These devices are integral to the functioning of many electrical and electronic systems, and are used in a wide range of applications. Iron core inductors can be found in everything from computer power supplies to radios and televisions. In this blog post, we’ll take a closer look at how these devices work and their importance in the world of electronics. Read on to learn more!
What is an Iron Core Inductor?
Built with a coil of wire wrapped around an iron core, the iron core inductor is used to store electrical energy and regulate current flow. The use of this type of inductor is widespread in electronics due to its capacity for energy storage and the generation of magnetic fields. Depending on the purpose, iron cores can differ in shape and size. For added strength and effectiveness, material such as steel or ferrite may be combined with the core. An iron core inductor has several advantages compared to other types of inductors, including increased efficiency at high frequencies, greater power dissipation capacity, higher current ratings for a given size and weight, reduced noise levels, and better temperature stability. Furthermore, using an iron core also boosts the inductor’s self-resonance frequency, allowing for reduced noise in electronic circuits.
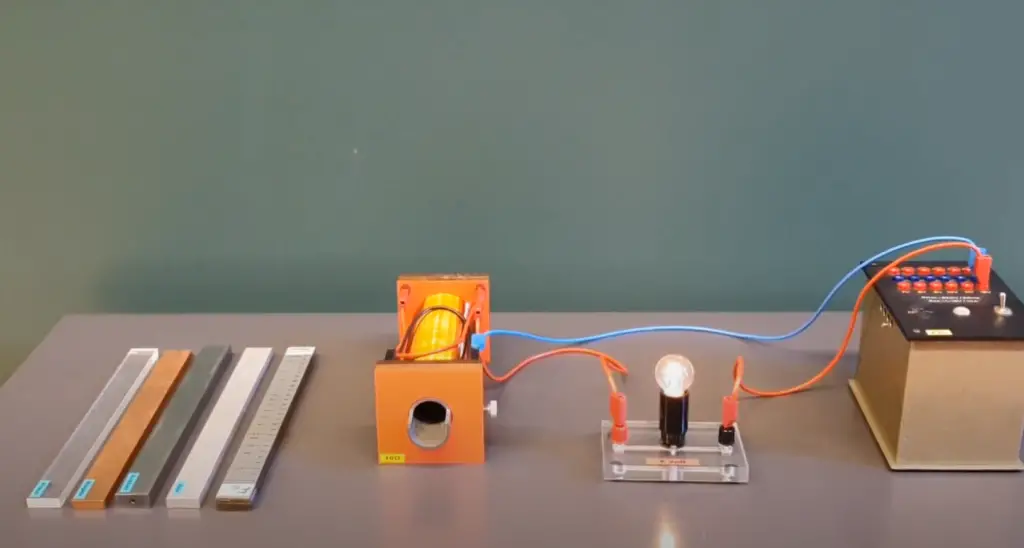
Iron core inductors are often used in applications such as power supplies, filters, and amplifiers. They can also be used to form resonant circuits to provide tuning of an oscillator or frequency selection for a radio receiver. The use of an iron core increases the inductor’s self-resonance frequency which can reduce interference in electronic circuits. For optimum efficiency, appropriate sizing and placement of inductors is imperative.
In conclusion, an iron core inductor is a type of inductor that uses an iron core to increase efficiency, reduce noise levels, improve temperature stability, and increase current ratings. It has several advantages over other types of inductors and is commonly used in electronics due to its ability to store energy and create magnetic fields. Proper sizing and placement is still needed for optimal performance, however, so proper research should be conducted before using an iron core inductor in a given application. [1]
Construction of Iron Core Inductor
Constructed from an iron core, insulated wire and a coil, the iron core inductor is an essential element in electrical engineering. The iron core is formed from laminated steel plates that are stacked together to form a ferromagnetic material. The windings are then wound around the lamination which increases the inductance of the winding, meaning more current can flow for a given voltage drop across the inductor. This makes them ideal for use in power supplies, filters, and DC to AC converters as they are able to withstand high currents without overheating or burning out.
Additionally, because of their construction, these inductors have very low losses due to their low resistance compared to other types of inductors.
Lastly, the size of an iron core inductor is usually quite small compared to other types of inductors, making them ideal for applications where space is limited.
Overall, due to their construction and size benefits, iron core inductors are popular in many different industries including automotive, telecommunications, aerospace and more. The use of these inductors is constantly increasing as technology improves and new applications are developed. [2]
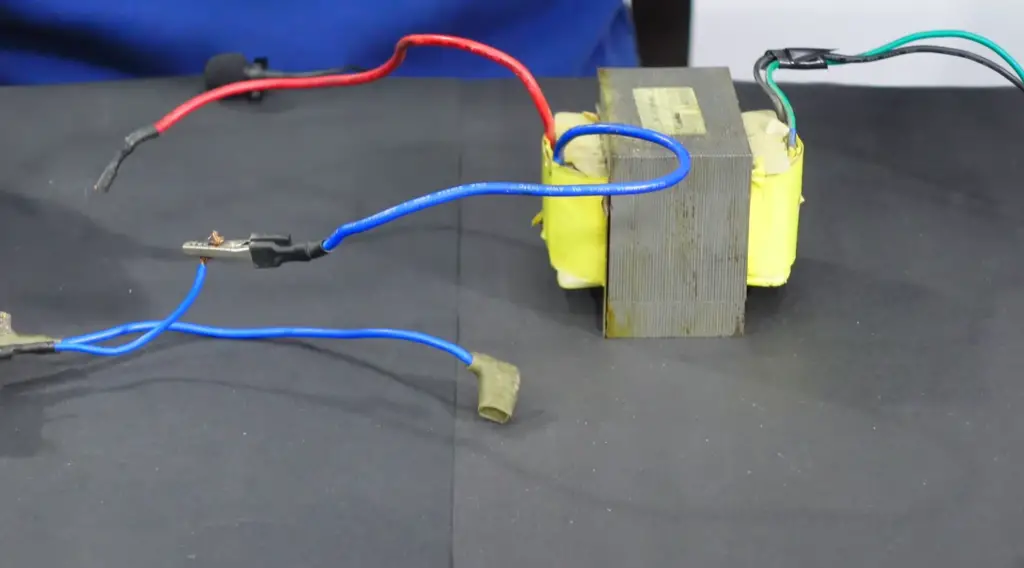
Iron Core Inductor Design
The purpose of the iron core inductor is to increase the strength of an electrical signal. It does this by increasing the inductance, which causes a signal’s voltage to increase and decreases its current.
The design of an iron core inductor involves winding insulated wire around a ferrite or iron-silicon alloy cylinder or drum called a bobbin in order to create multiple turns or loops. The number of turns will determine how much inductance is created and can range from 1 turn up to thousands depending on the intended application. Additionally, the size and shape of the bobbin will affect how much energy can be stored within it.
Working of Iron Core Inductor
It consists of a coil of wire wrapped around an iron core, usually in the shape of a cylinder. Once electricity flows through the coil, a magnetic field is induced within its iron core. This magnetic field then induces an electric current in any conductive material that is present near the inductor. In this way, it can be used to control and regulate electrical currents in circuits and other electronics. For example, when power is turned on or off, an inductor will help smooth out any sudden spikes or drops in voltage by absorbing some of the energy from the circuit and dissipating it as heat.
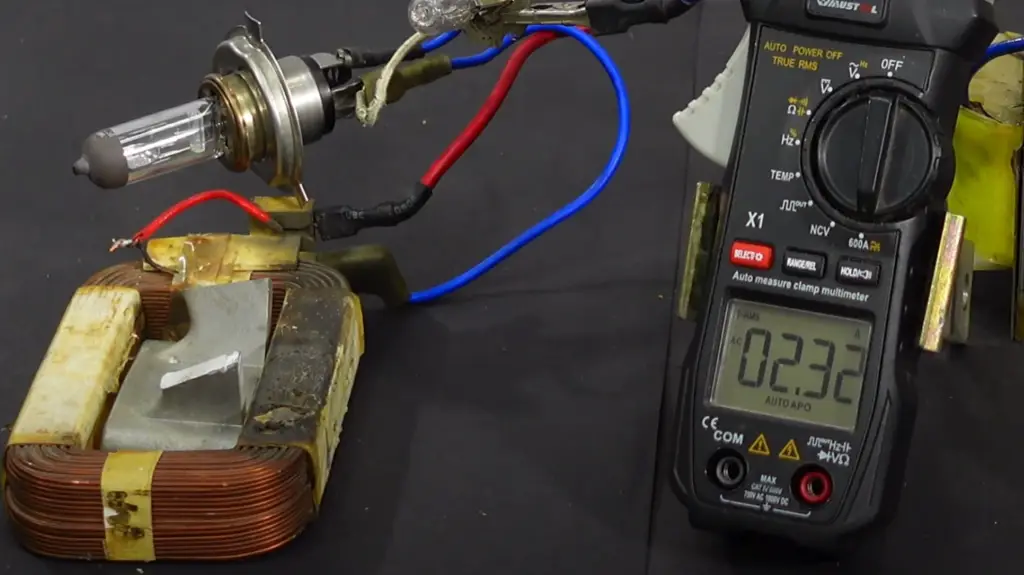
Additionally, they are often used to filter noise from signals or create resonance with other electronic components. Iron core inductors can also be used to detect changes in electrical current, allowing them to act as sensors or triggers for other electronic functions. [3]
Advantages of Iron Core Inductor
An iron core inductor is a type of electrical component that has a coil of wire wound around an iron or ferrite core. This gives it the ability to store energy in the form of a magnetic field, converting back and forth between electrical energy and magnetic fields. There are many advantages to using an iron core inductor as opposed to other types of components.
One advantage of an iron core inductor is its high current rating. The use of an iron core allows for increased current flow due to the greater permeability of the material, which reduces power loss in comparison with other types of components. This makes them ideal for use in applications such as audio amplifiers, where currents need to be controlled accurately while also delivering maximum power output.
Another advantage of an iron core inductor is its ability to suppress electrical noise. The ferrite core material has a high magnetic permeability, allowing it to act as a shield against interference from other components or from external sources such as radio signals. This makes them ideal for use in installations where reducing interference and noise is important, such as automotive applications.
In addition, the design of an iron core inductor allows for smaller component sizes than other types of components due to their higher efficiency in storing energy. This reduced size makes them easier to fit into existing designs without having to redesign the entire system around larger components. Additionally, they are relatively inexpensive compared with other types of components, making them a cost-effective choice for many applications.
Overall, iron core inductors are a versatile and cost-effective choice for many electronic systems. Their high current rating, noise suppression, and small size make them ideal for use in various settings. With their versatility and affordability, they are an important component to consider when designing or building an electronic system. [4]
Disadvantages of Iron Core Inductor
One of the major disadvantages of an iron core inductor is its large size. Compared to air core and ferrite core inductors, iron core inductors are much larger and bulkier. This makes them difficult to place in certain applications where space is tight or at a premium. Iron core inductors also have a higher DC resistance than other types of induction coils, which can create losses in high frequency applications.
Additionally, their DC resistance can vary widely due to changes in temperature, meaning they may not be suitable for use in circuits that require stability over time.

Lastly, iron cores tend to saturate quickly at high currents which limits the amount of power they can handle without distorting the signal. Therefore, it’s important to choose an iron core inductor that can handle the current and power levels of your particular application.
In summary, iron core inductors are typically larger, offer a higher DC resistance, and have a reduced tolerance for high currents compared to other types of coils. Therefore, careful consideration should be taken when selecting an iron core inductor for any given application.
Applications of Iron Core Inductor
Iron core inductors are used in a variety of applications, including power supplies, electrical transformers, motors, solenoids, and radio frequency (RF) coils. Inductors also serve as filters that block high frequencies while allowing lower frequencies to pass through. These components are often found in audio equipment such as amplifiers and speakers. In addition, iron core inductors can be used for current sensing purposes; for example, they can be placed in between wires to detect changes in current flow. They can also be used to create magnetic fields and store energy for later use.
Finally, iron core inductors are commonly used in electrical circuits to shape the waveform of an AC signal or reduce noise interference from other devices on the same circuit. By controlling these factors, engineers can create circuits with more reliable operation and longer-term performance. Overall, iron core inductors are used in a wide range of applications due to their ability to store energy, regulate electric current, and reduce noise interference. [5]
Types of Inductors
In addition to iron core inductors, there are a few other types of inductors that are commonly used in electrical circuit designs.
- Air core inductors use air as the main component instead of an iron core and offer high frequency performance with low losses.
- Ferrite core inductors use ferrite powder for their cores and have lower losses than iron core inductors but are limited by their self-resonance frequency.
- Wire wound inductors are made up of wire wrapped around a form or frame and can provide very high levels of insulation resistance due to the air gap between the windings. They also offer excellent thermal stability.
Finally, multilayer ceramic chip (MLCC) inductors consist of several layers of ceramic material which act together as a single inductor. They offer excellent frequency response, low cost and high reliability.
No matter which type of inductor is used in a circuit design, they all serve the same purpose: to store energy in a magnetic field when current passes through them. This can be used to limit or filter currents and voltages, as well as improve the power factor and efficiency of electrical circuits. Inductors play an important role in many electronic devices, from radios and TVs to computers and cell phones. With the right type of inductor for your application, you’ll get maximum performance from your circuit design.

How To Choose an Iron Core Inductor?
When choosing an iron core inductor, there are several considerations. The size of the inductor is important to consider, as you need one that can fit into the available space in your circuit or project. Additionally, you should decide which type of material would work best for your application – ferrite or powdered iron cores are both common types used in inductors.
Other factors to consider include the maximum current rating, quality factor (Q), saturation flux density, and self-resonant frequency. Knowing how much power will be required from the inductor is also a key factor in choosing the right model. It’s important to ensure that the chosen model will be able to handle all desired applications without overloading or wasting energy due to inefficient performance.
Finally, it’s important to consider the cost of an iron core inductor when making your decision. Although cost is not a primary factor for all applications, there are still some instances where budget plays a role in selecting the best product. Taking all factors into consideration – size, material type, power requirements, and cost – will help you make an informed decision on which iron core inductor is right for your project.
FAQ
What is an iron core inductor used for?
It is most often used to increase the inductance of a circuit, which can be important for suppressing transients and providing better power factor correction. Additionally, it can also be used for filtering noise and creating DC bias levels. In some cases, it can even be used as part of the LC tank that stores energy so that it can later be released back into the supply line. This type of device has become popular because its low-cost construction makes it easy to produce and integrate into modern circuitry.
What is the difference between iron core and air core inductor?
An iron core inductor is an electrical component consisting of a coil of wire wrapped around an iron core. This type of inductor has higher magnetic permeability than air core inductors, which are simply coils of wire with no iron core. The increased permeability allows the iron-core inductor to store more energy in its magnetic field and therefore have higher inductance. Iron-core inductors also tend to be physically larger than their air-core counterparts. This is due to the size of the iron core itself, as well as the length and diameter of the coil needed to generate enough power in order to increase the magnetization of that same core material. As a result, they’re typically used in applications where greater levels of current or voltage are required. They’re also more expensive to manufacture than air-core inductors due to the cost of the raw materials and labor involved in making them. However, air core inductors are still used for certain applications where their smaller size and lower cost make them a better choice.
What is the difference between iron and ferrite core inductor?
Iron core inductors are typically made from an iron material such as steel and have a ferromagnetic core. The main purpose of the iron core is to increase the magnetic field strength of the inductor, which aids in achieving higher inductance and current levels than what would be possible with other materials. Ferrite core inductors are typically made from ceramic materials and their cores are composed of iron oxide (Fe2O3). Unlike iron cores, ferrite has no saturation point and can carry high amounts of current without becoming saturated or overheating. Ferrite also has low losses due to its low resistance compared to other materials. This makes it ideal for applications that require low-level signals or frequencies up to 1 MHz.
How does iron core affect inductance?
An iron core inductor is essentially a coil of wire wrapped around an iron core material. The presence of the iron core has two main effects on the inductance of the device. Firstly, it increases the magnetic flux through the inductor, increasing its ability to store energy and produce a stronger electromagnetic field. Secondly, it reduces losses due to eddy currents which are caused by alternating magnetic fields within a circuit. This makes an iron core inductor more efficient than traditional air-core ones as less power is lost in the form of heat and sound. All of these factors result in higher quality, more reliable electrical circuits with better performance characteristics when compared to their air-core counterparts.
Useful Video: Powdered Iron Core Inductor Tests
Conclusion
An iron core inductor is a type of electrical component that uses the principles of electromagnetic induction to store and release energy. It consists of an iron core, which acts as a magnetic field collector and concentrator, wrapped with a conductive material such as copper wire. The core stores the energy in its magnetic field, which can then be released slowly over time when connected to a circuit. Iron core inductors are used in many applications including power supplies, audio equipment, and motors. They are relatively simple components but are capable of producing strong fields that can handle large currents. By understanding how these components work and their different types, engineers can use them effectively for their specific application needs.
References
- https://www.electricalvolt.com/2022/12/iron-core-inductor/
- https://www.elprocus.com/iron-core-inductor/
- https://www.polytechnichub.com/iron-core-inductor/
- https://electronicsarea.com/iron-core-inductor/
- https://electricpowersystemsintl.com/electric-power-systems-blog/air-vs-iron-core-inductors/













Leave a Reply