A transistor is a three-terminal active device used either as an electronic switch or amplifier. In digital circuits, it is used to build logic gates and other complex circuits. Analogously, in analog circuits transistors are used as amplifiers [1].
In this article, experts will show you how to make an amplifier using a transistor. This is a great project for beginners, and it only requires a few simple components. You will need a transistor, a resistor, and an audio input jack. We will also show you how to connect the amplifier to your speaker. Let’s get started!
Why Should You Make an Amplifier Using Transistor:
There are many reasons why you should make an amplifier using a transistor:
- Transistor amplifiers are much more efficient than other types of amplifiers;
- They are smaller in size and require less power;
- Transistor amplifiers can be made to operate over a wide range of frequencies;
- They are relatively simple to design and construct;
- And they can be made relatively cheaply;
- Additionally, transistor amplifiers can be easily customized to meet your specific needs;
- Finally, making your own amplifier gives you a much better understanding of how they work;
How to Make Audio Amplifier Using D882 Transistor:
1) Take All Components
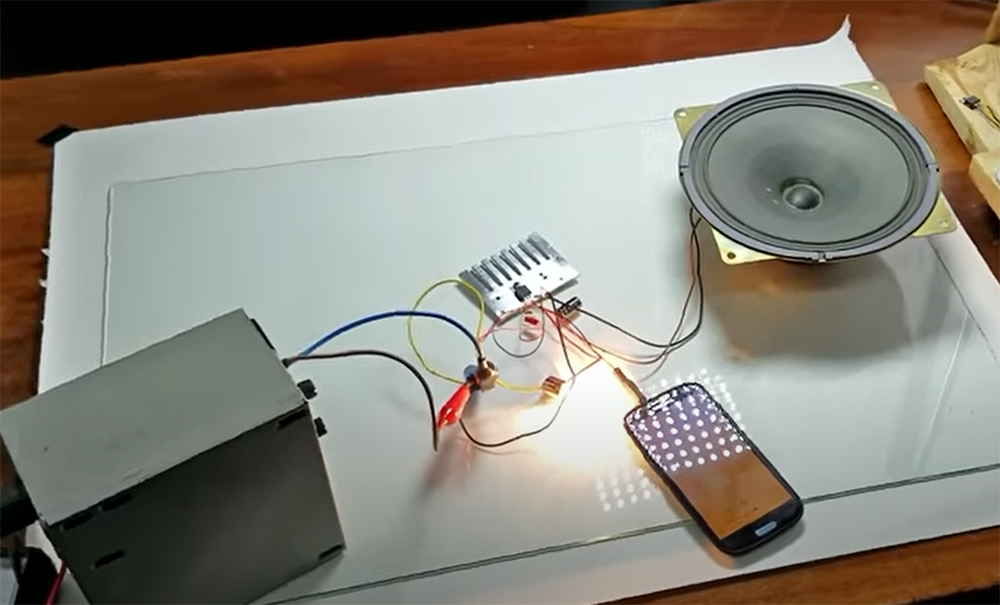
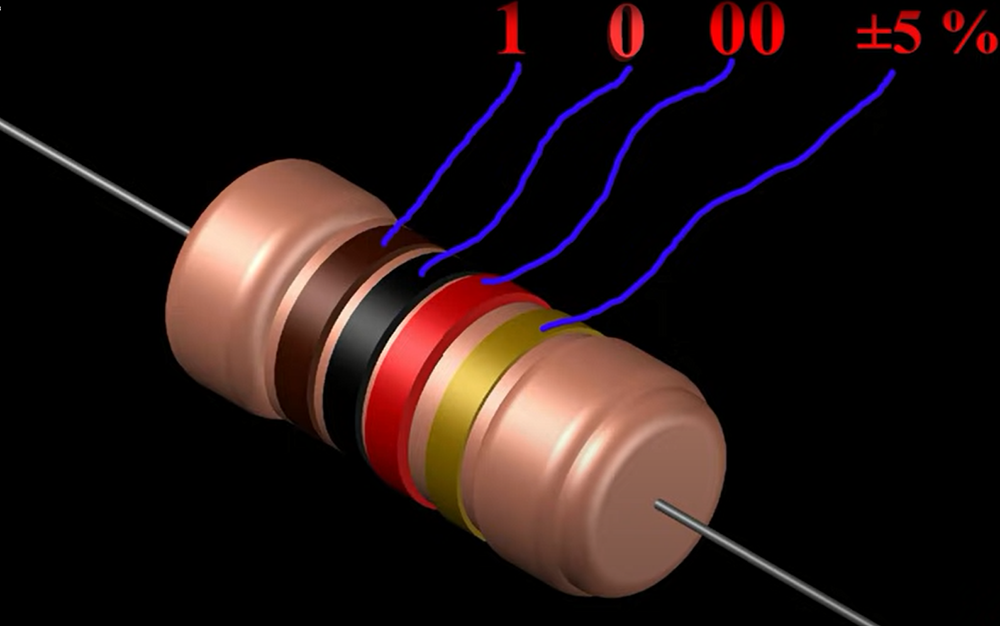
First of all, take all the components which are mentioned in the circuit diagram. You will need a 9V battery, battery clipper, 1K resistor, Capacitor (16V 100uf), 1 speaker, and D882 transistor [2].
2) Pins of Transistor D882
3) Connect 1K Resistor
Now, take the one end of the resistor and connect it with the base pin of transistor D882.
The other end of the resistor is connected to the positive terminal of the battery (Vcc).
This will provide a biasing voltage to the transistor.
Provide a DC voltage or current to a device such as a transistor so that it operates in its linear region.
4) Connect Capacitor
5) Connect Aux Cable Wire
Connect the auxiliary cable to the circuit. Connect the negative (-ve) wire of the aux cable to the capacitor’s -ve pin and the positive (+) wire of the aux cable to its Emitter pin.
6) Connect Speaker Wire
Now, take the other end of the speaker wire and connect it to the positive terminal of the battery. The other end of the speaker is connected to the Collector pin of transistor D882.
7) Connect Battery Clipper Wire
Connect the positive terminal of the battery clipper to the positive terminal of the battery. And connect the negative terminal of the battery clipper to transistor D882’s Collector pin.
8) Circuit Is Completed
To listen to songs, connect the battery clipper to the phone and insert the Aux cable into a music source. The amplifier will provide a louder sound than that of the mobile phone.
Tips for Making an Amplifier Using Transistor
Assuming that you have all the necessary components, making an amplifier using a transistor is not difficult. The most important thing is to choose the right type of transistor for your project. There are different types of transistors available in the market, so it is important to select the one that suits your requirements.
Once you have selected the transistor, the next step is to determine the value of resistors required for your circuit. You can use a calculator or online tool to calculate the values of resistors. After calculating the values, you need to connect the components together to build the circuit.

You might also be interested in these posts:
- Logic Analyzer vs. Oscilloscope
- How to Tune an Amp with a Multimeter?
- How to Solder Wires to Connectors?
Comparison of Amplifiers Made Using Transistors
This table presents a comparison of various indicators for amplifiers that are constructed using transistors. Amplifiers are electronic devices that increase the amplitude of electrical signals, and transistors play a crucial role in their construction. The indicators compared in the table are essential in understanding the performance and characteristics of these amplifiers.
| Indicator | Class A Amplifier | Class B Amplifier | Class AB Amplifier |
|---|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | 25-30% | 70-78% | 50-70% |
| Linearity | High | Low | Moderate |
| Distortion | Low | High | Low-Moderate |
| Power Consumption | High | Low | Moderate |
| Heat Dissipation | High | Low | Moderate |
| Frequency Range | 20 Hz – 20 kHz | 20 Hz – 20 kHz | 20 Hz – 20 kHz |
| Applications | Audio amplification in high-fidelity systems | Audio amplification in low-power devices | Audio amplification in mid-power devices |
The table compares three common types of amplifiers that use transistors: Class A, Class B, and Class AB amplifiers.
- Efficiency: Class B amplifiers are more efficient as they use one transistor for each half of the signal cycle, resulting in less power wastage.
- Linearity: Class A amplifiers have high linearity, meaning they reproduce the input signal with minimal distortion.
- Distortion: Class B amplifiers have higher distortion due to their operation involving two transistors turning on and off at specific points.
- Power Consumption: Class B amplifiers consume less power as they only draw current when the input signal is present.
- Heat Dissipation: Class A amplifiers generate more heat since the transistors are always conducting.
- Frequency Range: All three types typically cover the standard audio frequency range.
- Applications: Class A amplifiers are suitable for high-fidelity audio applications, while Class B and AB amplifiers are used in low-power and mid-power devices, respectively.
This comparison can help in choosing the appropriate amplifier type based on specific application requirements.
FAQ
How can I make a transistor amplifier?
You’ll need a few basic components to make a transistor amplifier: transistors, resistors, capacitors, and an inductor. You can find all of these components at your local electronics store.
Once you have all of your materials, follow these steps:
- First, build the circuit;
- Next, connect the negative lead of your power supply to the ground (GND) rail on your breadboard;
- Now connect the positive lead of your power supply to the collector (C) terminal of transistor Q_T_P;
- Connect a resistor from the base (B) terminal of Q_T_P to the positive lead of your power supply;
- Finally, connect a capacitor from the emitter (E) terminal of Q_T_P to the ground;
Now that your circuit is complete, you can test it out by applying a signal to the base of transistor Q_T_P. If everything is working properly, you should see an amplified signal at the collector of Q_T_P.
Which transistor is best for an amplifier?
In most electronic circuits, the NPN transistor amplifier circuit is used.
Consider a voltage divider biasing circuit, which is often known as a single-stage transistor amplifier circuit.
It provides the necessary DC bias voltages to the transistor so that it can operate in its active region. The NPN transistor is used as an amplifier because of its low input impedance, which means that it doesn’t draw much current from the input signal source.
The two most popular types of transistors are bipolar junction transistors (BJTs) and field-effect transistors (FETs). BJTs are made of two p-type semiconductor materials sandwiching an n-type material. FETs are made of a single continuous strip of p-type or n-type material with regions of the opposite type at either end [3].
How do you wire a transistor as an amplifier?
To wire a transistor as an amplifier, you need to connect the collector to the load, and the emitter to the ground. The base is where the input signal is applied. When wiring a transistor as an amplifier, it’s important to remember that the current flow is from collector to emitter, not from emitter to collector.
If you want to increase the gain of your amplifier, you can do so by adding more transistors in parallel. Just be sure that each transistor has its own resistor connected to the base. You can also add capacitors to your circuit to filter out any unwanted noise.
If you’re looking to build a powerful amplifier, transistors are a great option. By following a few simple steps, you can easily wire them up to create a circuit that amplifies your signal. Just be sure to pay attention to the current flow and use the appropriate diagram for your configuration. With a little bit of effort, you can create a powerful amplifier that will serve you well.
How can I make a speaker amplifier at home?
To make a speaker amplifier at home, you will need [4]:
- A power source (batteries work great);
- An audio input source (like a phone or laptop);
- A speaker;
- Some basic electronic components (wires, breadboard, etc.);
- A transistor;
The first step is to connect your power source to the breadboard. Then, you’ll want to add the transistor. The collector of the transistor should be connected to the positive lead of the power source, and the emitter should be connected to the ground. The base will be where you connect your audio input.
Next, you’ll want to add your speaker. The positive lead of the speaker should be connected to the collector of the transistor, and the negative lead should be connected to the ground.
Now, when you provide audio input to the base of the transistor, it will amplify the signal and play it through the speaker. You can experiment with different values for your resistors to get different levels of amplification. Just be sure not to exceed the power rating of your transistor.
With a little bit of effort, you can easily build a speaker amplifier at home using just a few simple electronic components.
How do you make a 12-volt amp?
You’ll need:
- a 12V power supply;
- a transistor;
- two resistors;
- some wires;
- a breadboard (optional);
Instructions:
- First, you need to connect the power supply to the Collector of your transistor. Then, you need to connect one resistor from the base of your transistor to the ground;
- After that, you need to take another wire and connect it from the Emitter of your transistor to the ground;
- Finally, you’ll want to connect your last resistor from the power supply to the Emitter of your transistor;
- If you want, you can also add an LED indicator by connecting it between the base and the ground;
What is the difference between a transistor and an amplifier?
The purpose of an amplifier is to increase the signal. A circuit and components are called amplifiers (elements).
The transistor is a component that, when utilized in a certain way, acts as an electronic amplifier.
Although most electronic amplifiers are made out of transistors, not all amplifiers include only transistors [5].
An amplifier takes a small input signal and produces a much larger output signal. The amount of amplification provided by an amplifier is measured by its gain. Gain is usually expressed in terms of the ratio of output voltage to the input voltage, or output power to input power.
There are two types of amplifiers: voltage amplifiers and current amplifiers. Voltage amplifiers amplify the voltage of a signal, while current amplifiers amplify the current of a signal. Most transistor circuits are voltage amplifiers.
A transistor can be used as an amplifier in one of two ways: a common emitter or a common collector. The common emitter is the most popular configuration and will be discussed here. In a common emitter amplifier circuit, the transistor is configured so that the input signal is applied to the base, and the output signal is taken from the collector.
The transistor acts as a current amplifier, meaning that it amplifies the current flowing through it. The amount of current amplification is determined by the transistor’s beta (β). Beta is a measure of how much a transistor amplifies the current flowing through it.
Why is a transistor used?
The transistor is used as an amplifier because it can control the amount of current that flows through a circuit. By controlling the current, the transistor can amplify a signal.
A transistor can be used as an amplifier in two ways:
- As an active component in amplifying circuits such as audio power amplifiers and oscillators;
- As a switch to turn electronic devices on and off;
When used as an amplifier, transistors are usually operated in one of three regions: cut-off, saturation, or linear.
In the cut-off region, the transistor is turned off and no current flows through it. This is also known as the “OFF” state.
In saturation mode, the transistor is turned “ON” and maximum current flows through it.
In linear mode, the transistor is turned “ON” but only enough current flows through it to allow a linear change in voltage. Linear mode is also known as the “active” region.
Transistors can be used as amplifiers because they can control the amount of current that flows through a circuit. By controlling the current, the transistor can amplify a signal.
How can a PNP transistor be used as an amplifier?
A PNP transistor can be used as an amplifier in a circuit by connecting the collector to the positive voltage supply, and the emitter to the ground. The base is connected to the input signal. When a small current flows through the base, it allows a larger current to flow through the collector-emitter circuit. This amplifies the input signal [6].
This method of using a transistor as an amplifier is called common-collector amplification. It is often used for audio signals because it has low distortion and high impedance levels. It is also used for RF (radio frequency) signals because it can handle high frequencies well. In general, though, any type of signal can be amplified using this method.
Why is the transistor used as a switch?
The transistor is used as a switch because it can control the flow of electricity. When the transistor is turned on, the electricity can flow through it and when it is turned off, the electricity cannot flow through it. This makes it ideal for use in amplifiers because it can be used to control the amount of amplification that is taking place [7].
Another reason why the transistor is used as a switch is that it can be used to create an electronic circuit. By connecting two transistors together, you can create a circuit that will allow you to control the flow of electricity. This can be useful for creating amplifiers or other electronic devices.
Finally, the transistor is also used as a switch because it is relatively easy to manufacture.
Does a transistor amplify current or voltage?
A transistor is a current-controlled current amplifier. As a result, it does not increase voltage but rather amplifies current.
However, to introduce electrical energy into a transistor without any voltage is impossible. As a result, we bias the transistor appropriately such that we may provide input current for amplification.
What are the basic components required to make a transistor amplifier?
To make a transistor amplifier, you will need the following basic components: a transistor (NPN or PNP), resistors, capacitors, a power supply, and an audio source (e.g., microphone or music player).
How do I choose the right transistor for my amplifier project?
Selecting the appropriate transistor for your amplifier project depends on the power requirements and the type of amplifier circuit you want to build. Consider factors such as voltage and current ratings, power dissipation, and the gain (hFE) of the transistor.
What is the difference between NPN and PNP transistors in amplifier circuits?
NPN and PNP transistors are used differently in amplifier circuits. NPN transistors are commonly used for low-side switching and amplification, while PNP transistors are used for high-side switching and amplification. The polarity and current flow through the transistors are opposite in NPN and PNP types.
How can I bias a transistor for amplifier operation?
Biasing a transistor is essential to ensure it operates in the active region for amplification. You can use a voltage divider network with resistors to provide the correct biasing voltage at the transistor’s base terminal.
Can I use a single transistor to build an audio amplifier?
Yes, you can build a simple audio amplifier using a single transistor. This is typically known as a Class A amplifier and is suitable for low-power applications. However, for higher power and efficiency, you may need to use multiple transistors in amplifier configurations like Class AB or Class D.
What are the common amplifier configurations using transistors?
Some common amplifier configurations using transistors are:
– Common Emitter (CE) configuration: Offers high voltage gain but medium input and output impedance.
– Common Collector (CC) configuration: Provides voltage gain close to unity with high input and low output impedance.
– Common Base (CB) configuration: Offers high input impedance but low voltage gain.
How can I prevent thermal issues in my transistor amplifier?
Thermal issues can arise when the transistor dissipates excessive power. To prevent this, use heat sinks on the transistors, ensure proper ventilation, and avoid operating the amplifier at its maximum ratings for extended periods.
Can I use an operational amplifier (op-amp) instead of a transistor for amplification?
Yes, you can use an op-amp for amplification as it’s designed specifically for this purpose. Op-amps have high gain, high input impedance, and low output impedance, making them suitable for many amplifier applications.
What safety precautions should I follow while making a transistor amplifier?
When working with transistors and amplifiers, observe the following safety precautions:
– Disconnect the power supply when making connections or modifications.
– Double-check your circuit connections to avoid short circuits.
– Choose appropriate resistors and components to prevent excessive currents.
– Be cautious of high voltages that may be present in the circuit.
How can I test and troubleshoot my transistor amplifier circuit?
To test and troubleshoot your transistor amplifier circuit, you can use a multimeter to measure voltages and currents at various points. Check for loose connections, damaged components, and incorrect wiring. Using an oscilloscope, you can also visualize the input and output waveforms to identify potential issues.
Useful Video: Audio Amplifier using Transistor
References:
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transistor
- https://www.instructables.com/How-to-Make-Audio-Amplifier-Using-D882-Transistor/
- https://www.elprocus.com/transistor-as-an-amplifier-circuit-diagram-and-its-working/
- https://www.instructables.com/Make-your-first-Serious-Amplifier/
- https://www.elprocus.com/transistor-as-an-amplifier-circuit-diagram-and-its-working/
- https://circuitdigest.com/article/pnp-transistor
- https://www.allaboutcircuits.com/textbook/semiconductors/chpt-4/transistor-switch-bjt/














Leave a Reply