A resistor is a component in an electrical circuit that helps to control the flow of electricity. In many cases, resistors get hot when they are used. This can be a problem, as it can damage the resistor and shorten its lifespan.
There are a few things that you can do to prevent your resistors from getting hot:
- One is to use a lower wattage resistor. This will help to reduce the amount of heat that is generated;
- Another option is to use a heat sink. A heat sink helps to dissipate the heat away from the resistor, which will keep it cooler;
- Finally, you can try using a higher voltage resistor. This will also help to reduce the amount of heat that is generated;

By following these tips, you can help to prolong the life of your resistors and prevent them from getting damaged by overheating.
In this blog post, we will discuss in detail some ways to stop resistors from getting too hot. Stay tuned!
Why Do Resistors Get Hot?
Resistors are devices that are used to create resistance in an electrical circuit. They are made of materials that have a high resistance to electricity, such as carbon or ceramic. When a current flows through a resistor, the electrons collide with the atoms of the material, and this creates heat. The more current that flows through the resistor, the more heat is generated.
If too much current flows through a resistor, it can get hot enough to damage the material or even cause a fire. That’s why it’s important to choose the right size resistor for your circuit.
A Closer Look at Current and Resistor
Before experts will look at how to stop resistors from getting hot, let’s take a closer look at the current.
Current is the flow of electrons through a material. It is measured in amperes (amps). The higher the number of amps, the more electrons are flowing through the material.
Resistance is a measure of how much a material opposes the flow of electrons. The higher the resistance, the more opposition to electron flow there is.
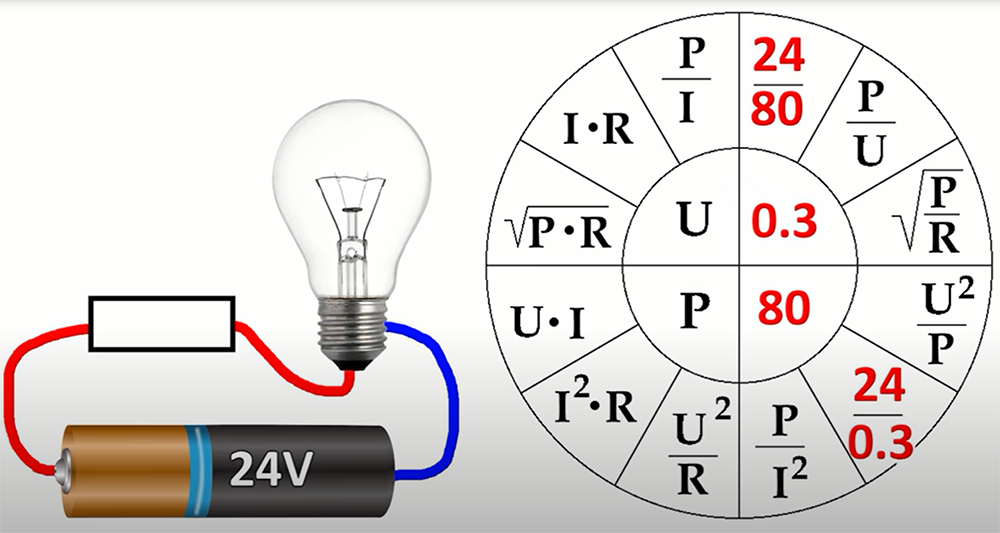
This opposition creates heat as electrons collide with atoms in the material.
The amount of current that flows through a resistor depends on two things: the voltage (measured in volts) and the resistance (measured in ohms).
The formula for calculating current is I = V/R. This formula is known as Ohm’s Law.
If you increase the voltage, the current will increase. If you increase the resistance, the current will decrease [2].
Construction Of A Resistor And How It Provides Resistance
A resistor is made of two conductors (usually metal wires) that are separated by an insulating material. The most common type of resistor is the carbon-composition resistor [3].
The ends of the resistive element are connected to the metal wires (called leads). The leads are then connected to the circuit.
Resistor Power Ratings
The power rating of a resistor is the maximum amount of power that the resistor can dissipate without being damaged.
The power rating is usually printed on the body of the resistor, and it is given in watts (W).
For example, a common power rating for resistors is ½ watt (0.50 W). This means that the resistor can safely dissipate up to 0.50 watts of heat without being damaged [4].
If a resistor is used at a higher power than its rated value, it will get hot and may be damaged.

It’s important to choose the right size resistor for your circuit so that you don’t damage it or cause a fire. The best way to do this is by using Ohm’s Law (I = V/R).
The Main Reasons Resistors Get Hot
There are three primary reasons that resistors get hot: too much current, too much voltage, or a combination of the two [5]. Let’s take a closer look at each one.
When there is too much current flowing through a resistor, it will start to heat up. This is because the electrical resistance of the resistor converts some of the electrical energy into heat energy. The more current that flows through the resistor, the more heat energy is produced.
If there is too much voltage across a resistor, it will also start to get hot. This is because the higher voltage creates a larger electric field within the resistor. This increases the amount of current flowing through the resistor, which in turn produces more heat energy.
Finally, if there is a combination of too much current and too much voltage, the resistor will get even hotter. This is because both effects are amplifying each other, leading to even greater production of heat energy.
What Happens To The Resistors When They Get Too Hot:
1) Resistance Of Resistors Change If It Gets To Hot
The first consequence of a resistor getting too hot is that its resistance may fluctuate.
There’s another critical factor to consider when it comes to resistors: the Temperature Coefficient of Resistance (or TCR). The TCR of materials tells us how a material’s resistance varies with temperature change. Each substance has its own TCR value.
When the temperature rises, so do the electrical resistance of a resistor. The resistance varies depending on the material and the fixed length and area of the resistor (but some resistors are more resistant to changes in temperature than others).
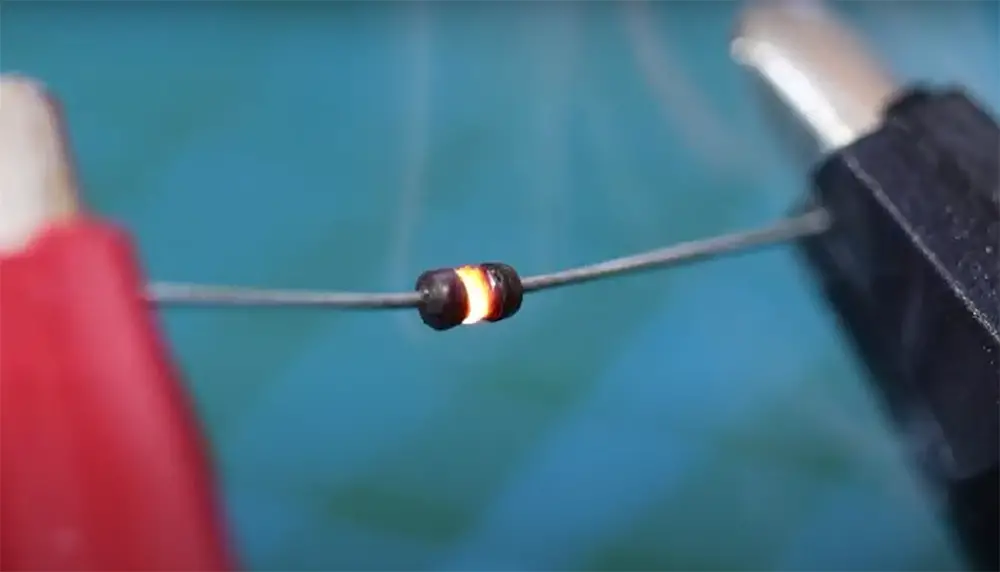
When the temperature rises, atoms in a material become excited, resulting in increased mobility. The atoms move about more swiftly as a result, making it harder for electrons to pass through.
The resistance of a resistor is typically altered by external temperature. However, if a resistor is kept in an enclosed location and becomes too hot, the heat given off by it as it gets hotter can raise the ambient temperature, causing its resistance to rising [6].
2) Resistor Can Get Physically Damaged If It Gets Too Hot
If the resistor gets too hot, it can actually be physically damaged.
The most common type of damage is called “electrical overstress”, or EOS. This is when the current flowing through a component (in this case, a resistor) exceeds its design limits.
This can happen for a number of reasons, but one of the most common is heat. When components get too hot, they can expand and contract unevenly. This can cause cracks in the solder joints that hold them in place.
Another problem that can occur is called “thermal runaway”. This is when the heat generated by a component causes it to get even hotter, leading to even more problems.
Thermal runaway can be caused by a number of things, but one of the most common is when a resistor is placed in an enclosed space.
If a resistor gets too hot, it can actually catch fire. This is because resistors are made of combustible materials.
When a resistor catches fire, it can release harmful chemicals into the air. These chemicals can be breathed in and cause serious health problems [7].
Do All Resistors Dissipate The Same Amount Of Heat?
The answer to this question is no, all resistors do not dissipate the same amount of heat. This is because there are many factors that affect how much heat a resistor will dissipate.
Some of these factors include:
- The size of the resistor;
- The material the resistor is made from;
- The type of load the resistor is handling;
- The temperature of the surrounding environment;
All of these factors play a role in how much heat a particular resistor will dissipate. As such, it is important to consider all of these factors when selecting a resistor for your application.
How To Stop Resistors From Getting Hot?
One way to stop your resistors from getting too hot is to use a lower wattage resistor. By using a lower wattage resistor, you’ll be able to dissipate less heat and keep your resistors cooler.
Another way to stop your resistors from getting too hot is to use a resistor with a higher wattage rating. By using a resistor with a higher wattage rating, you’ll be able to dissipate more heat and keep your resistors cooler.
You can also try using a heatsink. A heatsink helps to conduct heat away from the resistors and into the air, which prevents the resistors from getting too hot.
If you’re still having trouble keeping your resistors cool, you can try cooling them with a fan. By blowing air over the resistors, you’ll help to keep them cool and prevent them from getting too hot.
How to Stop Resistors Getting Hot: Comparison Table
Resistors are electronic components that dissipate power and can get hot during operation. Excessive heat can lead to resistor failure or affect the performance of the entire circuit. Here, we compare various indicators to understand how to prevent resistors from getting excessively hot.
| Indicator | Explanation |
|---|---|
| Power Rating | The power rating of a resistor indicates the maximum power it can safely handle. Using a resistor with a higher power rating than required ensures it can handle the current without overheating. |
| Ambient Temperature | The surrounding temperature can affect the resistor’s performance. Operating the resistor in a cooler environment helps dissipate heat more efficiently. |
| Derating | Derating involves operating the resistor at a lower power rating than its maximum capacity. This practice ensures the resistor runs cooler and reduces the risk of overheating. |
| Heat Sinks | Using heat sinks with resistors helps in dissipating heat more effectively, especially when dealing with high-power applications. |
| Airflow | Proper airflow around the resistor aids in dissipating heat. Adequate ventilation prevents heat buildup and maintains the resistor’s temperature within safe limits. |
| Resistor Type | Different resistor types have varying thermal properties. Choosing resistors optimized for low heat generation can reduce the risk of overheating. |
Explanation of the Table:
- Power Rating: The power rating of a resistor determines how much power it can safely handle without overheating. It is essential to choose a resistor with a power rating higher than the actual power it will dissipate in the circuit to avoid overheating.
- Ambient Temperature: The temperature of the environment in which the resistor operates significantly impacts its performance. Higher ambient temperatures can hinder heat dissipation, leading to potential overheating. Operating the resistor in a cooler environment is beneficial.
- Derating: To ensure the resistor remains cool, it is common practice to operate it at a lower power rating than its maximum capacity. This technique, known as derating, provides an additional safety margin against overheating.
- Heat Sinks: Heat sinks are thermal conductive devices that help dissipate heat from the resistor more efficiently. They are particularly useful in high-power applications, preventing the resistor from reaching excessive temperatures.
- Airflow: Proper ventilation and airflow around the resistor aid in dissipating heat. Adequate airflow prevents heat buildup and maintains the resistor’s temperature within safe limits.
- Resistor Type: Different resistor types (e.g., metal film, wire wound, carbon composition) have varying thermal properties. Choosing resistors optimized for low heat generation can reduce the risk of overheating in specific applications.
Read our guides to improve your knowledge in electronics:
FAQ
How do you reduce the heat of a resistor?
There are a few ways to reduce the heat of a resistor:
- Reduce the power dissipation by using a lower wattage resistor;
- Reduce the current flowing through the resistor;
- Increase the surface area of the resistor so that more heat can be dissipated;
- Use a material with a higher thermal conductivity for the resistor body;
- Add heatsinking to increase the rate at which heat is conducted away from the resistor;
Why would a resistor get hot?
There are a few reasons why a resistor might get hot [8]:
- The first is if there is too much current flowing through it. This can happen if the circuit is not designed properly, or if there is a problem with the components;
- The second reason is if the resistor is placed in a location where it gets too much heat from other components or from the environment. This can happen if the resistor is placed near a hot surface, or in a cramped space where it doesn’t have enough airflow to cool itself down;
- The third reason why resistors get hot is because of something called self-heating. This happens when the current flowing through the resistor creates heat, which then raises the temperature of the resistor. This can be a problem in high-power circuits, or in circuits that are switched on and off frequently;
How much heat can a resistor dissipate?
The amount of heat that a resistor can dissipate depends on its power rating.
The power rating is usually printed on the body of the resistor and is given in watts (W).
For example, a common power rating for resistors used in electronic circuits is ½ W. This means that the resistor can safely dissipate up to ½ W of power without getting too hot.
If a resistor gets too hot, it can be damaged or even destroyed. This is why it’s important to choose the right power rating for your resistors. In general, you should use the highest power rating that you can afford [9].
Why would a resistor smoke?
If a resistor gets too hot, it can start to smoke. This is usually a sign that the resistor is about to fail. When a resistor fails, it usually opens up the circuit so that no current can flow through it. This can cause problems in your circuit, and may even damage other components.
If you see a resistor smoking, you should remove it from the circuit as soon as possible and replace it with a new one.
You should also check the rest of your circuit to make sure that there are no other components that are getting too hot. If you find any, you should try to fix the problem so that they don’t get too hot and fail as well.
How do you know if a resistor is burnt?
When the resistor is heated and burned, it will become red hot and emit a faint smoke.
The burning smell comes from the breakdown of the components in the resistor: carbon, clay binding agent, and color code pigment [10].
How often do resistors fail?
In the short circuit mode, resistors that fail are uncommon and account for 3 to 9% of all resistor failures. The most common cause of resistor failure is heat.
Can you bypass a resistor?
If a resistor burns out, you can bypass it by connecting the two wires that were connected to the resistor directly to each other. This will allow the current to flow through the circuit without going through the resistor.
You should only do this as a temporary fix, and you should replace the resistor as soon as possible.
Bypassing a resistor can cause problems in your circuit, and may even damage other components.
You should also check the rest of your circuit to make sure there are no other components that are getting too hot. If you find any, you should try to fix the problem so that they don’t get too hot and fail as well.
How many watts can a resistor handle?
A resistor’s power rating is measured in watts, and it ranges from 0.125W to 1W or more. Power resistors are those with power ratings of 1W or greater that are used for their capacity to dissipate energy [11].
What are the common reasons for resistors getting hot?
Resistors can get hot due to factors such as excessive current flow, high ambient temperatures, voltage spikes, or incorrect power dissipation ratings.
How can I select the right resistor for high-power applications to prevent overheating?
To avoid resistors getting hot in high-power applications, choose resistors with higher power ratings, lower resistance values, or use multiple resistors in parallel to distribute the load.
What are some ways to improve the airflow around resistors and prevent overheating?
You can use heat sinks, fans, or ensure proper ventilation in the circuit design to improve airflow and dissipate heat from the resistors effectively.
How does the ambient temperature affect the temperature of a resistor?
Resistors dissipate more heat in high-temperature environments. To prevent overheating, consider using resistors with higher power ratings or reducing the ambient temperature around the resistors.
Can I use a resistor with a higher wattage rating to reduce heating?
Using a resistor with a higher wattage rating can help reduce the risk of overheating, as it can handle more power without getting excessively hot.
Are there any design considerations to prevent resistors from getting hot?
Yes, you can use voltage dividers, current-limiting circuits, or pulse-width modulation (PWM) to manage power dissipation and prevent resistors from overheating.
What are some tips to avoid hotspots on resistors in densely packed circuits?
To prevent hotspots in densely packed circuits, ensure proper spacing between components, use heat-resistant materials, and consider thermal simulations during the design phase.
Can soldering techniques affect the temperature of a resistor?
Yes, improper soldering techniques, such as using excessive heat or soldering for too long, can damage resistors and lead to overheating issues.
How can I troubleshoot overheating resistors in a circuit?
To troubleshoot overheating resistors, check for incorrect circuit connections, short circuits, or excessive current flow. Also, ensure that the resistors used have the appropriate power rating for the application.
What are some safety precautions to prevent resistors from getting too hot?
Always follow the datasheet guidelines and use resistors within their specified power ratings. Avoid operating circuits in extreme conditions, and regularly inspect the circuit for any signs of overheating.
Useful Video: Why resistors get hot
References:
- https://electronicguidebook.com/why-do-resistors-get-hot
- https://electronicguidebook.com/why-do-resistors-get-hot
- https://www.seniorcareto.com/how-hot-can-a-ceramic-resistor-get/
- https://www.electronics-tutorials.ws/resistor/res_7.html
- https://sciencing.com/calculate-temperature-resistance-power-known-6617540.html
- https://electronicguidebook.com/why-do-resistors-get-hot
- https://sciencing.com/calculate-temperature-resistance-power-known-6617540.html
- https://forum.allaboutcircuits.com/threads/what-causes-a-resistor-to-get-too-hot.105494/
- https://electronics.stackexchange.com/questions/65200/is-it-possible-to-calculate-how-much-heat-dissipation-and-temperature-rise-will
- https://sciencing.com/happens-resistor-burns-up-8556222.html
- https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/resistors/power-rating














Leave a Reply