Do you need to know about solenoid switches? Are you looking for a comprehensive guide that will answer all of your questions? You’ve come to the right place! In this article, we will discuss what a solenoid switch is, how it works, and some tips on using them. We’ll also answer some common questions that people have about solenoid switches. So whether you’re just curious about these devices or are in the market for one, read on!
Definition of a Solenoid Switch
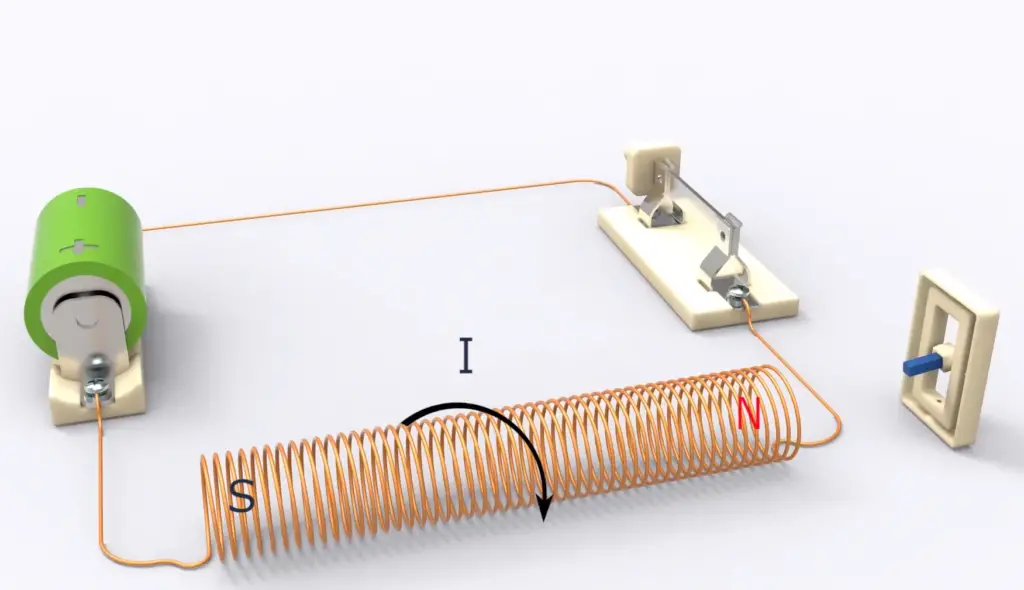
The device consists of a coil, usually encased in metal, which when activated with electric current creates a magnetic field. This magnetic field causes a plunger inside the coil to move up or down, depending on the direction of the current. When the plunger reaches its destination, it makes contact with two metal contacts attached to either side of the switch; this connection then completes (or breaks) an electrical circuit.
Solenoid switches are commonly used in many everyday items such as car door locks and starting systems, air conditioners, washing machines, elevators and vending machines. They find their way into industrial settings as well, where they are used in machinery for applications such as controlling servos and pumps. Because of the simplicity of their design, solenoid switches are relatively inexpensive and easy to work with.
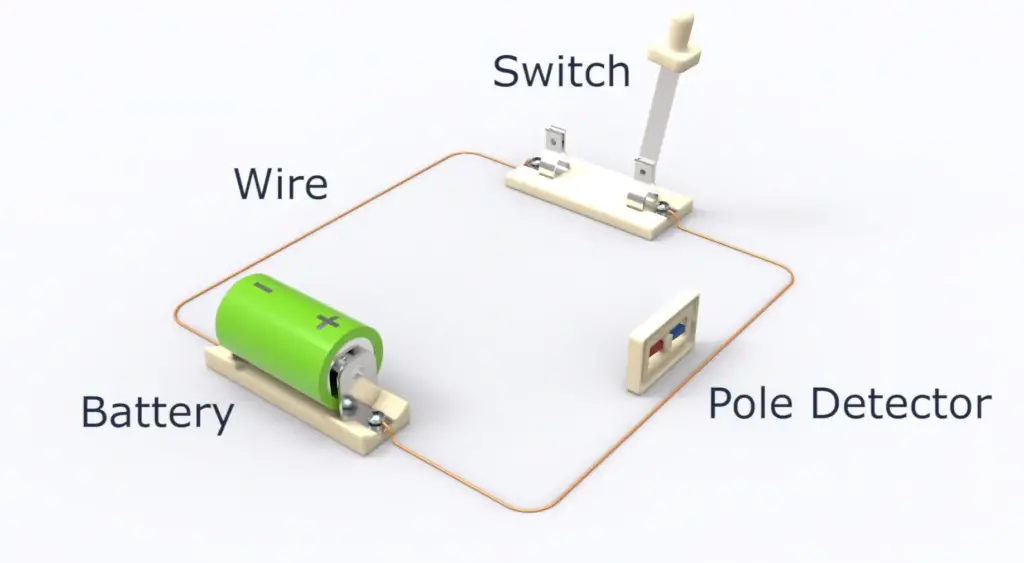
The working principle of a solenoid switch can also be explained using basic physics principles. You already know that solenoid consists of a coiled wire embedded inside a magnetic field. The solenoid functions thanks to the fundamentals of electromagnetism. When electrical current runs through its coil, a magnetic field is created and if an iron core is set inside it, the flux lines are concentrated on said element which boosts the induction in comparison with air core coils. To strengthen the magnetic force of a solenoid, you can upsurge both its turns’ density and current flow.
The solenoid switch is thus useful for controlling other electrical components as it can be used to open and close different types of circuits. The plunger’s movement also provides a physical representation of an action that has taken place – such as turning off a light switch when it is pressed – allowing users to easily see what effect their actions have had on the device or circuit in question. [1], [2], [3]
Solenoid Switch Types
Solenoid switches are available in a variety of configurations and designs. In this section, we will discuss the three main types of solenoid switches and what makes them unique from one another.
AC- Laminated Solenoid
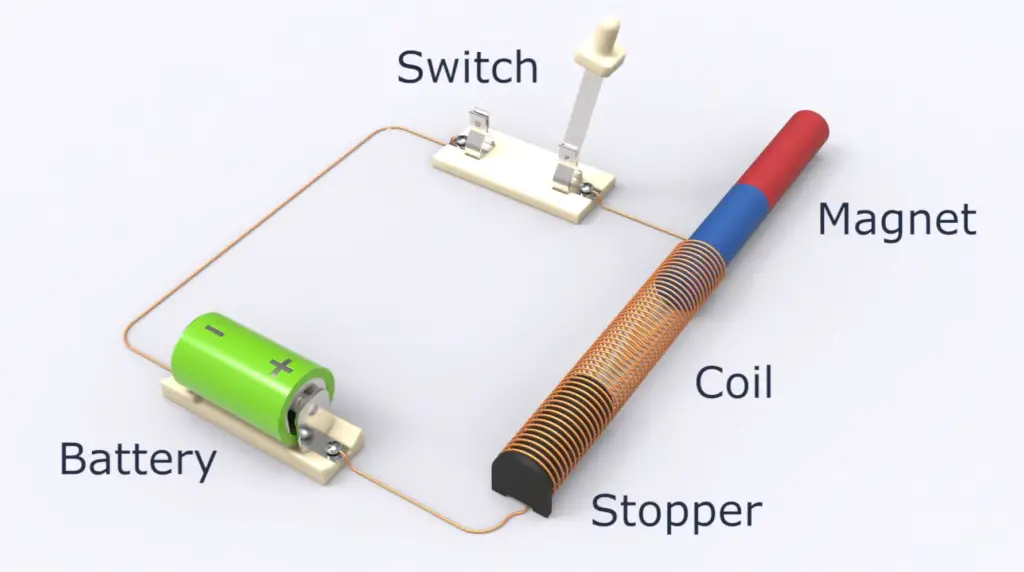
The foundation of this solenoid is built on a laminated metal, which lowers the presence of stray current and thus boosts its performance.
The main advantage of an AC solenoid lies in its capacity for delivering a tremendous amount of strength with only one stroke. They are capable of using more strokes than a DC solenoid and can thus provide more power.
AC-laminated solenoids are also noted for a variety of different configurations including open frame, closed frame and encapsulated. The encapsulated type is noted for its strength and durability which makes it highly suitable for various electronic applications.
DC C-Frame Solenoid
DC C-Frame Solenoid is an electrical device that converts energy into mechanical motion. The design comprises a letter “C” shaped frame, which is enveloped around the coil.
This solenoid is mainly used in gaming machines, vending machines, automotive starters, and other applications that require a high-voltage DC current. The device is designed to provide consistent output power for the entire duration of the operation.
DC D-Frame Solenoid
A DC D-Frame Solenoid is a type of solenoid that has a two piece frame covering the coils. These solenoids can be used with AC power and have a controlled stroke operation.
DC D-Frame solenoids are very versatile and can be used both in conventional and medical applications. For example, in medical applications, DC D-Frame solenoids can be used to control the movement of robotic arms or other components within a surgical procedure.
The coils in the DC D-Frame solenoid are wound around metal cores which provide an electromagnetic field when they are energized by current flowing through them. This magnetic field induces a force on surrounding ferromagnetic parts such as plungers and switches attached to the coil assembly. This force causes the plunger or switch to move in a linear fashion, creating mechanical motion.
Linear Solenoid
Linear solenoid consists of a coil of wire which is wrapped around a movable metal core used to convert electrical energy into mechanical force or linear motion.
This type of solenoid is primarily utilized in starting devices, providing a convenient switching mechanism which enables current to flow through it. By completing the circuit, these solenoids make an essential contribution to any device that requires electrical activation.
Rotary solenoid
A typical rotary solenoid consists of a cylindrical metal core that is mounted to a disk and has small grooves under it.
Rotary solenoids are ideal for automation applications that require linear motion, such as door locks and industrial machinery. The solenoid’s core rotates within the disk in response to electric current passing through it. The solenoid’s core and body are connected by a spring, which pushes the disk core back to its original position when power is disconnected.
The main advantage of a rotary solenoid is its robustness and reliability, which makes it ideal for a wide range of applications. Additionally, rotary solenoids can be used in different configurations to achieve specific functions. [2]
How to Wire a Solenoid Switch
Usually, solenoid switches are used to control a circuit with a large current by using a switch with low current.
Delivering a small current to the solenoid causes its core to move, which then forces the switch connected with it into a closed position. Depending on its size, these switches have four terminals that energize when supplied with sufficient power. To regulate the current flow, two terminals are used for low-current circuits and the remaining ones for high-current circuits of the solenoid. Let’s discuss the steps to wire a solenoid switch.
- Carefully connect the two terminals of your high current switch to the solenoid switch, and then follow all instructions provided in your documentation for setting up this type of switch. Once complete, observe that everything is properly wired according to these directions.
- Subsequently, cut two pieces of black wire and attach one end of the original black wire to the negative terminal of the battery. Additionally, attach the other end of the wire to one of the high-current terminals on the switch.
- Securely connect the black wire to a high-current terminal of the switch, then attach its opposite end onto the negative pole of your DC motor.
- Carefully cut one end of the red wire and link it to the positive terminal on both the motor and battery.
- Cut a two-part black wire and attach one end of the cable to the first low current terminal above the switch. Establish the remaining polarity to one of the 6V switch’s terminals, then join up the other terminal with the negative pole of your 6V battery.
- Arrange one red color wire among the +ve terminal of the battery & fix the remaining finish to the next low-current terminal over the switch.
- Finally, switch ON the 6V switch and watch your DC motor come to life! [1]
Applications of a Solenoid Switch
Solenoid switches come in a variety of configurations and can be used for a wide range of applications. Some common uses include, but are not limited to:
Medical equipment
One of the most important applications of solenoid switches is in medical devices. Solenoids are used to control various pieces of medical equipment, including wheelchairs, hospital beds and life support systems.
Solenoids can also be used for minor tasks such as controlling a simple motor to open or close a door in a medical facility. Additionally, they are often integrated into infusion pumps and ventilators which help regulate and monitor intravenous drug delivery and artificial respiration respectively.
High power circuits
High power circuits may require a solenoid switch as they can withstand large amounts of current, allowing for control of large motors or other high-power items. A solenoid switch ensures the device is switched off when not in use and prevents overloads from occurring.
Automation
Solenoid switches are also used in automation systems, where they can be used to trigger processes or machines with a simple electrical signal. This is often employed in industrial settings where safety measures must be taken and quick responses are required.
Engine starting systems
Solenoid switches are commonly used in engine starting systems, as they can be set up to control the flow of electricity from the battery to the starter motor. This helps prevent any unnecessary current draws on the battery and ensures a smooth start for the vehicle. [1]
FAQ
Where is solenoid used?
Solenoid switches are typically used in motor control applications and industrial automation. They are most commonly used to start and stop motors, often with the help of a timer or other mechanism. In addition, they can be used for the activation of relays, valves, circuit breakers, sensors and other electrical devices.Solenoids can also be found in many consumer appliances such as washing machines and refrigerators as well as medical equipment such as X-Ray machines. Because of their durability and low cost compared to other forms of actuators solenoids are often seen as a desirable alternative in these products. They are also widely used in automobiles for controlling fuel injection systems, immobilizers, power window mechanisms and power locks.
How does a solenoid switch work?
The current passing through the coil creates enough force to pull the plunger and activate the switch. This is how a solenoid switch works.
What is a solenoid, and what does it do?
A solenoid is an electromechanical device that converts electrical energy into linear motion. It consists of a coil of wire, usually made of copper or aluminum, wound around a movable rod. When the coil is electrically charged, it creates a magnetic field which then pulls on the armature and forces it to move in one direction. This movement can be used to control valves or switches as part of larger mechanisms such as in automatic door openers and other automated systems.
What is a solenoid switch also known as?
A solenoid switch is also commonly referred to as an electromagnetic switch, a contactor, an actuator, or a starter relay. It is an electrical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical force and motion. A solenoid switch consists of a coil wrapped around a movable metal core which moves when the electric current passes through it, allowing for the opening and closing of contacts inside the switch. This action allows electricity to pass through specific circuits in order to control different motors or appliances.
Why do you need a solenoid?
A solenoid is a component of an electric circuit that acts as a switch, allowing current to flow through it when activated. When the coil inside the solenoid is energized, it creates a magnetic field that moves a plunger and opens or closes the contacts of the switch. This provides an efficient way to turn electrical circuits on and off without having to manually move any parts.
Solenoids are often used in applications where remote control is desired, such as home automation systems, vehicle engines, security systems, and medical equipment. They can also be used to trigger alarms or activate other components of a circuit like relays and motors.
What happens when a solenoid fails?
When a solenoid fails, it can cause a wide range of issues. Depending on the type and severity of the failure, some of these issues may include: loss of power to the vehicle; an inability to start or stop the engine; excessive noise and vibration when starting or stopping; difficulty shifting gears; decreased fuel economy; and more. In serious cases, failure can even lead to engine damage.
To troubleshoot a failed solenoid switch, it is important to first identify the symptoms and then isolate the source of the problem (the faulty component). Once this has been done, repairs may be made using replacement parts or by making adjustments to existing components. To ensure long-term reliability, it is also important to regularly inspect and maintain all electrical components related to the solenoid switch. This should include regular cleaning, lubrication, and testing of connections. If repairs are not possible or necessary, a professional can be called for advice or assistance in replacing the faulty component.
Useful Video: Solenoid Basics Explained – Working Principle
Conclusion
Solenoid switches are an essential component in many industrial and commercial applications. They offer the benefits of high speed, long life, low power consumption, easy installation and maintenance. Whether used for switching on/off high-voltage circuits or controlling movements in automated systems, a solenoid switch can provide reliable current or voltage control. The ability to be configured for different types of operations make them versatile components for a wide range of applications. With proper design and installation, a well-made solenoid switch can serve your needs well for years to come.
In this article, we’ve explored some of the basics about solenoid switch technology, as well as their types and applications.
When choosing a solenoid switch, it is important to consider its performance parameters such as coil resistance and contact rating; operating environment temperature; ventilation requirements; enclosure type; electrical connection type; recommended maintenance schedule and more. Additionally, it is also important to check the certifications and warranties offered by the manufacturer in order to ensure that the product you are purchasing meets all of your requirements.
By understanding what a solenoid switch is and its wide range of applications, you can make an informed decision when selecting the right type for your specific needs. If you understand the basics of how they work and use them properly, solenoid switches can provide reliable current or voltage control with long-term durability and dependability.
References
- https://www.elprocus.com/what-is-a-solenoid-switch-working-its-applications/
- https://offroadingpro.com/solenoid-switch/
- https://circuitdigest.com/article/what-is-solenoid-its-working-principle-and-types











Leave a Reply