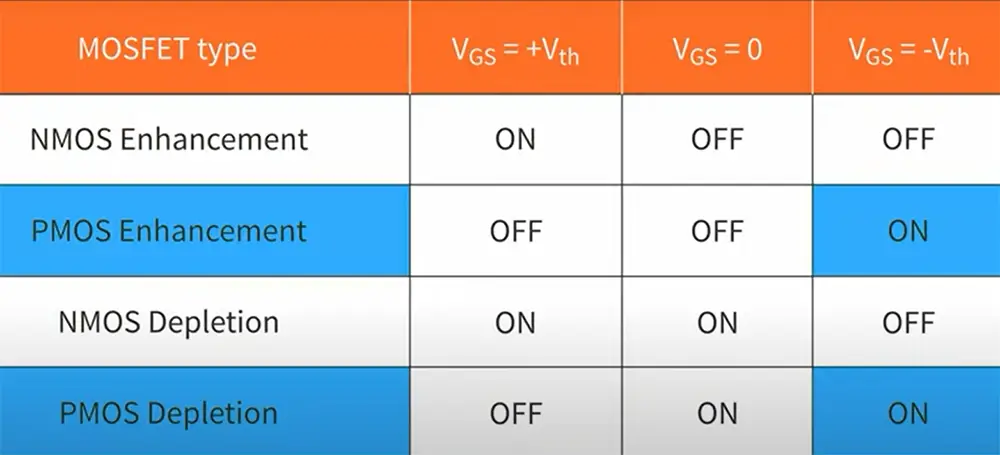
The construction
The main difference between PMOS and NMOS is the conductivity type of the channel. The type of semiconductor material used in the channel region determines the direction of current flow through the transistor.
The construction of a PMOS transistor is the opposite of an NMOS transistor. In a PMOS transistor, the source and the drain are made of p-type semiconductor material. Given PMOS have holes as charge carriers, these charge carriers flow from source to drain. The direction of the current in PMOS transistors is equal to the direction of the carriers.
In an NMOS transistor, the channel is made of n-type semiconductor material, and the direction of charge carriers (in this case its electrons) is the exact opposite, from drain to source. When it comes to the direction of the current flow, here it’s the opposite from the charge flow. [3], [4]
Carrier type
This difference in construction also means that PMOS and NMOS transistors are made of different types of carriers. In a PMOS transistor, the carriers are holes, and in an NMOS transistor, the carriers are electrons.
The type of carrier affects the way the transistor works. Holes have a lower mass than electrons, so they can move more quickly through the channel. This means that PMOS transistors can be turned on and off more quickly than NMOS transistors. [1], [3], [4]
Footprint size
Another difference between PMOS and NMOS transistors is the size of their footprint. The footprint is the area on a circuit board that the transistor occupies.
PMOS transistors have a larger footprint than NMOS transistors because they require more space for the p-type channel. NMOS transistors have a smaller footprint because they only require an n-type channel.
This difference in size can be important in applications where space is limited, such as in integrated circuits (ICs). [6]
ON resistance
Another difference between PMOS and NMOS is ON resistance. The ON resistance of a transistor is the resistance of the channel when the transistor is turned on.

The ON resistance of a PMOS transistor is higher than the ON resistance of an NMOS transistor. This is because p-type semiconductor material has lower conductivity than n-type semiconductor material.
The ON resistance of a PMOS transistor can be reduced by increasing the width of the channel. However, this also increases the size of the transistor, which may not be desirable in some applications. [3], [4], [6], [7]
Speed
One of the main differences between PMOS and NMOS transistors is speed. NMOS transistors are faster than PMOS transistors because they have a shorter channel length. This means that electrons can travel through the transistor more quickly.
PMOS transistors are slower than NMOS transistors, but they are still fast enough for most applications. [6]
Noise
One final difference between PMOS and NMOS transistors is that PMOS transistors are less noisy than NMOS transistors. Noise is any unwanted electrical signal that can interfere with the operation of a circuit.
PMOS transistors are less noisy because the holes in the p-type channel can cancel out the noise generated by the electrons in the n-type channel. This property can be important in applications where low noise levels are required, such as in audio amplifiers. [6]
FAQ
Which one is better: NMOS or PMOS?
It depends on what application you are using them for. NMOS is typically used for digital circuits where it can switch faster than PMOS. PMOS is often used in analog circuits where a lower voltage is required to turn it on.
Both types of transistors have their pros and cons, so it really comes down to what your specific needs are.
Is PMOS or NMOS faster?
This is a difficult question to answer because it really depends on the application. In general, though, NMOS is considered to be faster than PMOS. This is because NMOS has a shorter channel length and can therefore carry a current more quickly. Additionally, the electrons in an NMOS transistor are lighter than the holes in a PMOS transistor, which also makes them faster.
How do PMOS and NMOS transistors work?
PMOS and NMOS transistors both use an electric field to control the flow of current through a semiconductor. The main difference between PMOS and NMOS transistors is the type of charge carrier that they use. PMOS transistors use positive charges, holes, while NMOS transistors use negative charges, electrons.
Another key difference between PMOS and NMOS transistors is the way that they are biased. In order for a PMOS transistor to be turned on, the voltage at the gate must be LOW. For an NMOS transistor to be turned on, however, the voltage at the gate must be HIGH.
What does an NMOS transistor do?
The NMOS transistor is a type of MOSFET transistor. It is made of two n-type semiconductor materials, which are separated by a thin layer of insulating material. When a voltage is applied to the gate, it creates an electric field that attracts electrons from one of the n-type materials to the other. This creates a conducting path between the two materials, and current can flow through the transistor.
Useful Video: NMOS vs PMOS and Enhancement vs Depletion Mode MOSFETs | Intermediate Electronics
Conclusion
So, PMOS and NMOS are both types of MOSFET transistors, but they are different in a few ways. Most notably, their construction is different – PMOS transistor source is built with p-type material while NMOS transistors are built with n-type material as the source. Additionally, the speed at which these two transistor types operate is different; NMOS transistors are faster than PMOS transistors. Another key difference between these two transistor types regards carrier type: PMOS transistors use holes as carriers while NMOS transistors use electrons as carriers. Finally, footprint size and noise amount vary between PMOS and NMOS devices. That’s it, thanks for reading!
References:
- https://www.watelectronics.com/types-of-mosfet-applications/
- https://www.easytechjunkie.com/what-is-a-mosfet-amplifier.htm
- https://pediaa.com/difference-between-nmos-and-pmos/
- https://www.etechnog.com/2021/11/difference-pmos-nmos-cmos-symbol.html
- https://electronics.stackexchange.com/questions/567586/what-affirms-channel-current-direction-in-nmos-and-pmos
- https://anysilicon.com/introduction-to-nmos-and-pmos-transistors/
- https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/technical-articles/mosfet-channel-length-modulation/






 In my perspective, MOSFETs stand out as the go-to choice among Field Effect Transistors (FETs). Their prowess lies in the ability to achieve remarkably small dimensions, facilitating high-speed operation and minimizing power consumption. This makes MOSFETs a cornerstone in modern electronics, offering a winning combination of efficiency and performance.
In my perspective, MOSFETs stand out as the go-to choice among Field Effect Transistors (FETs). Their prowess lies in the ability to achieve remarkably small dimensions, facilitating high-speed operation and minimizing power consumption. This makes MOSFETs a cornerstone in modern electronics, offering a winning combination of efficiency and performance.






Leave a Reply