A run capacitor is an essential component of an HVAC system as it aids the compressor in starting and running more efficiently. It is crucial to have a properly sized run capacitor to ensure that your compressor has enough power to start and run smoothly. However, there may be instances when you wonder if using a larger run capacitor is feasible. Unfortunately, finding an answer to this question can be challenging. In this article, we’ll provide a comprehensive guide on how to determine if you can use a larger run capacitor and offer tips on how to make the switch if it’s possible. Whether you want to upgrade your current capacitor or are just starting your research, this article contains all the information you need.
Brief Summary
The article explains what a capacitor is and its uses in electronic circuits. It distinguishes between start capacitors which provide a temporary voltage boost to start motors, and run capacitors which provide continuous voltage to keep motors running. The microfarad (MFD) rating measures a capacitor’s ability to store electric charge. Capacitors wear out over time or can fail prematurely from overheating, excessive charging/discharging cycles, or other stresses.
The article then focuses on whether you can replace an AC system’s run capacitor with a larger MFD capacitor. It explains that you can use a larger run capacitor up to 20% greater MFD rating but you should not use a smaller capacitor as that risks motor damage or appliance inefficiency. The replacement capacitor’s voltage rating should equal or exceed the original. Reasons to replace a run capacitor include visible damage or testing shows out-of-spec capacitance/resistance. The article concludes that, with proper voltage rating and not too large an increase in MFDs, a larger run capacitor can replace an original capacitor and may even improve system performance.
What is a Capacitor?
A capacitor is an electronic component that stores and releases electrical energy. Capacitors are found in a wide range of electronic devices, from small capacitors used in digital cameras to large capacitors used in power supplies.
The capacitor can be used to smooth out the ripple voltage in a DC power supply. Ripple is the AC component of the DC voltage that appears at the output of rectifier circuits. The capacitor stores energy during the positive half-cycle of the AC waveform and supplies it to the load during the negative half-cycle. This action effectively increases the average value of the DC voltage at the output of the rectifier circuit.
The capacitor can also be used to filter the AC component from a signal. For example, if we want to measure the DC voltage of a circuit that contains an AC component, we can use a capacitor to remove the AC component from the signal.
Timing circuits are another common application of a capacitor. The time constant of a capacitor-resistor (CR) circuit is determined by the value of the capacitor and resistor. The time constant is the time it takes for the voltage across the capacitor to charge or discharge to 63% of its final value. [1], [2]
The Definition of MFD Rating
The microfarad (µF) rating of a capacitor is its capacitance value. The farad is the unit of capacitance in the International System of Units (SI). One farad is equal to one coulomb per volt, which is a very large amount of capacitance. Most capacitors used in electronic circuits have values that are measured in microfarads or picofarads.
In other words, the MFD rating is the measure of a capacitor’s ability to store an electric charge. The MFD number will be printed on the case or label of the capacitor. You might also see uF, mfd, or MF written.
Larger capacitors have the ability to store more electrical energy than smaller capacitors. This is why mfd is an important rating to look for when selecting a capacitor. The larger the mfd rating, the more electrical energy the capacitor can store. [1], [2]
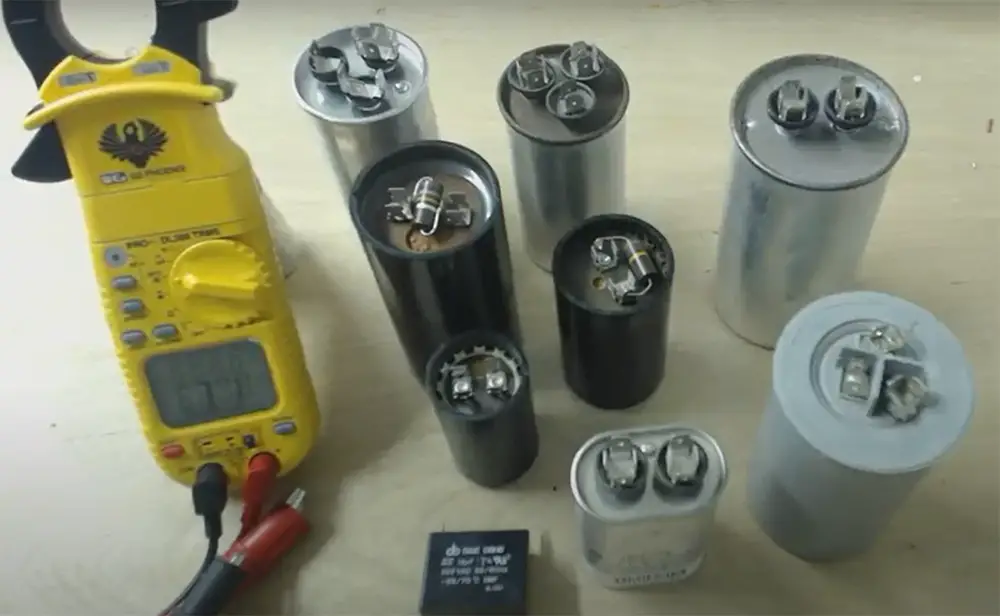

Difference Between Start and Run Capacitors
There are two main types of capacitors: start and run and there’s a big difference between them.
Start Capacitors
Start capacitors are used to help motors start up. They are connected to the motor’s winding and provide a boost of energy when the motor starts. Start capacitors are usually larger than run capacitors and have a higher voltage rating.
Run Capacitors
A run capacitor is an electrolytic capacitor with a relatively high capacitance value. A run capacitor is used to store electrical energy and to help maintain a constant voltage level. Run capacitors are designed to stay connected to a circuit for long periods of time and can handle large amounts of current. Run capacitors are typically cylindrical in shape and come in a variety of sizes.
From this we can conclude that start capacitors are used to briefly increase the motor’s rotor speed at startup, while run capacitors provide continuous voltage to the motor once it’s up and running. This is why start capacitors are only engaged for a few seconds at a time, while run capacitors stay engaged 24/seven. [2]
What Does Capacitor Voltage Mean?
Before we move on to the question ‘can you use a larger run capacitor?’ we need to understand what capacitor voltage means. Capacitor voltage is the potential difference across the plates of a capacitor, and is measured in volts.
When Do You Need to Replace a Capacitor?
If your capacitor is bulging, leaking, or showing any signs of physical damage, then it needs to be replaced as soon as possible. A bad run capacitor can cause all sorts of problems, from reducing the lifespan of your HVAC unit to causing it to overheat.

The first thing you’ll want to do is check the condition of your capacitor. If it’s swollen or leaking, it definitely needs to be replaced. You should also check for any burnt marks or discoloration, as this could be a sign of overheating. If your capacitor looks corroded or damaged in any way, it’s best to change it as well.
If your capacitor isn’t visibly damaged, you can try testing it with a multimeter to see if it’s still functioning properly. To do this, you’ll need to remove the capacitor from its housing and disconnect the wires. Once you’ve done that, you can use the multimeter to test the capacitance and resistance values. If either of these values is out of the normal range, then your capacitor needs to be replaced.
Can I Replace a Run Capacitor With a Higher MFD Run Capacitor
Yes, you can use a larger run capacitor, but only if the mfd or uf rating is equal to or greater than the original capacitor by up to 20%. Using a larger capacitor will not damage the motor or the run capacitor. In some cases it can actually improve the performance of the motor.
However, if you use a smaller capacitor, it will not be able to store as much electrical energy, and your air conditioner or other appliance may not run as efficiently.
It is also important to make sure that the voltage rating of the new capacitor is equal to or greater than the original capacitor. If you use a capacitor with a lower voltage rating, it could affect the performance of your appliance or cause damage to the appliance. Under Voltage capacitors will fail much sooner than those that are properly rated.
If you are unsure about what size capacitor you need, it is best to consult a qualified technician. A technician will be able to determine the correct size and type of capacitor for your appliance. If you attempt to replace the capacitor yourself, make sure that you follow all safety precautions and instructions included with the new capacitor. [3], [4]
Can I Replace a Run Capacitor With a Lower Run Capacitor
No, you cannot replace a run capacitor with a lower mfd or uf rating. Doing so could damage your appliance or cause it to operate less efficiently. If you install the wrong sized capacitor, the motor will not have an even magnetic field. This can cause the motor to fail.
Start capacitors will suffer the same consequences if they are not the proper size. A start capacitor that is too small will not be able to provide enough electrical energy to get the motor started fast enough. In some cases, the motor may not start at all. [3], [4]
Why Can Capacitors Fail
Unfortunately, capacitors are not indestructible, and they will eventually fail.
Time
Just like anything else, capacitors have a limited lifespan. The length of time a capacitor can last depends on a number of factors, including the type of capacitor, the quality of the capacitor, and the operating conditions. In general, electrolytic capacitors have a shorter lifespan than film capacitors. This is because the electrolyte inside electrolytic capacitors is more likely to dry over time and become less conductive. This causes the capacitor to slowly lose its ability to hold a charge. But there are many other reasons capacitors can fail.
Excessive heat
One of the most common reasons for capacitor failure is heat. Most capacitors are rated for a maximum temperature, and if they exceed this temperature, they will fail. There are two main ways that heat can damage a capacitor. The first is by causing the electrolyte inside the capacitor to dry. This reduces the capacitance of the capacitor and can eventually cause it to fail entirely. The second way heat can damage a capacitor is by causing the dielectric material to break down. This also reduces the capacitance of the capacitor and can eventually lead to failure.
Short cycling
Another common cause of capacitor failure is short cycling. This occurs when the capacitor is constantly charged and discharged, which can cause the electrolyte to break down and the dielectric material to degrade. Short cycling can also cause the terminals of the capacitor to corrode, which can lead to a loss of conductivity and eventually failure.
There are many other reasons why capacitors can fail, but these are some of the most common. If you suspect that your capacitor has failed, it’s important to replace it as soon as possible to avoid damage to your electrical system. [3]
FAQ
How long do capacitors last?
The lifespan of capacitors can vary greatly depending on the quality of the capacitor, as well as the conditions under which it is used. In general, however, most capacitors will last for several years before needing to be replaced.
If you are using a high-quality capacitor in ideal conditions, it is not uncommon for the capacitor to last for over ten years. However, if you are using a lower quality capacitor or if the conditions under which it is used are less than ideal, the lifespan of the capacitor may be significantly shorter.
What happens if you oversize a run capacitor?
Oversizing a run capacitor won’t affect the device’s operation, but it will affect your wallet because you’ll be paying for more electricity that your system may need. However, in certain cases you might see an increase in system performance if you oversize your run capacitor.
Can you use a higher rated capacitor?
Yes, you can use a capacitor with a higher voltage rating. However, using one with a lower voltage rating is not recommended as it could potentially damage your compressor. If you’re unsure about which capacitor to purchase, always err on the side of caution and go with a higher voltage rating.
Final thoughts
As you can see, it’s entirely possible to use a larger run capacitor than what is recommended by the manufacturer. In most cases, it’s actually beneficial to do so. The only time you need to be careful is when the voltage rating of the capacitor has a smaller MFD rating than what the manufacturer recommends. You also shouldn’t use a lower run capacitor, as that can lead to issues. Thanks for reading! We hope this article was helpful. If it was, please share it with your friends or colleagues! And if you have any questions or comments, please let us know in the comments section below. We love hearing from our readers. Until next time!
References:
- https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/capacitors/all
- http://www.dnr.louisiana.gov/assets/TAD/education/ECEP/hvac/d/d.htm
- https://www.achrnews.com/articles/136836-troubleshooting-reasons-for-failing-start-capacitors
- https://whoatwherewhy.com/can-i-use-a-larger-run-capacitor/






 Capacitors are like electronic multitool wonders. They combat voltage ripples, enhancing DC power supply stability, and serve as signal surgeons, deftly removing unwanted AC noise. In timing circuits, they’re the maestros orchestrating the rhythm of electronic processes, all while subtly dictating the tempo of voltage change.
Capacitors are like electronic multitool wonders. They combat voltage ripples, enhancing DC power supply stability, and serve as signal surgeons, deftly removing unwanted AC noise. In timing circuits, they’re the maestros orchestrating the rhythm of electronic processes, all while subtly dictating the tempo of voltage change.






Leave a Reply