When it comes to mini PCs, the Raspberry Pi and Orange Pi are two of the most popular options on the market. Both devices offer a low-cost way to get into computing, and they both have their own strengths and weaknesses. In this article, we will compare these two devices and help you decide which is the better option for you.
What Is Single Board Computing?
This board includes everything required to run an operating system and connect to peripheral devices.
The term “single board computer” might conjure up images of ancient computers like the Commodore 64 or early Apple II, but modern SBCs are powerful machines that can handle demanding tasks.
The two most popular SBCs on the market today are the Orange Pi and Raspberry Pi. [1]
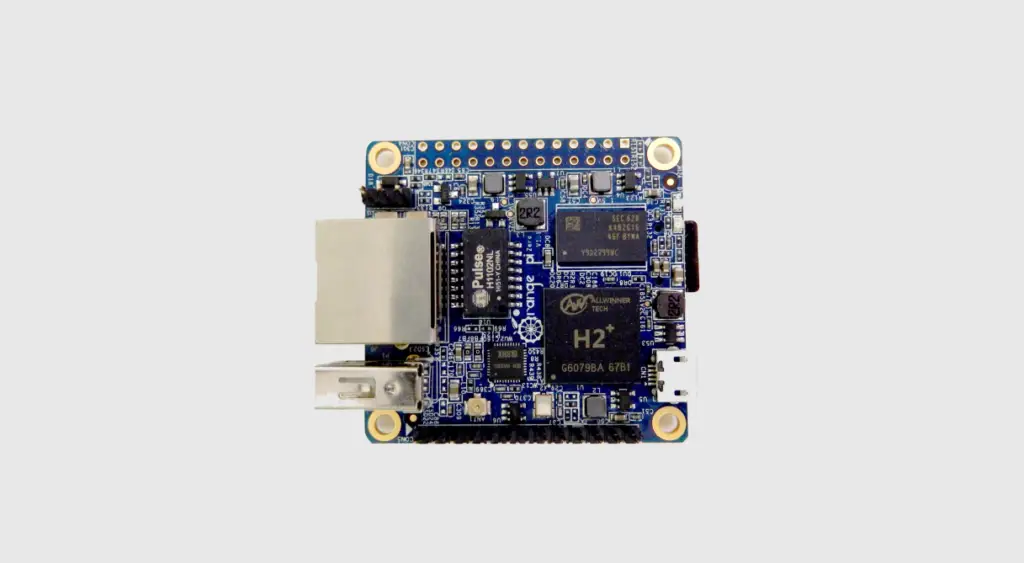
What Is Orange Pi?
Its main aim is to promote the use of open source hardware in computing, and it offers a range of affordable, single-board computers based on various chipsets. The company is best known for its Orange Pi series of boards, which are similar in many respects to the Raspberry Pi.
Like the Raspberry Pi, Orange Pi boards are available in a variety of sizes and styles. The most popular model is the Orange Pi Plus 2, which features an Allwinner H3 quad-core Cortex-A7 CPU and 1 GB of RAM.
Other models include the Orange Pi Lite (Allwinner H3, 512 MB RAM), Orange Pi Zero (Allwinner H2+, 512 MB RAM), and Orange Pi PC Plus (Allwinner A20, 1 GB RAM). [2]
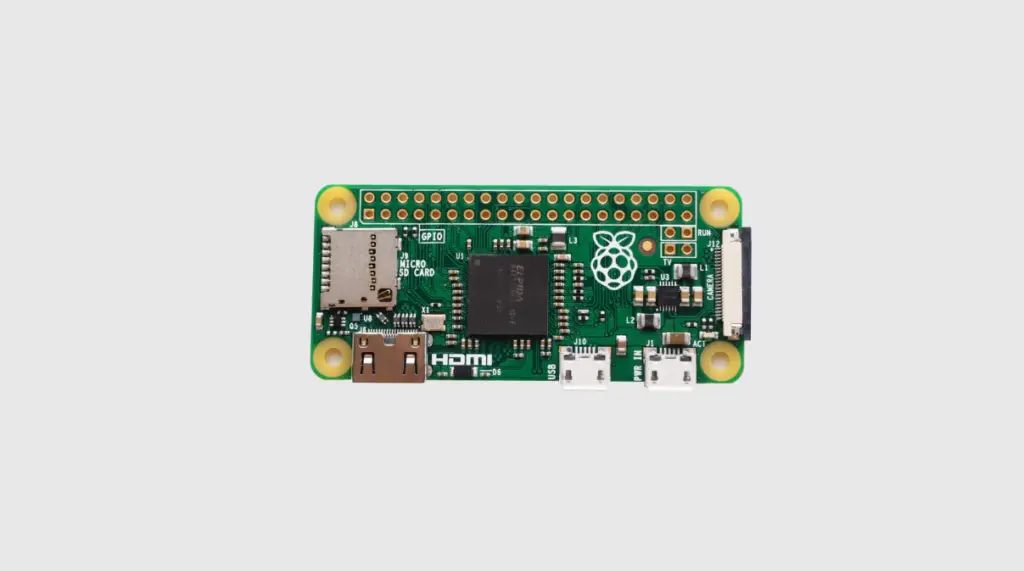
What Is Raspberry Pi?
This PC can handle many of the things you do on a desktop computer, such as spreadsheets, word-processing and games. It also plays high-definition video.
Orange Pi vs Raspberry Pi: Differences
RAM
The Orange Pi has double the RAM of the Raspberry Pi.
Video and audio output
Both boards can output 1080p video, but the Orange Pi can do so over HDMI while the Raspberry Pi requires an adapter for that. As for audio, the Orange Pi can output sound over HDMI or 3.5 mm jack while the Raspberry Pi only offers HDMI output.
Ports and GPIO
The Orange Pi has more ports than the Raspberry Pi, including 4 USB 2.0 ports vs 2 on the Raspberry Pi, and an Ethernet port while the Raspberry Pi requires an adapter to connect to the internet. The Orange Pi also has a 40-pin GPIO while the Raspberry Pi only has a 26-pin GPIO.
Processor and speed
The Orange Pi uses a faster processor than the Raspberry Pi, an Allwinner H3 at 1.6 GHz vs the Broadcom BCM2837 at 1.2 GHz used by the Raspberry Pi 3. As a result, the Orange Pi is about 50% faster than the Raspberry Pi.
Price
The Orange Pi costs more than the Raspberry Pi, but it is still very affordable at around $20.
GPU
The Orange Pi has a more powerful GPU than the Raspberry Pi, which is important for tasks such as video streaming and gaming.
Storage
The Orange Pi also has a better storage option, with an eMMC module slot vs the microSD card used by the Raspberry Pi.

Ethernet
The Orange Pi also has an Ethernet port while the Raspberry Pi requires an adapter to connect to the internet.
Bluetooth
The Orange Pi also has Bluetooth while the Raspberry Pi does not.
WiFi
The Orange Pi Plus 2E has 802.11 b/g/n WiFi while the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ has 802.11 b/g/n/ac WiFi. This means that the Orange Pi Plus 2E is limited to speeds of up to 150Mbps while the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ can reach speeds of up to 433Mbps. [3]
4K Compatible
The Orange Pi Plus 2E is not 4K compatible while the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ is. This means that the Orange Pi Plus 2E can only output 1080p video while the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ can output up to 4K video.
OS Supported
The Orange Pi Plus 2E can run on a variety of operating systems including Android, Linux, and Windows while the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ is only compatible with Linux and Windows.
Weight
The Orange Pi Plus 2E weighs 45 grams while the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ weighs 50 grams.
Ease of Use
The Orange Pi Plus 2E is easier to use than the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+. This is because the Orange Pi Plus 2E has a built-in WiFi and Bluetooth while the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ does not.
UART
The Orange Pi Plus 2E has two UARTs while the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ only has one. The applications for the Orange Pi Plus 2E are vast, GPS tracking and home automation among them. The Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+, on the other hand, is limited to one UART.
PWM
The Orange Pi Plus 2E has four PWMs while the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ only has two. This means that the Orange Pi Plus 2E can be used for a variety of applications such as LED dimming and motor control while the Raspberry Pi 3 Model B+ is limited to two PWMs.

Suitable Projects
Raspberry Pi is best for traditional computing and gaming, while Orange Pi is better suited for more embedded projects.
Some people might try to use the Raspberry Pi for more industrial applications, but it’s really not made for that. It’s a great little computer for school projects and simple applications, but when it comes to more demanding tasks, you’re better off with an Orange Pi. The main difference between the two boards is that the Orange Pi has a faster processor and can handle more intensive tasks. It also has more I/O ports, so you can connect more peripherals. If you need a mini PC for basic tasks, the Raspberry Pi is a great choice. But if you need something more powerful, go with the Orange Pi.
Both the Orange Pi and the Raspberry Pi are great for hobbyists and students. They’re both affordable and easy to use. If you’re just getting started with mini PCs, either one would be a great choice. But if you need more power, go with the Orange Pi. It’s the better mini PC for more demanding tasks.
Pros and Cons of Raspberry Pi
There are several reasons for the popularity of the Raspberry Pi mini computer. Firstly, it is very affordable compared to other options on the market.
Secondly, it is relatively easy to use and set up, which makes it a great option for first-time users or those who are not particularly tech savvy.
Finally, the Raspberry Pi comes with a wide range of accessories and support from both the manufacturer and the large online community, making it a very versatile platform.
However, there are also some drawbacks to using a Raspberry Pi. One of the biggest issues is that it can be quite slow compared to more expensive options, such as the Orange Pi. Additionally, the Raspberry Pi does not have as many features as some of its competitors, meaning that it might not be the best option for more experienced users or those who want a mini computer with more bells and whistles.

Pros and Cons of Orange Pi
Pros:
- Much cheaper than the Raspberry Pi.
- Can be used as a server.
- Has more GPIO pins.
- Supports Wi-Fi and Bluetooth.
Cons:
- Not as widely supported as the Raspberry Pi.
- Lacks some of the features of the Raspberry Pi.
So, which mini PC is better? The answer may depend on your needs. If you’re looking for a cheap and cheerful way to get started with mini PCs, then the Orange Pi is a great option. However, if you need something that’s more widely supported and has more features, then the Raspberry Pi is the better choice. Ultimately, it all comes down to what you need from your mini PC.
Things to Consider When Using SBCs
When it comes to single-board computers (SBCs), there are a few key factors that you need to consider before making your purchase. These include:
- Price
- Processing power
- Connectivity options
- Operating system compatibility
- Community support
Types of SBCs
There are two primary types of SBCs available on the market: those based on ARM processors and those based on x86 processors. The Orange Pi and Raspberry Pi boards are both based on ARM processors.
ARM vs. x86 Processors
ARM processors are generally more power-efficient than x86 processors, which is one of the reasons why they are used in mobile devices like smartphones and tablets. They typically provide better performance per watt than x86 processors as well.
x86 processors, on the other hand, offer more raw processing power than ARM processors. This type of computer is also better for resource-intensive tasks, like video editing or gaming.

When it comes to mini PCs, both ARM-based and x86-based boards have their own advantages and disadvantages. [4]
Advantages of ARM-based Boards
The biggest advantage of ARM-based mini PCs is their power efficiency. They are therefore perfect for when power is an issue, like in embedded systems or portable devices.
Another advantage of ARM-based boards is that they are typically less expensive than their x86 counterparts. This is due to the fact that there are many different companies manufacturing ARM processors, which increases competition and drives down prices.
Disadvantages of ARM-based Boards
One downside of ARM- based mini PCs is that they often have less processing power than x86-based boards. This can be a problem for tasks that require a lot of computational power, such as video editing or gaming.
Another potential disadvantage of ARM-based mini PCs is that they may not be compatible with all software. The reason for this is that the x86 processor is widely compatible with many types of software. As a result, you may need to use special versions of some programs or find workarounds to get them to run properly on an ARM-based board.
Advantages of x86-based Boards
The biggest advantage of x86-based mini PCs is their processing power. They are typically much faster than ARM- based boards, which makes them better suited for tasks that require a lot of computational power.
Another advantage of x86-based mini PCs is that they are compatible with the vast majority of software. This is because most software is designed to run on x86 processors. As a result, you should have no problem running any program on an x86-based board.
Disadvantages of x86- based Boards
One downside of x86-based mini PCs is that they often consume more power than ARM-based boards. This can be a problem for use cases where power consumption is a concern, such as in embedded systems or portable devices.
Another potential disadvantage of x86-based boards is that they may be more expensive than their ARM counterparts. This is due to the fact that there are fewer companies manufacturing x86 processors, which decreases competition and drives up prices.
What is the Difference Between Gateway and SBC?
A gateway is a device that connects two or more networks.
An SBC typically includes a CPU, RAM, storage, and I/O ports. A gateway typically includes a CPU, RAM, storage, and one or more communication ports.

The main difference between an SBC and a gateway is that an SBC is designed to be a complete computer while a gateway is designed to connect two or more networks. [5]
How Do You Identify Your SBC Engine?
The best way to identify your SBC engine is to look at the board layout and compare it to known SBC engines. You can also check the specifications of the CPU and other components to see if they match those of a known SBC engine.
If you are still unsure, you can always contact the manufacturer of the board and ask them directly.
What is an SBC Form Factor?
The most common form factor is the CompactPCI, which is used in industrial and military applications.
Other popular form factors include the PC/104, which is used in embedded systems, and the Mini-ITX, which is used in small form factor PCs. [6]
What is an SBC Carrier Board?
A carrier board is a circuit board that provides power, data, and/or communication connections to a single-board computer (SBC). Carrier boards are typically used in industrial and military applications where the SBC needs to be mounted in a specific environment.
The carrier board typically has connectors for the SBC’s I/O ports, power inputs, and other interfaces. It may also have expansion slots for additional Daughter Boards.
How to Use SBC?
There are a few different ways to use an SBC. The most common way is to mount it on a carrier board and then install it in a specific environment, such as an industrial control panel or a military vehicle.
Another way to use an SBC is to plug it into a standard computer case and use it as the main computer. This is often done with the Mini-ITX form factor.
General Tips on Using an SBC
Here are a few general tips on using an SBC:
- Make sure the power supply is adequate for the SBC and any additional devices that will be connected to it.
- Check the manufacturer’s website for recommended operating conditions, such as temperature and humidity ranges.
- Read the documentation carefully before connecting any devices or installing any software.
- Follow the manufacturer’s recommendations for mounting the SBC in a specific environment.
- Use caution when handling the SBC, as static electricity can damage sensitive components.
What is SBC Security?
SBC security typically involves installing a firewall and/or antivirus software on the SBC, as well as physically securing the SBC itself.
SBC security is important in any application where the SBC could be accessed by unauthorized individuals, such as in industrial control systems or military vehicles.
How to Secure Your SBC?
Here are a few tips on how to secure your SBC:
- Install a firewall and/or antivirus software on the SBC.
- Physically secure the SBC so that it cannot be easily accessed or removed.
- Disable any unused network ports and services.
- Change the default password for any user accounts on the SBC.
- Keep the SBC software up to date with the latest security patches.
Why is SBC Needed?
SBCs are needed in any application where a complete computer is required in a small form factor. SBCs are often used in industrial and military applications where space is limited and the environment is harsh.

SBCs are also used in consumer electronics, such as set-top boxes and media centers. In these applications, the SBC provides all the features of a full-fledged computer in a package that is small enough to fit inside the device.
What Are The Benefits of Using an SBC?
There are many benefits to using an SBC, including:
- Small form factor – SBCs are much smaller than traditional PCs, making them ideal for applications where space is limited.
- Low power consumption – SBCs consume less power than traditional PCs, making them ideal for battery-operated devices.
- Rugged design – SBCs are often designed to operate in harsh environments, such as industrial control panels or military vehicles.
- Wide range of capabilities – SBCs can be equipped with a wide range of capabilities, such as video and audio processing, making them ideal for multimedia applications.
- Cost-effective – SBCs are often more cost-effective than traditional PCs, making them ideal for budget-conscious applications.
FAQ
What is better than Raspberry Pi?
There are a variety of ways to answer this question, but for the most part, the Raspberry Pi is simply a more powerful device. It has a faster processor, more RAM, and just generally better performance overall. Additionally, it offers more features and options than the Orange Pi. If you’re looking for a mini PC that can do more, the Raspberry Pi is the way to go.
Does Raspberry Pi make Orange Pi?
No, Raspberry Pi does not make Orange Pi. They are two separate companies. However, both devices are designed for similar purposes – to be used as mini PCs or single-board computers.
What is the difference between Orange Pi and Raspberry Pi?
The main differences between the Orange Pi and the Raspberry Pi are in terms of power and performance. The Orange Pi is a less powerful device, with a slower processor and less RAM. Additionally, it doesn’t offer as many features and options as the Raspberry Pi. However, it is still a perfectly capable mini PC and can be used for a variety of tasks.
Which is better: Raspberry Pi or Banana Pi?
This is a difficult question to answer, as it depends on your specific needs and preferences. However, in general, the Raspberry Pi is the better choice. It offers more power and performance, as well as more features and options. If you’re looking for a mini PC that can do more, the Raspberry Pi is the way to go.
Is Orange Pi or Raspberry Pi better for gaming?
There’s no clear answer when it comes to gaming on Orange Pi vs. Raspberry Pi. It depends on what kind of games you want to play and what level of performance you’re expecting. If you’re looking for the best possible gaming experience, you’ll probably be better off with a more powerful mini PC like the ODROID-XU4. However, if you’re just looking to play some basic games or emulator games, either the Orange Pi or the Raspberry Pi should be able to handle that just fine.
Is Orange Pi easy?
It can be, depending on your level of experience. If you’re new to single-board computers, the Orange Pi might be a better option since it’s generally easier to set up and use. However, if you’re more experienced with these types of devices, the Raspberry Pi might be the better choice since it offers more flexibility and customization options.
What are some cons of the Orange Pi?
Some potential cons of the Orange Pi include its relative lack of power compared to other mini PCs on the market and its relatively high price point. Additionally, it can be difficult to find compatible software for the device, which can limit its usefulness.
What OS can Orange Pi run?
The Orange Pi can run a variety of operating systems, including Android, Ubuntu, and Raspbian.
Can I install Raspbian on Orange Pi?
Yes, you can install Raspbian on the Orange Pi. However, since the Orange Pi is a different type of device than the Raspberry Pi, some software that is designed for the Raspberry Pi might not work on the Orange Pi.
Why are Raspberry Pis so hard to get?
The Raspberry Pi is in high demand and can be difficult to find in stock. This is due to its relatively low price point and its powerful hardware.
What is so great about Raspberry Pi?
It’s also relatively inexpensive, which makes it a great option for budget-conscious consumers. Additionally, the Raspberry Pi is easy to use and has a large community of users who can offer support and assistance.
What are some cons of the Raspberry Pi?
Some potential cons of the Raspberry Pi include its relatively low power compared to other mini PCs on the market and its lack of built-in storage. Additionally, the device can be difficult to set up and use, which can deter some users.
Useful Video: Raspberry Pi 2 VS Orange Pi 2 VS BPi-M2
Conclusion
So, which is the better mini PC? The Orange Pi or the Raspberry Pi?
The answer really depends on what you need it for. If you are looking for a low-cost computer for basic tasks and general use, then the Raspberry Pi is a great choice. It is also a great platform for learning programming and tinkering with electronics.
On the other hand, if you need more power and functionality, then the Orange Pi is the better option. It offers more powerful hardware, more features, and more flexibility. However, it does come at a slightly higher price tag.
Ultimately, the decision comes down to your specific needs and preferences. Whichever mini PC you choose, you are sure to get a great little computer that can handle a variety of tasks.
References
- https://www.baesystems.com/en-us/definition/what-are-single-board-computers
- https://www.educba.com/orange-pi-vs-raspberry-pi/
- http://www.orangepi.org/html/hardWare/computerAndMicrocontrollers/details/Orange-Pi-Plus-2E.html
- https://all3dp.com/2/single-board-computer-x86-sbc/
- https://www.ecguc.com/sbc-vs-gateway/dds,number%20to%20reach%20the%20gateway.
- https://www.winsystems.com/so-many-form-factors-how-do-i-choose/











Leave a Reply