Do you know what a rheostat is? If not, don’t worry – you’re not alone. Here we will find out what rheostat is. Moreover, in this blog post, we will discuss the construction and operation of a rheostat, and we will explore some of its applications!
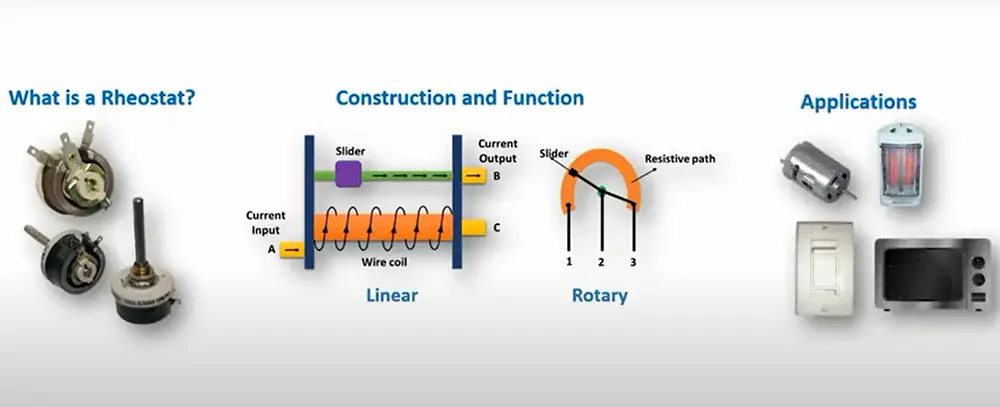
What is a rheostat?
Rheostats are used in a variety of applications, such as in lighting fixtures, motor speed controls, and volume controls.
- Rheostats are commonly used as dimmers for lights and other electrical devices. They can be used to lower the power output of a device, which can in turn be used to dim lights or reduce the speed of motors.
- Rheostats can also be used to control the flow of current in a circuit without interrupting the flow of current. This is known as a shunt resistor. By placing a rheostat in parallel with a load, the amount of current flowing through the load can be controlled without affecting the voltage across the load.
- Rheostats are also used as potential dividers. By placing a rheostat in series with a voltage source, the voltage across the load can be controlled. This can be used to create a voltage-controlled resistor, which can be used to control the current flowing through a circuit in response to changes in voltage.
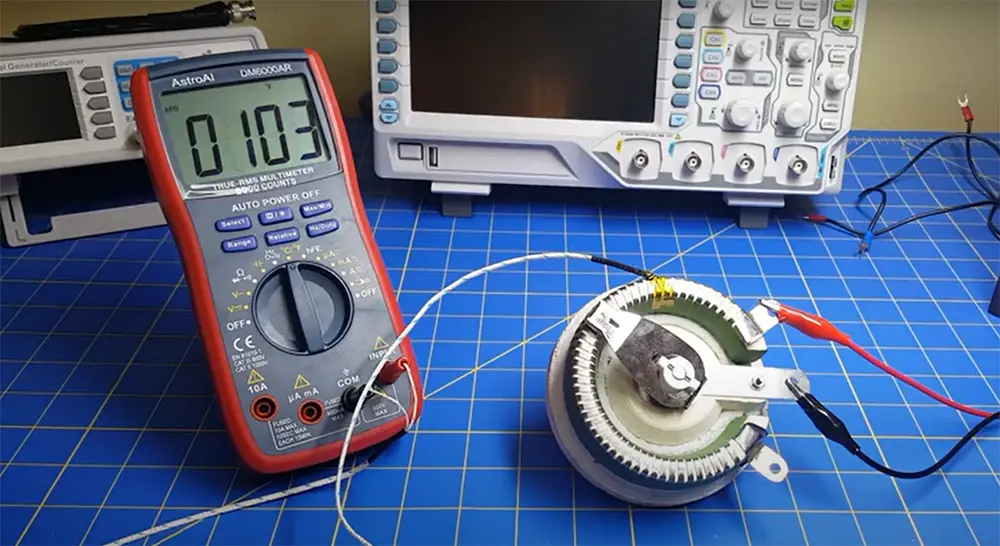

- Rheostats can be used in a variety of other applications where it is necessary to control the flow of current. For example, they can be used as inrush current limiters, which are used to prevent damage to electrical devices by limiting the amount of current that flows through them when they are first turned on.
- Rheostats are also used in motor speed controls, such as those used to control the speed of electric fans and pumps. By varying the resistance in the circuit, the speed of the motor can be controlled.
- Rheostats can also be used in audio applications, such as volume controls and tone controls. By varying the resistance in the circuit, the amount of current flowing through the speaker can be controlled, which will, in turn, control the volume or tone of the sound.
- Rheostats are also used as load banks, which are devices that are used to test the performance of electrical equipment by providing a variable resistive load.
Rheostats are available in a variety of different sizes and shapes and can be made from a variety of different materials.
Rheostats are an essential component of many electronic devices. Choose the right one for your application to ensure optimal performance.
How does a rheostat work?
A rheostat is a device that controls the flow of electricity in a circuit. It is made up of two conductive plates that are separated by an insulating material, such as glass or plastic. The plates are connected to the power source and the load. The amount of current flowing can be controlled by adjusting the distance between the plates.
When you turn the knob on a rheostat, you are actually changing the resistance in the circuit. Resistance is what limits the flow of electricity.
Moreover, a rheostat can be used to control the amount of power dissipated in a circuit. By increasing the resistance, you can decrease the amount of power dissipation.
Types of rheostats
There are four main types of rheostats: linear, rotary, ohmite, and plug-in. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages, so it’s important to choose the right one for your needs.
- Linear rheostats are the most common type. They’re simple to use and can be mounted in any orientation. Moreover, linear rheostats have a low resistance, so they’re ideal for use with high-power devices. However, they’re not as accurate as other types of rheostats and can be affected by temperature changes.
- Rotary rheostats are less common than linear rheostats, but they offer some advantages. Rotary rheostats are more durable and can handle higher power levels. They’re also easier to control precisely than linear rheostats. They also can’t be mounted in any orientation, so you’ll need to take that into account when choosing a location for them. However, rotary rheostats are more expensive and can be difficult to mount in some applications.
- Ohmite rheostats are the most accurate type of rheostat, but they’re also the most expensive. They’re not affected by temperature changes, so they can be used in applications where temperature stability is important. However, they’re not as durable as other types of rheostats and can’t handle as much power.
- Plug-in rheostats are the most versatile type of rheostat. They can be used in any orientation and are easy to mount. They’re also less expensive than ohmite rheostats. However, this type of rheostat is less accurate than other types and can’t handle as much power.
When choosing a rheostat, it’s important to consider the type of application you’re using it for. If accuracy is important, then an ohmite rheostat is the best choice. However, if you need a more durable rheostat that can handle higher power levels, then a rotary rheostat is a better choice. If you need a versatile rheostat that’s easy to mount, then a plug-in rheostat is the best choice.
You should also consider the power requirements of your application, the accuracy you need, and the environment in which the rheostat will be used. By taking all of these factors into account, you can choose the best rheostat for your needs.
Why is a rheostat connected in series?
There are several reasons for it:
- The very first reason is that if the rheostat were placed in parallel, it would draw too much current and possibly overheat or damage itself. It would also cause the voltage drop across it to be too small to have any effect on the circuit.
- Another reason has to do with efficiency. When a rheostat is placed in series, all of the current flowing through the circuit must flow through the rheostat. This means that the rheostat can dissipate all of the power being dissipated in the circuit. If the rheostat were placed in parallel, only a portion of the current would flow through it, and much of the power would be wasted.
- Finally, when a rheostat is placed in series with a load, the voltage across the load will be proportional to the resistance of the rheostat. This is because the voltage drop across a resistor is given by V=IR. If the rheostat were placed in parallel with the load, the voltage would be independent of the rheostat’s resistance.
So, in summary, the reasons for connecting a rheostat in series are: to protect it from too much current, to make it more efficient, and to make the voltage across the load proportional to the resistance of the rheostat.
What is the difference between rheostat and potentiometer?
Potentiometers are used to measure electric potential (voltage). Both potentiometers and rheostats are resistors, meaning they are devices that resist the flow of current.
The main difference between a rheostat and a potentiometer is that a rheostat is used to control the current in an electric circuit while a potentiometer is used to measure electric potential.
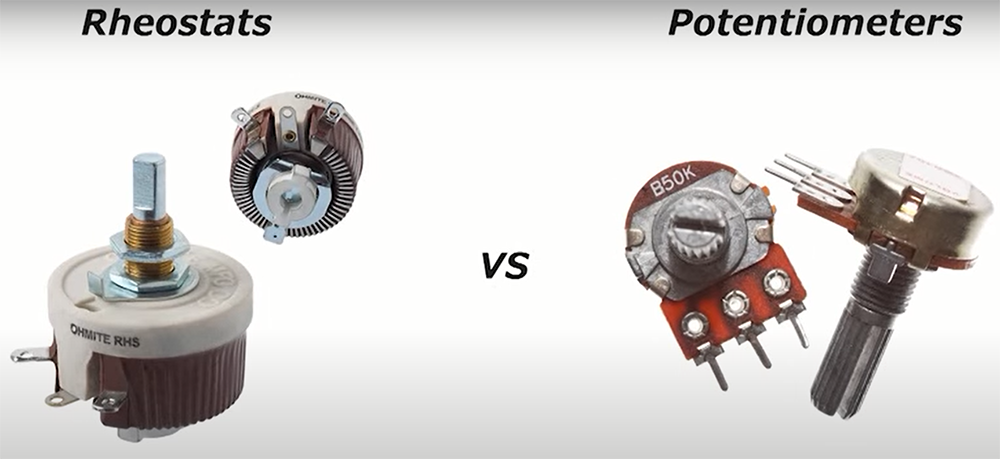

- A rheostat is made up of two parts: a resistive element and a wiper. The resistive element can be made of carbon, metal, or other material, and it typically has two terminals. The wiper is attached to one end of the resistive element and makes contact with it as it moves along the surface. This allows the resistance between the two terminals to be varied.
Rheostats are used in a variety of applications, such as controlling the intensity of a light bulb or the speed of an electric motor.
- Potentiometers, on the other hand, are made up of three terminals: a resistive element, a wiper, and a third terminal known as the tap. The tap is connected to the resistive element at a point that is not at either end. This allows the voltage across the resistive element to be measured.
Potentiometers are used in devices such as radios and volume controls to adjust the level of an audio signal.
Check more guides to improve your knowledge in electronics:
- Bleeder Resistor: What is it, and Where is it Used?
- How to Stop Resistors Getting Hot?
- How to Test a Varistor?
FAQ
Who invented rheostat?
The first rheostat was invented by Sir Charles Wheatstone in 1833. He used it to control the amount of current flowing through an electromagnet.
What can be used instead of rheostat?
There are several alternatives to rheostats, including potentiometers and light-dependent resistors (LDRs).
You can also wire a potentiometer in a way that it acts as a rheostat.
What is the symbol of rheostat?
The symbol for a rheostat is a triangle with two resistors in series. The point where the resistors meet is called the tap.
Can you use a rheostat outside?
Rheostats are not designed for outdoor use and can be damaged by exposure to the elements.
How to Wire a Potentiometer as Rheostat?
To wire a potentiometer as a rheostat, you will need to connect the wiper (the middle terminal) to one of the outside terminals. Then, connect the other outside terminal to either the positive or negative terminal of your power source. Finally, connect the other end of your power source to the ground.
But remember, a potentiometer is not designed to handle the same amount of power as a rheostat. So, if you are using a potentiometer as a rheostat, make sure that the power rating of the pot is higher than the power that you are trying to control.
What are some potential applications for rheostats?
Rheostats have a wide range of potential applications. They can be used to control the current in an electric circuit, to regulate the power output of a heater, or to adjust the brightness of a light. Rheostats can also be used as part of a security system, where they can be used to trigger an alarm if the current in a circuit exceeds a certain level. Rheostats can also be used in electrical motors and generators.
While rheostats are not as commonly used as they once were, due to the development of more advanced electronic devices, they still have a place in many industries and applications. As technology continues to evolve, it is likely that rheostats will find even more uses in the future.
What are some examples of devices that use rheostats?
Some examples of devices that use rheostats are light dimmers, audio volume controls, and ovens.
Rheostats are also used in some electric vehicles as a way to control the speed of the motor. By controlling the amount of current flowing through the rheostat, the speed of the motor can be varied.
In many cases, rheostats are used as a replacement for potentiometers. Potentiometers are similar to rheostats but they have a limited range of resistance values. Rheostats, on the other hand, can be made with a wide range of resistance values.
Rheostats can also be used in DC power supplies. By varying the resistance, the voltage can be controlled. This is useful for devices that require a specific voltage, such as laptops and cell phones.
Rheostats are also used in some welding machines. By controlling the amount of current flowing through the rheostat, the heat of the weld can be controlled. This is important because too much heat can damage the material being welded.
Is there a specific time when you would use a rheostat over another type of resistor?
There is no specific time when you would use a rheostat over another type of resistor, but there are some applications where a rheostat would be more beneficial. For example, if you need to adjust the resistance in a circuit without interrupting the current flow, a rheostat would be ideal. Additionally, if you need a high-powered resistor for heavy duty applications, a rheostat can handle more power than other types of resistors.
Rheostats are also used as variable speed controls for electric motors. By adjusting the resistance in the circuit, you can change the speed at which the motor runs.
Are there any special precautions you need to take when using a rheostat?
When using a rheostat, it is important to take precautions against electrical shock. Rheostats can generate high voltage and current levels, so always disconnect the power source before working on or around the device. Also, be sure to wear insulation gloves and use other safety measures when necessary.
Another thing to keep in mind is that rheostats can generate heat, so be careful not to touch any exposed metal parts while the device is in use. If you must handle the rheostat during operation, use a cloth or another insulating material to protect your hands.
Finally, remember that rheostats are precision devices and should be handled with care. Avoid dropping or otherwise damaging the rheostat, as this can affect its performance.
What is a rheostat Class 10?
A rheostat is a device that helps control the flow of electricity in a circuit. It is made up of a resistive element, such as a coil of wire, and two terminals. The resistance can be varied by adjusting the position of the slider or wiper that connects to the resistive element. This allows for precise control over the amount of current flowing through the circuit. Rheostats are used in a variety of applications, including light dimmers, power supplies, and electrical motors.
What is the SI unit of rheostat?
The SI unit of rheostat is the Ohm. Ohms are a measure of resistance, and rheostats are devices that control the flow of current in a circuit by varying the resistance. They are made of a material that has a high resistance to electricity, such as carbon or graphite.
Rheostats can also be used to measure voltage and current in a circuit. By measuring the voltage across a rheostat, we can calculate the amount of current flowing through it. This information can be used to troubleshoot electrical problems or determine whether
Why is rheostat used in electric circuits?
Rheostats are used in electric circuits for a variety of purposes. The most common use is to control the flow of current in a circuit. By controlling the amount of current flowing through a circuit, rheostats can be used to regulate the voltage in a circuit, or to control the power being consumed by a load.
Rheostats can also be used as sensors in some applications. By measuring the resistance of a rheostat, it is possible to determine the position of a moving object, such as a motor shaft or potentiometer knob. In this application, the rheostat acts as a variable resistor, whose resistance varies with the position of the moving object.
Finally, rheostats can be used as variable resistors in electronic circuits. By varying the resistance of a rheostat, it is possible to change the characteristics of a circuit, such as the gain of an amplifier or the cutoff frequency of a filter.
Does rheostat change voltage?
Rheostats don’t affect voltage directly. However, by changing the current flowing through a circuit, they indirectly change the voltage drop across that circuit.
In general, the higher the resistance of a rheostat, the greater the voltage drop. By increasing resistance, rheostats can be used to effectively lower voltage in a circuit.
Conversely, decreasing resistance will result in increased current flow and a corresponding increase in voltage drop. Therefore, by reducing resistance, rheostats can also be used to raise voltage in a circuit.
How do you connect a rheostat?
There are a few different ways to connect a rheostat, depending on the type of device you’re using it with. But generally you will need to connect one wire of rheostat to the voltage source, and the other wire to the device you wish to control the current to. Don’t forget to connect the other wire of your device to the voltage supply as well!
Once everything is set, turn on the power and observe the current flow through the device. If everything is working properly, you should be able to control the amount of current flowing through the device by adjusting the position of the rheostat’s knob.
What is the disadvantage of using rheostat?
There are a few disadvantages to using rheostats. One is that they tend to be large and bulky, so they may not be ideal for use in small spaces. Another is that they can generate a lot of heat, so they need to be used with caution in applications where heat could be an issue. Finally, because they have a lot of moving parts, they can be somewhat delicate and may require more maintenance than other types of electrical components.
Still, for many applications, the advantages of using a rheostat outweigh the disadvantages. Rheostats are rugged and reliable, and can handle a lot of power without problems. They’re also relatively easy to find and purchase, making them a good choice for many applications.
Is variable resistance and rheostat the same?
The terms variable resistor and rheostat are often used interchangeably, but there is a difference between the two. A rheostat controls the current in a circuit by adjusting the resistance in the circuit using two terminals, while a variable resistor is an electrical component that varies the amount of current in circuit while having three terminals.
Useful Video: What is a Rheostat?
Final Thoughts
Rheostats are a versatile and essential tool in many industries. By regulating the flow of electricity, they can be used to control everything from the speed of an electric motor to the intensity of a light bulb. If you need to control the flow of electricity in your home or workplace, a rheostat is likely the best solution.
While rheostats are relatively simple devices, it is important to choose the right one for your application. Be sure to consider the voltage and current rating of the rheostat, as well as the power rating. With so many different types and sizes of rheostats available, you should have no trouble finding one that meets your tasks!
Rheostats play a vital role in keeping our homes and businesses running smoothly. So next time you see one, take a moment to appreciate its humble power!
Did you find this article helpful? Let us know in the comments below! And be sure to check out our other blog posts for more great content like this.
Thanks for reading! Come back soon for more!
References:
- http://www.electricalterminology.com/rheostat/













In my opinion, adjustable rheostats are incredibly useful tools in controlling the flow of electricity and adjusting the amount of resistance in a circuit. They allow for fine-tuning and precise control, which can be crucial in certain applications. However, it is important to use them properly and carefully to avoid damage or danger. Because from what I’ve seen, people tend to either use them too much or not enough.