If you’re looking for an introduction to logic analyzers, look no further! In this blog post, we will discuss what a logic analyzer is, what it’s used for, and some of the features that you should look for when purchasing one. We’ll also provide a few tips on how to get started with using your new logic analyzer.
What is a Logic Analyzer?
In simple terms, a logic analyzer is like having an X-ray machine for electronics. This means that you can take a look “inside” of a circuit and see what is going on without having to actually open up the device. This is extremely useful for troubleshooting or debugging purposes.
Logic analyzers are also very helpful when trying to reverse engineer a piece of equipment. By being able to see the communication between different parts of a circuit, you can start to understand how the device works and what each component does. [1]
Most logic analyzers have two parts: the hardware, which connects to your circuit, and the software, which runs on your computer. The hardware collects data from your circuit and sends it to the computer, where the software displays it in a way that you can understand.
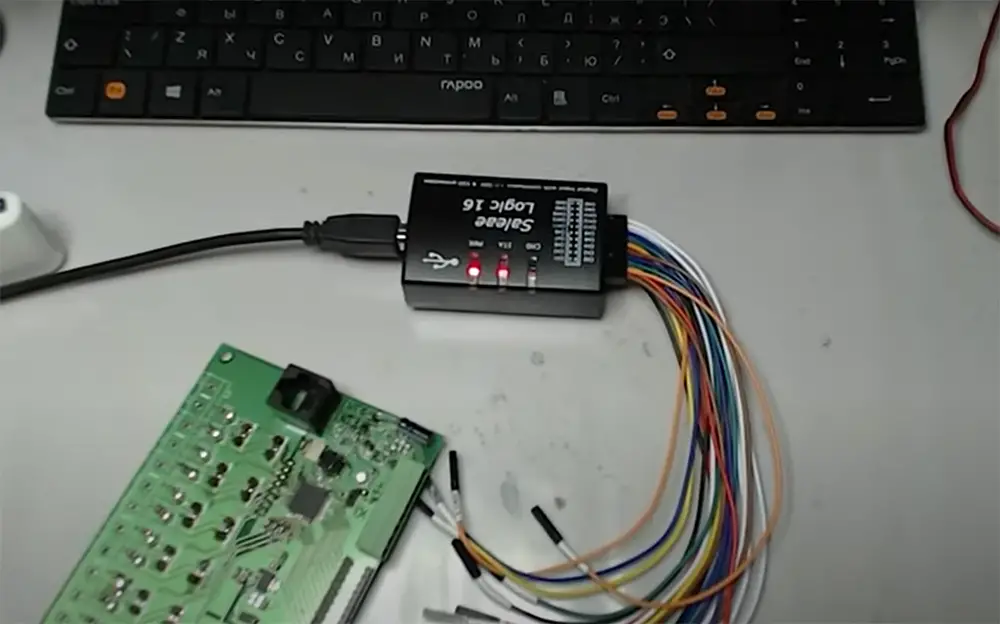

Logic analyzers are now an essential tool for debugging digital electronics. They are used in a wide variety of applications such as computer engineering, telecommunications, automotive electronics, and consumer electronics. These analyzers are available in a variety of form factors, from handheld units to benchtop units to modular units that can be configured for specific applications.
History of development
The first logic analyzer was created in 1974 by Jerry Ungerman and Dave Cronquist. This tool was originally designed to debug the hardware of early personal computers such as the Altair 88000. The first commercial logic analyzer was introduced in 1976 by Hewlett Packard. These analyzers became more widely used in the 1980s as digital electronics became more commonplace. The number of logic analyzer channels and the speed at which they could sample data increased dramatically during this time period.
Later in the 1990s, logic analyzers began to incorporate features such as protocol decoding and trigger sequences. This allowed engineers to not only see the digital signal but also to understand the meaning of that signal.
As digital electronics have become more complex, analyzers have evolved to meet the needs of engineers. Today, logic analyzers are widely used in a variety of industries such as automotive, aerospace, and communications.
Types of Logic Analyzers
There are a few various types of logic analyzers, but they all essentially do the same thing. Some analyzers are stand-alone devices, while others are software that is installed on a computer. The stand-alone devices tend to be more expensive, but they are also more versatile and can be used for a wider range of tasks.
- A digital analyzer is a type that samples the digital signals on a piece of electronic equipment and then displays the data in a format that is easy to understand. This type of analyzer is very useful for troubleshooting digital circuits.
- Analog analyzers are used to measure analog signals. These signals can be anything from voltage to current. Analog analyzers are often used in audio applications. They can be used to measure the quality of an audio signal and to identify any problems with the signal.
- Mixed-signal analyzers are used to measure both digital and analog signals. This type is the most versatile and can be used for a wide variety of tasks. For example, if you were troubleshooting a circuit that had both digital and analog signals, you would need a mixed-signal analyzer.
Digital analyzers can be further classified into two types: those that use a sampling method and those that use a trigger method.
- Sampling analyzers sample the signal at a fixed rate and then store the samples in a buffer. The advantage of this type is that it can be used to capture very fast signals. However, the disadvantage of this type is that it can only capture a finite number of samples.
- Trigger-based analyzers, on the other hand, do not sample the signal at a fixed rate. Instead, they wait for a specific event or condition to occur before they start sampling the signal. The advantage of this type is that it can capture very complex signals. The only downside is that it can take longer to capture a signal with a trigger-based logic analyzer.
There is one more classification:
- PC-based analyzers – these are the most common type. PC-based logic analyzers connect to a computer via a USB or Ethernet connection. Once connected, they can be used to capture digital or analog signals. PC-based analyzers typically have a wide range of features.
- Embedded logic analyzers – these are analyzers that are built into a system. Embedded analyzers have the advantage of being able to capture signals without the need for a computer. However, they typically have a limited number of features.
- Handheld logic analyzers – these are analyzers that can be held in your hand. Handheld analyzers are typically used to troubleshoot portable devices such as cell phones and PDAs. They are typically small and lightweight and can be used to capture digital or analog signals. [1]
Logic analyzer applications
There is a wide range of potential applications for logic analyzers.
Some of the most common use cases include: [1]
- Verifying the behavior of digital circuits – if a design is not behaving as expected, a logic analyzer can be used to observe the waveforms of the digital signals in the circuit and identify the root cause of the problem.
- Debugging digital circuits – a logic analyzer can be used to observe and debug complex digital systems by providing insight into the behavior of individual signals and components within the system.
- Profiling digital systems – a logic analyzer can be used to measure the performance of digital systems by observing the timing and behavior of signals within the system.
- Analyzing embedded system communication protocols – a logic analyzer can be used to decode and analyze communication protocols used by embedded systems, such as I²C, SPI, UART, and CAN.
- Measuring timing characteristics of digital signals – a logic analyzer can be used to measure the rise time, fall time, propagation delay, and other timing characteristics of digital signals.
- Monitoring bus traffic – a logic analyzer can be used to observe the traffic on buses such as PCI Express, USB, and Ethernet.
Logic analyzers are an essential tool for anyone working with digital circuits. If you’re working with digital electronics, a logic analyzer is a tool that you need in your toolbox.
Pros and Cons of Using a Logic Analyzer
There are some definite advantages to using a logic analyzer.
Pros:
- A logic analyzer can save you a lot of time by helping you to debug your circuit quickly and efficiently.
- A logic analyzer is also very useful for analyzing complex digital signals.
- Another advantage of using a logic analyzer is that it can be used to verify the functionality of a design before it is implemented in hardware.
- It is convenient to record and save the data collected by a logic analyzer for future reference.
However, there are also some disadvantages to using a logic analyzer.
Cons:
- One of the main disadvantages of using a logic analyzer is that it can be quite expensive.
- Another disadvantage is that they can be complex to use and may require some training to use effectively.
- Logic analyzers also require a certain amount of setup time and may not be well suited for real-time analysis.
Overall, the pros of using a logic analyzer outweigh the cons. If you are working with digital circuits, then a logic analyzer can be a valuable tool in your debugging arsenal.
Logic analyzer characteristics
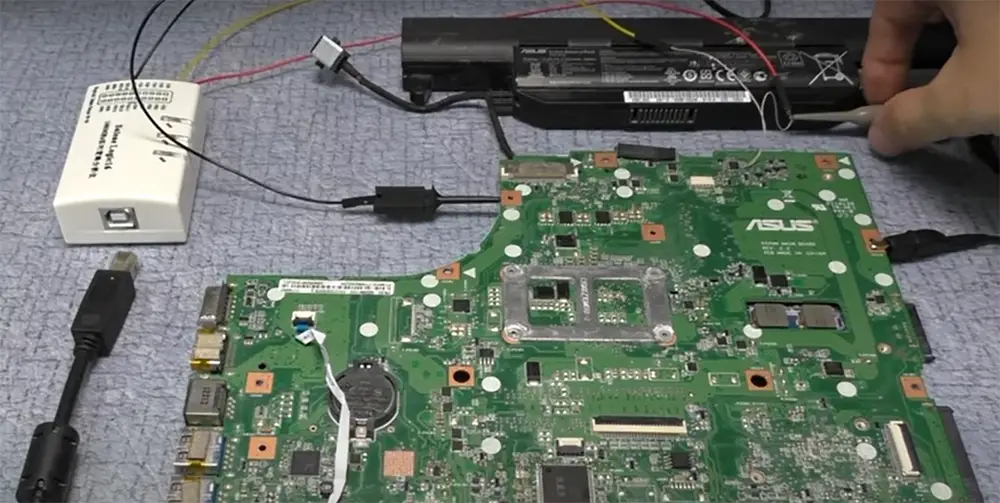

Here are some key characteristics of logic analyzers:
- These analyzers usually have between two and hundreds of input channels that can be probes connected to the device under test or directly to integrated circuits on a board.
- They have deep buffers that can sample data at very high rates (often hundreds of MHz) for long periods of time (seconds to hours). This is necessary because often the behavior being analyzed only occurs infrequently or sporadically.
- The buffer memory is generally proprietary to the logic analyzer vendor.
- Some analyzers have the ability to trigger specific patterns in the data and capture only a portion of the total data acquired. This is useful for analyzing intermittent problems or for capturing rare events.
- Others have special hardware that allows them to do things like perform real-time calculations on captured data or generate test stimuli based on captured data.
- Logic analyzers are generally controlled by a personal computer running analysis software provided by the logic analyzer vendor.
- This software allows the user to do things like define triggers, display and analyze data, and export data for further analysis.
- One of the great things about analyzers is that they can be used to debug all kinds of digital systems. For example, they can be used to debug bus protocols, digital signal processing algorithms, and embedded software. They are also useful for analyzing system-level behavior and for debugging FPGA designs.
FAQ
What should I look for in a logic analyzer?
There are a few things you should keep in mind when shopping for a logic analyzer. The first is the number of channels you need. The second is the sampling rate, which is how often the logic analyzer takes a reading. And finally, make sure to check the memory depth, which is how much data the analyzer can store.
Another important consideration is protocol support. If you’re working with a specific type of protocol, like I²C or SPI, you’ll want to make sure that your logic analyzer can decode it. Otherwise, you’ll just be looking at a bunch of meaningless numbers!
Do I need a logic analyzer?
If you’re just getting started with electronics, you might not need a logic analyzer right away. But if you find yourself debugging complex digital circuits, it’s an invaluable tool. Logic analyzers can save you a lot of time and frustration by helping you figure out what’s going on in your circuit.
Can you use a logic analyzer as an oscilloscope?
Yes, you can use a logic analyzer as an oscilloscope. In fact, many analyzers have built-in oscilloscopes. However, keep in mind that a logic analyzer is not designed to be an oscilloscope replacement. It’s best used for analyzing digital signals rather than analog waveforms.
What is a USB logic analyzer?
A USB logic analyzer is a type that connects to a computer via USB. This makes it convenient for use with laptops or other portable computers. USB analyzers are often used for debugging embedded systems or for analyzing high-speed digital signals.
Do I need special software to use a logic analyzer?
Most logic analyzers come with their own software, which is used to control the analyzer and view the data. However, some analyzers can be used with third-party software, such as Sigrok or LogicPort.
Do I need a special cable to use a logic analyzer?
No, you don’t need a special cable to use a logic analyzer. Most analyzers use standard cables, such as USB or Ethernet.
Useful Video: What is a Logic Analyzer? | Prodigy Technovations
Final Thoughts
In this article, we’ve covered what a logic analyzer is and how it can be used to help you troubleshoot digital circuit issues. With this knowledge in hand, you’ll be able to get the most out of your logic analyzer on your next project.
A logic analyzer is a powerful tool that can be used to debug and test digital circuits. While it may not be necessary for every project, it can save a lot of time and frustration when troubleshooting complex issues.
In addition to the traditional use of a logic analyzer, some newer models include features such as protocol decoding and trigger conditions. These can be extremely helpful when working with serial protocols or debugging timing-sensitive issues.
When shopping for a logic analyzer, it’s important to consider the features that are most important for your needs. There are many different models on the market, so be sure to do your research before making a purchase.
Now you know a bit more about logic analyzers and how they can be used, so get out there and start using one on your next project!
Hopefully, this article has helped to demystify this useful piece of equipment and you’ll consider adding one to your electronics toolkit. Thanks for reading!
What are your thoughts on logic analyzers? Have you used one before? As always, if you have any questions or comments, please feel free to reach out to us on our website or social media. We’d love to hear from you!
References:
- https://www.electronics-notes.com/articles/test-methods/logic-analyzer/basics-tutorial.php
- https://articles.saleae.com/logic-analyzers/what-is-a-logic-analyzer






 A logic analyzer serves as the electronic world’s X-ray machine, allowing you to peek into a circuit’s inner workings without cracking it open. This is a game-changer for troubleshooting and debugging. Moreover, it’s a potent tool for reverse engineering, shedding light on the communication between circuit components and unveiling their functions. Logic analyzers typically comprise hardware to connect to your circuit and software to visualize and interpret the collected data on your computer. It’s an indispensable asset for electronics enthusiasts and professionals alike.
A logic analyzer serves as the electronic world’s X-ray machine, allowing you to peek into a circuit’s inner workings without cracking it open. This is a game-changer for troubleshooting and debugging. Moreover, it’s a potent tool for reverse engineering, shedding light on the communication between circuit components and unveiling their functions. Logic analyzers typically comprise hardware to connect to your circuit and software to visualize and interpret the collected data on your computer. It’s an indispensable asset for electronics enthusiasts and professionals alike.







Leave a Reply