Do you ever wonder how a robotic arm performs precise, complex tasks with ease? In this blog post, we will explore the role of one of the most important components that makes these feats possible – a servo motor. By learning about how servo motors are used in robotic arms, we can gain an insight into their function and importance to modern automation processes. We’ll discuss why they stand out from other types of motors as well as provide examples so you can see for yourself just how powerful these machines are. By investing just a short amount of time reading this article and exploring our resources, you’ll be equipped with all the knowledge necessary to understand what goes on under the hood when it comes to deploying advanced robotics technology.
What Is A Servo?
Servos come in two major types: continuous rotation and digital/limited rotation which are characterized by their rotational speed and range of motion. Continuous rotation servos can rotate continuously while digital/limited rotation have limited angles of movement such as 180 degrees or 270 degrees respectively. Depending on the application, one or both types may be used in a robotic arm.
Servo motors are ideal for robotics applications as they provide precise positioning and speed control with minimal effort. They also have the ability to hold their position without additional power, making them energy-efficient and reliable. Furthermore, servos can be programmed with various settings such as acceleration/deceleration rate and maximum torque limits which help protect against damage due to overloading.
To summarize, robotic arms utilize servo motors due to their ability to deliver precise movement control, energy efficiency, and reliability. With programmable features, they can easily be adjusted for a variety of tasks. [1]
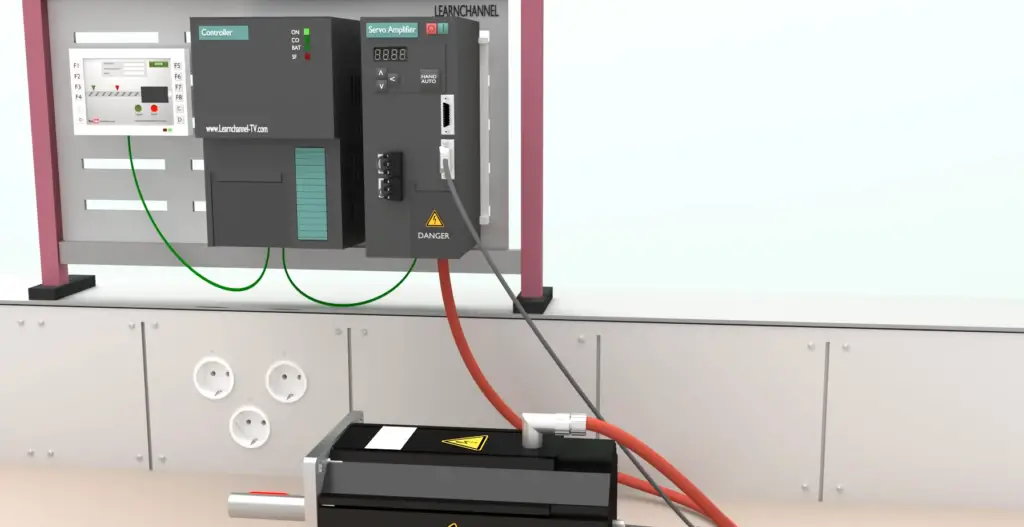

How Does A Servo Work?
A typical servo consists of three main components: a gearbox, a motor, and a feedback system. The gearbox allows the user to customize the output power from the motor to match their needs while the feedback system monitors position and speed information so the servo can adjust accordingly. This closed-loop system ensures that all movements are accurate and consistent.
The servos are controlled with Pulse Width Modulation (PWM) signals sent through an external controller or robot brain. When these pulses reach the servo, the motor rotates in a direction determined by the pulse sequence. The longer the pulse is, the more powerful and further it will move.
How Are Servos Useful In Robotics?
Servos are often used in robotic arms because they provide precise and accurate movement. Servo motors have a built-in feedback system that allows them to accurately measure the position of the arm and adjust accordingly. This helps robots to repeat movements precisely, which is essential for tasks like welding and drilling. Additionally, servos can be programmed to turn on and off quickly, which makes them ideal for speed and agility tasks such as pick-and-place operations.
Furthermore, servo motors consume much less energy than other types of motors, making them highly efficient for powering robotic arms without draining precious resources or increasing operational costs.
Finally, most servo motors are small in size which makes it easy to integrate them into robotic arm designs, allowing for even more intricate movements. This is especially useful for tasks requiring delicate and precise manipulation such as assembling small parts or holding an object in place. [2]
Why Are Servo Motors Used So Widely in Robotics?
Expense
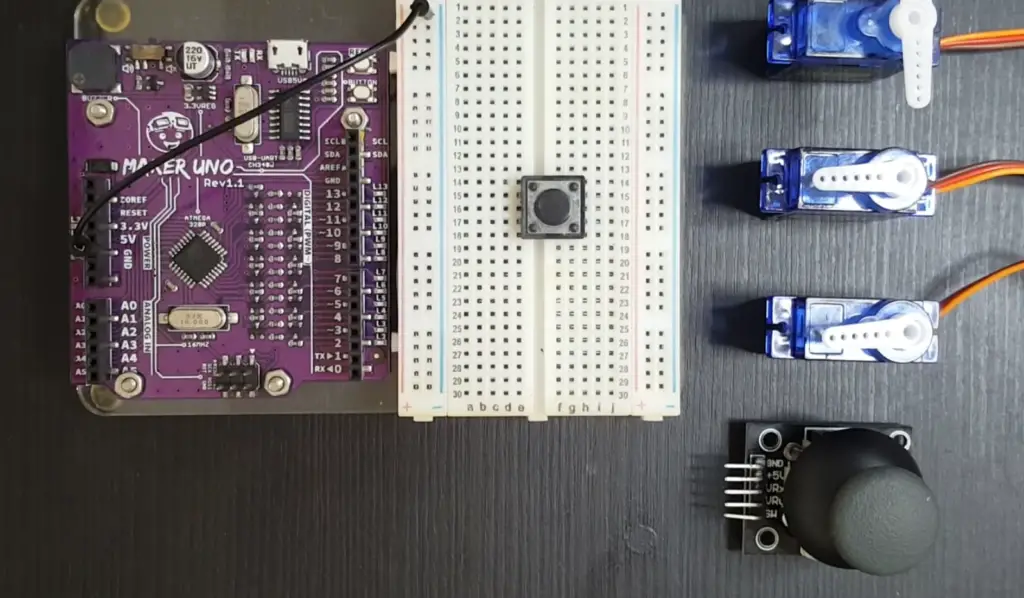
Servo motors are relatively inexpensive when compared to other types of motors such as stepper and brushless DC motors. Their cost-effectiveness means that they can be used in a wide range of robotics applications without breaking the bank.
Power
Servos are able to produce a great deal of torque for their size and weight, making them ideal for use in robotic arms where powerful movement is necessary. This power also ensures accuracy in movements and makes it easier to control objects with precision.
Flexibility
Unlike other motor technologies which require significant energy input, servo motors only need minimal energy input to function properly, making them very efficient and flexible in terms of energy consumption. They can also be programmed quickly and easily, allowing for a wide range of movements to be programmed in a short amount of time.
Durability
Servo motors are designed to withstand long-term use and have a long lifespan, so they can be used for many years without needing significant maintenance or repairs. This makes them ideal for robotics applications where accuracy is essential but downtime must be kept to a minimum. [3]
Different Sizes
Servo motors come in many different sizes, from tiny micro-servos to larger industrial-grade units. This means that they can be used for a wide range of robotic applications, such as building miniature robots or powering industrial automation systems. This variety makes them one of the most versatile and ubiquitous motor technologies available.
Ease of Use
Servo motors are designed to be user-friendly and easy to install, which makes them ideal for use in robotics applications. They can be programmed quickly and easily, allowing robots to be built with minimal technical expertise.
Availability
Servo motors are widely available from many different manufacturers, so finding compatible parts and components is usually straightforward. This ensures that robotics projects can be completed quickly and easily without having to wait for parts from overseas suppliers or rare components.
Weight
Servo motors are relatively light compared to other types of motors, making them ideal for use in robotics applications. This makes it easier to build robots with reduced weight and improved mobility without sacrificing power or accuracy. [4]
The Future of Servo Motor Arm Robotic Technology
The use of servo motor arm robotics is becoming increasingly popular, and the technology is advancing rapidly.
In addition to this, servo motors are energy-efficient and reliable when compared with other types of motors used for robotics applications. This makes them ideal for robotic arms since they don’t require as much energy as other types of motors, yet still provide excellent precision and speed. Moreover, servo motor arms have a wide range of uses in manufacturing, agriculture, aerospace, and other industries.
The use of servo motors in robotic arms is expected to grow in the coming years due to their many advantages. With advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning, it is likely that these robotic arms will become even more sophisticated and accurate as time goes on. This means that they can be used for a variety of applications from simple pick-and-place operations to complex assembly tasks. In addition, with the increase in automation, robots are also becoming more affordable which makes servo motor arm robotics an increasingly attractive option for businesses and consumers alike.
Types of Robotic Arms
Robotic arms come in a variety of shapes and sizes, depending on the application. They typically consist of several movable joints that are powered by various types of motors. The most common type is the servo motor which is used to control precise movements in robotic arms. A servo motor uses feedback from an encoder or potentiometer to move to a specific angle or position with high accuracy and repeatability. This makes it ideal for applications such as welding, assembly, packaging, material handling, and more.
Servo motors can be further divided into two categories: brushless DC (BLDC) motors and stepper motors. Brushless DC motors offer higher torque than stepper motors but require more complex electronic controllers. Stepper motors are ideal for situations where precise positioning and high speed are required, such as in robotic arms that must move quickly with repeatable accuracy.
A robotic arm powered by servo motors has a number of advantages over other robots powered by different types of motors. Servo motors are more efficient than brushed DC or stepper motors and require less power to operate. Additionally, they can provide higher torque at lower speeds compared to brushed DC or stepper motors. This makes them ideal for applications that require precise movements or high precision work, such as assembly tasks. Finally, servo motors provide better speed control when compared to brushless DC and stepper motor-powered robots which can experience acceleration issues at high speeds. [5]
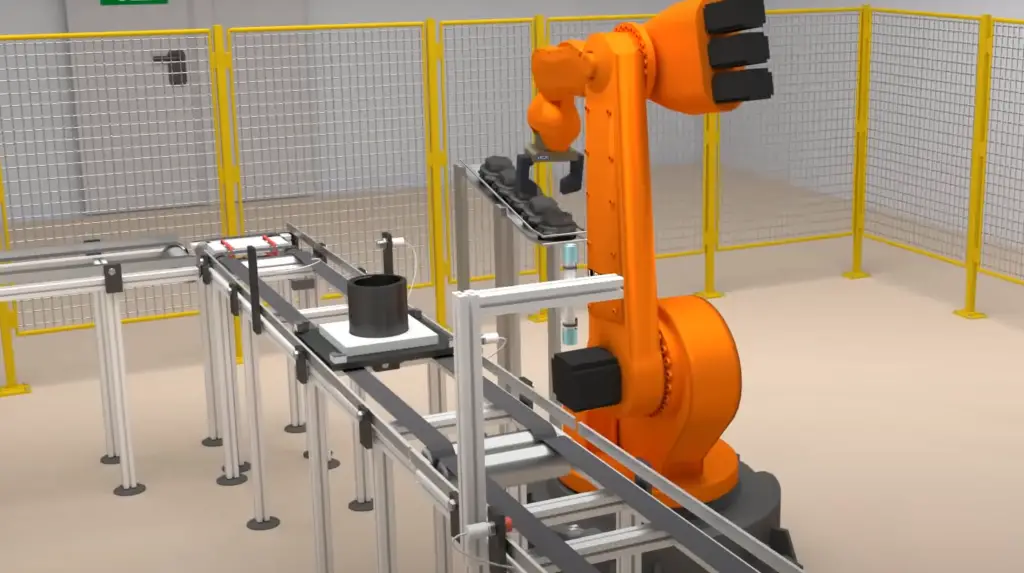

How Do You Select the Servo Motor?
When selecting the servo motor for a robotic arm, it is important to consider several factors.
Firstly, you should determine the load capacity of your robotic arm and select a motor that can handle this load.
Secondly, you should decide on the speed and torque requirements of your robot arm; these details will guide you in selecting a motor with sufficient power.
Thirdly, you need to consider the type of environment in which the arm will be operating; some motors are better suited to certain environments than others.
Finally, reliability is key when selecting a servo motor for use in a robotic arm – choosing one with a reliable track record and good customer reviews is always advised.
By taking all these factors into consideration before making your decision, you can ensure that you select the best motor for your robotic arm.
What Are Other Alternatives?
Besides servo motors, there are other types of motors used in robotic arms. DC motors and stepper motors are some of the commonly used alternatives for robotics applications.
DC Motors have two main advantages: they are relatively cheap compared to servo motors, and can provide a wide range of speeds. The downside is that these motors require a more complicated control system than servo motors, as their speed needs to be constantly adjusted.
Stepper Motors offer precise control over positioning and motion. They rely on cycles of electrical pulses to move the motor’s shaft in a specific direction by a predetermined number of steps per revolution. This makes them ideal for applications where accuracy is key, such as 3D printing or assembly line automation.
Regardless of the type of motor used, all robotic arms need a controller to manage their movements. A controller can be programmed with instructions and is responsible for sending pulses to the motors, telling them how to move in order to achieve a certain task.
As technology advances, more efficient alternatives to servo motors will become available for robotics applications. For now, servos are still the most widely used option due to their simplicity and cost-effectiveness. They are also reliable and provide superior control over robotic arm movements compared to other types of motors. [6]

Why Can’t You Use DC Brushless Motors For a Robotic Arm?
DC brushless motors are often used in consumer products and appliances due to their low cost and ease of use. However, they are not suitable for robotic arms because of their limited torque capabilities. Robotic arms require a great deal of torque to move objects accurately and efficiently; DC brushless motors simply don’t have the power needed to accomplish these tasks.
That’s why you need a servo motor with higher torque output when building a robotic arm. Servo motors also offer more precise positioning control that is vital for successful manipulation tasks.
Finally, servo motors can be positioned accurately without requiring complex algorithms or external sensing devices, which makes them much easier to implement in robotics projects. For all these reasons, servo motors are the preferred choice for robotic arms and other applications requiring precise motion control.
In summary, DC brushless motors are not suitable for robotic arms due to their low torque output and lack of precision. Servo motors offer the power and accuracy needed for these demanding tasks, making them the ideal choice for robotics projects. With the right servo motor, you can create a powerful robotic arm that performs complex manipulation tasks with ease. [7]

FAQ
Why are servo motors used?
Servo motors are used on robotic arms because they enable precise positioning and speed control. This is extremely important in robotics applications, as the robot arm must be able to move accurately and quickly to complete specific tasks. Servo motors run on electricity and are designed for reliable, repetitive motion when called upon. They range in size from very small (like those used in toys and models) to very large sizes that can be used on industrial robots. When combined with feedback devices such as encoders, servo motors help robotic arms achieve precision movement at high speeds.
What advantages do servo motors offer?
Servo motors have many advantages over other types of motor systems. They provide excellent torque output at low speed, which is essential for precise movement. Servo motors are also relatively easy to configure and program, making them ideal for robotic arms that require frequent adjustments. Additionally, servo motors are typically very efficient and can run for a long time without needing maintenance or repairs. Their small form factor makes them a good choice when space is limited, such as in smaller robots.
Which motor to use in a robotic arm?
The type of motor to use in a robotic arm depends on the application and environment. Generally speaking, servo motors are the most popular choice for robotic arms because they offer precise positioning, high torque output, and reliability. However, other types of motors, such as stepper motors or DC motors may also be suitable depending on the needs of the robot arm. In addition to choosing a motor based on performance considerations, it is important to make sure that the motor can handle any environmental factors or safety requirements such as vibration dampening or overload protection. Additionally, careful consideration should be given to power consumption and runtime when selecting a motor for a robotic arm. This will help ensure that you get the best electrical efficiency from your motor over time.
How many servo motors are needed for a robotic arm?
The number of servo motors needed for a robotic arm depends on the complexity of the arm and its intended motion. Generally, two to four servos are required for an entry-level robotic arm, while more complex arms may require up to six or even eight servos. More advanced arms can also use custom designed actuators that incorporate multiple degrees of freedom, allowing them to move in a wide range of motions and directions. Ultimately, the number of servo motors needed will depend on the specific design and application requirements of each type of robotic arm. Additionally, it is important to consider mounting options when selecting the right number of servos; some may need special mounts due to their size or weight.
What is the difference between servo motor and stepper motor for robotic arm?
Servo motors and stepper motors are both commonly used for robotic arms, but they offer different advantages. Servo motors can move quickly and accurately with a high degree of torque, making them ideal for fast movements like grabbing and releasing objects. They also provide feedback on the position of the arm in real-time to ensure accuracy. Stepper motors are best suited for slow, precise movements due to their excellent control over position and speed, which makes them perfect for more delicate tasks such as painting or welding. Additionally, while servos require an external controller to operate, stepper motors can be controlled directly from within the robot’s electronics.
Useful Video: Technical animation: How a Servo Motor works
Conclusion
Servo motors play an important role in the development of robotic arms and other automated machinery. By allowing for precise positioning and control, servos enable robots to perform accurate tasks with minimal human intervention. Additionally, the use of a servo motor minimizes the amount of energy needed to move a part or object exactly where it needs to go. Servo motors will continue to be an invaluable tool for robot designers as technology advances and robotics become more commonplace in our lives. With its flexibility, precision, and low power consumption capabilities, the servo motor looks set to remain at the heart of robotic arm technology for many years to come.
References
- https://roboticsandautomationnews.com/2022/02/25/why-are-servo-motors-used-so-widely-in-robotics/49608/
- https://www.automate.org/blogs/servo-motors-explained-and-why-they-re-useful-in-robotics
- https://www.evsint.com/servo-motor-for-robotic-arm/
- https://rozum.com/servos-as-robot-components/
- https://electronicguidebook.com/why-is-a-servo-motor-used-in-a-robotic-arm-top-5-reasons/
- https://www.b2eautomation.com/insights/stepper-motors-vs-servo-motors-understand-your-robotics-needs
- https://www.universal-robots.com/in/blog/robotic-arm-mechanism/













Leave a Reply