Dielectric grease is a versatile and valuable product known for its ability to provide electrical insulation and protection to various electrical connections and components. Its non-conductive properties make it an ideal choice for safeguarding spark plug boots, battery terminals, electrical connectors, and light bulb sockets from moisture, corrosion, and oxidation.
While dielectric grease plays a crucial role in maintaining the integrity and longevity of electrical systems, improper application or excess use can lead to challenges such as attracting dirt, hindering proper electrical conductivity, and affecting overall performance. Therefore, understanding how to remove dielectric grease effectively becomes essential in ensuring the proper functioning of electrical components.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore step-by-step methods to remove dielectric grease from various components and surfaces safely. By following these techniques, you can maintain the cleanliness and optimal performance of your electrical connections while avoiding potential issues associated with excessive grease application. Let’s delve into the process of effectively cleaning dielectric grease to keep your electrical systems in top-notch condition.
What Is Dielectric Grease?

Physical Properties
You can identify dielectric grease by its physical properties, which make it unique from other lubricants:
- Firstly, dielectric grease is electrically insulating, meaning it cannot conduct an electricity current;
- Also, this water-resistant lubricant keeps moisture out of electrical connections. As a result, it lowers the possibility of corrosion, which leads to costly repairs;
- Dielectric grease is also non-conductive, non-curing, and silicone-based;
Ingredients
Dielectric grease is made up of several ingredients, including silicone oil, a thickening agent, and a softener. There are two types of dielectric grease- silicone-based and synthetic.
Silicone-based dielectric greases are composed of around 70% silicone oil, which makes them useful for high-heat applications, such as spark plug boots, ignition parts, and other engine applications.
Synthetic dielectric grease, on the other hand, is made up of a combination of several synthetic chemicals that provide lubrication while offering electrical insulation. Synthetic dielectric grease is also known for working on a wider range of temperatures than silicone-based grease.
Cautions
As with any lubricant, there are precautions to take when handling dielectric grease.
Firstly, it is important to know that dielectric grease is not suitable for use with bearings and other moving parts because it doesn’t provide enough lubrication as and when required.
Secondly, using too much dielectric grease can lead to an increase in temperatures. In it turn, it leads to a spike in resistance. As a result, this leads to an electrical breakdown. Thirdly, when applying dielectric grease, ensure that it doesn’t affect other parts of the equipment, such as sensors, switches, or cooling systems.
Lastly, we should remember that dielectric grease should be used to coat the surface of the materials and not be applied like a paste. This will help to prevent it from building up and attracting dust and other particles.
What Does Dielectric Grease Do?
Dielectric grease is a versatile and essential product used in various industries and applications, from automotive maintenance to electronics. This non-conductive lubricant serves a specific and crucial purpose – to protect electrical connections and components from moisture, corrosion, and other environmental factors. In this post, we will explore what dielectric grease does and why it is an important tool in many fields.
Electrical Insulation and Protection
One of the primary functions of dielectric grease is to provide electrical insulation. When applied to electrical connections, it forms a protective barrier that prevents current leakage and short circuits. The grease’s non-conductive properties ensure that electricity does not flow through it, maintaining the integrity and efficiency of the electrical system.

Moisture and Corrosion Resistance
Moisture is a significant enemy of electrical systems. It can seep into connectors, terminals, and other electrical parts, leading to rust and corrosion. Dielectric grease creates a water-resistant seal around electrical connections, safeguarding them from the harmful effects of moisture. By preventing the formation of rust and corrosion, the grease helps maintain the electrical system’s performance and prolongs its lifespan.
Preventing Oxidation
Electrical connections are susceptible to oxidation, which occurs when metals react with oxygen in the air. Oxidation can cause poor conductivity and result in signal degradation or even failure of electrical components. Dielectric grease acts as a protective barrier against oxygen exposure, reducing the likelihood of oxidation and ensuring the smooth flow of current through the system.
Temperature Resistance
Dielectric grease is designed to withstand a wide range of temperatures, making it suitable for use in both hot and cold environments. It remains stable and effective even in extreme conditions, preventing it from melting or evaporating at high temperatures or becoming stiff and ineffective at low temperatures.
Anti-Fouling Properties
In some applications, such as marine environments, electrical systems are at risk of fouling by debris, salt water, or other contaminants. Dielectric grease’s anti-fouling properties help repel such substances, keeping electrical connections clean and free from harmful deposits.
Lubrication
Apart from its electrical insulating properties, dielectric grease also acts as a lubricant. When applied to moving parts, it reduces friction and wear, ensuring the smooth operation of mechanical components associated with electrical systems.
How To Use Dielectric Grease?
Dielectric grease is a versatile and valuable product known for its ability to protect electrical connections from moisture, corrosion, and other environmental factors. It is commonly used in automotive, electrical, and marine applications.

If you’re wondering how to use dielectric grease effectively, follow these steps to ensure proper application and optimal protection:
Step 1: Identify the Appropriate Areas for Application
Before applying dielectric grease, identify the electrical connections and components that require protection. These may include spark plug boots, battery terminals, electrical connectors, light bulb sockets, and any other exposed electrical connections.
Step 2: Clean the Surfaces
For the best results, it is essential to work with clean and dry surfaces. Use a cleaning solution or isopropyl alcohol to remove any dirt, debris, or existing grease from the electrical connections. Ensure that the components are completely dry before proceeding to the next step.
Step 3: Apply the Dielectric Grease
Using a clean and disposable applicator, such as a brush or a cotton swab, apply a thin layer of dielectric grease to the surfaces of the electrical connections. Be sure to cover the metal contacts and any exposed parts thoroughly. Remember that a little goes a long way – you don’t need to apply a thick coat.
Step 4: Avoid Excessive Grease
While dielectric grease is beneficial, using too much of it can be counterproductive. Excessive grease can attract dirt and debris, potentially leading to more significant issues over time. Therefore, use it sparingly and only on the appropriate surfaces.
Step 5: Reassemble the Components
Once you have applied the dielectric grease, reassemble the electrical components carefully. Make sure all connections are secure and properly seated. For spark plug boots or connectors, push them firmly into place to ensure a tight fit.
Step 6: Wipe Off Excess Grease
If you accidentally apply too much dielectric grease, wipe off the excess with a clean, lint-free cloth. Leaving excess grease on the surface may not only attract contaminants but also cause a messy appearance.
Step 7: Test the System
After reassembly, test the electrical system to ensure everything is working correctly. Turn on the engine, and check lights and other electrical components to verify that the dielectric grease has not impeded any functionality.
Step 8: Reapply Periodically
Dielectric grease does not last indefinitely, especially in harsh environments. To maintain optimal protection, reapply the grease periodically, especially after performing maintenance that requires disconnecting electrical connections [2].

Pros of Dielectric Grease
Dielectric grease offers numerous advantages and is widely used in various industries due to its unique properties. Here are some of the key pros of dielectric grease:
- Electrical Insulation: One of the primary advantages of dielectric grease is its ability to provide electrical insulation. It forms a non-conductive barrier between electrical connections and components, preventing current leakage and short circuits. This property is crucial for maintaining the integrity and safety of electrical systems;
- Moisture and Corrosion Resistance: Dielectric grease is highly effective in protecting electrical connections from moisture and corrosion. By creating a water-resistant seal around the connections, it helps to prevent rust and corrosion, which can compromise the performance and lifespan of electrical components;
- Oxidation Prevention: Electrical connections are susceptible to oxidation, leading to poor conductivity and potential failure. Dielectric grease acts as a protective barrier against oxygen exposure, reducing the likelihood of oxidation and ensuring consistent current flow;
- Temperature Stability: Dielectric grease is designed to withstand a wide range of temperatures, making it suitable for both hot and cold environments. It remains stable and effective even in extreme conditions, providing continuous protection to electrical components;
- Versatility: This type of grease is versatile and can be used in various applications, including automotive, electrical, marine, and electronic systems. It is compatible with a wide range of materials, making it suitable for different types of connectors and terminals;
- Anti-Fouling Properties: In marine or harsh environments, electrical connections are prone to fouling by debris and contaminants. Dielectric grease’s anti-fouling properties help repel such substances, keeping electrical components clean and functional;
- Longevity and Maintenance: By protecting electrical connections from environmental factors, dielectric grease helps extend the lifespan of electrical components. It reduces the need for frequent maintenance and replacements, saving time and money in the long run;
- Lubrication: Apart from its electrical insulation properties, dielectric grease also acts as a lubricant when applied to moving parts. It reduces friction and wear, ensuring smooth operation and extending the life of mechanical components associated with electrical systems;
- Easy Application: Applying dielectric grease is a straightforward process, and it doesn’t require special tools or equipment. It can be easily spread using a brush, cotton swab, or your fingers, making it accessible to both professionals and DIY enthusiasts;
- Prevents “Fretting Corrosion”: Fretting corrosion is a phenomenon that occurs when small movements or vibrations cause corrosion at electrical contact points. Dielectric grease helps prevent fretting corrosion, making it particularly useful in applications with moving parts or connections subject to vibrations;
Is Dielectric Grease Conductive?
No, dielectric grease is not conductive. In fact, its primary characteristic is its non-conductivity, which makes it an ideal insulating material for electrical connections and components.

Its non-conductive property is what makes dielectric grease effective in safeguarding electrical systems from moisture, corrosion, and other environmental factors. By creating a barrier that blocks the flow of electricity, it ensures that the current follows the intended path through the conductive metal components of the electrical connections rather than taking an unintended route through the surrounding materials.
Because of this property, dielectric grease is commonly used to protect spark plug boots, battery terminals, electrical connectors, light bulb sockets, and other exposed electrical connections in automotive, electronic, marine, and various other applications.
From Where Can You Remove Dielectric Grease?
To remove dielectric grease, you should focus on cleaning it from the areas where it was applied in excess or where its presence may interfere with proper electrical conductivity. While dielectric grease is non-conductive and serves as an insulating material for electrical connections, too much grease in certain areas can attract dirt, dust, and debris, potentially causing performance issues.
Here are some common areas where you might want to remove excess dielectric grease:
- Spark Plug Boots: Dielectric grease is often used on the inside of spark plug boots to facilitate easy installation and removal. However, excessive grease can attract carbon deposits and other contaminants, leading to misfires or poor performance. Wipe off any excess grease from the inside of the spark plug boots using a clean cloth or a cotton swab;
- Battery Terminals: While it’s beneficial to apply dielectric grease to battery terminals to prevent corrosion, applying too much can lead to a buildup of grime and inhibit proper electrical contact. Clean off any excess grease from the battery terminals using a cloth or a wire brush;
- Electrical Connectors: When applying dielectric grease to electrical connectors, it’s important to use it sparingly. Excessive grease can create a messy appearance and attract dirt. Wipe away any visible excess grease from the connectors carefully;
- Light Bulb Sockets: Dielectric grease can be applied to light bulb sockets to protect against corrosion and promote easy removal. However, too much grease can trap dirt and affect the connection between the bulb and the socket. Clean off any visible excess grease from light bulb sockets;
- Switches and Potentiometers: If you have applied dielectric grease to switches or potentiometers to reduce friction and wear, be cautious not to apply too much as it may interfere with their functionality. Remove any excess grease carefully, especially around the moving parts;
- Mechanical Components: If you used dielectric grease as a lubricant for mechanical parts associated with electrical systems, ensure that you remove any excess grease that might have accumulated. Too much grease could attract debris and hinder smooth operation [3];
Remember that dielectric grease should not be removed from the intended areas where it provides electrical insulation and protection. It is meant to stay on the external surfaces of electrical connections and components to prevent moisture, corrosion, and other environmental factors from affecting their performance.
How To Remove Dielectric Grease: Effective Methods
1. Safety First
Before starting the removal process, ensure the power source is disconnected to prevent any electrical accidents. For automotive applications, disconnect the battery or relevant power sources to avoid the risk of electrical shock.
2. Gather the Necessary Tools
To effectively remove dielectric grease, gather the following tools:
- Clean lint-free cloths or paper towels;
- Cotton swabs;
- Soft-bristled brush;
- Isopropyl alcohol (rubbing alcohol) or a suitable solvent;
3. Assess the Components
Begin by assessing the components or areas where dielectric grease needs to be removed. Focus on areas where the grease was applied in excess or where its presence may interfere with proper electrical contact or mechanical functionality.

4. Mechanical Components and Switches
For mechanical components, such as bearings or hinges, where dielectric grease was used as a lubricant, start by wiping away visible excess grease using clean cloths or paper towels. Be gentle and avoid dislodging any critical mechanical parts.
For switches and potentiometers, use cotton swabs slightly dampened with isopropyl alcohol to carefully clean the areas where the grease was applied. Ensure the alcohol evaporates completely before reassembling the components.
5. Battery Terminals
Dielectric grease is commonly used on battery terminals to prevent corrosion. To remove excess grease, follow these steps:
- Disconnect the battery;
- Use a soft-bristled brush to gently scrub the terminals, loosening any built-up grease and dirt;
- Wipe away the loosened grease and debris using a clean cloth or paper towel;
If necessary, dampen a cloth or cotton swab with isopropyl alcohol and wipe the terminals to further clean and remove any remaining grease.
6. Spark Plug Boots
Dielectric grease is often applied to the inside of spark plug boots to facilitate easy installation and removal. To clean spark plug boots:
- Carefully remove the spark plug boots from the spark plugs. Twist and pull gently to avoid damaging the wires;
- Use a cotton swab with isopropyl alcohol to clean the inside of the spark plug boots thoroughly. This will help remove the excess grease and any accumulated debris;
- Let the boots air dry or use a clean cloth to dry them before re-assembling;

7. Electrical Connectors and Light Bulb Sockets
For electrical connectors and light bulb sockets, where dielectric grease was used to protect against moisture and corrosion, follow these steps:
Use a clean cloth or paper towel to wipe away visible excess grease from the connectors and sockets.
Dampen a cotton swab or cloth with isopropyl alcohol and gently clean the areas where the grease was applied. Ensure no residue is left behind.
8. Cleaning Small Components
For small components or areas with tight spaces, use a cotton swab soaked in isopropyl alcohol to carefully clean and remove the dielectric grease.
9. Repeat as Necessary
For stubborn or hard-to-reach areas, you may need to repeat the cleaning process. Be patient and avoid using abrasive tools or excessive force, as this could damage delicate components.
10. Inspect and Reassemble
After completing the cleaning process, inspect the components to ensure all excess dielectric grease has been removed. Once you are satisfied with the cleanliness, reassemble the components carefully.
11. Proper Disposal
Dispose of used cleaning materials and excess dielectric grease properly. Check local regulations for guidelines on the disposal of chemical products.

12. Preventing Excessive Grease
To prevent excessive dielectric grease in the future, apply it sparingly and only to the external surfaces of electrical connections and components. Follow manufacturer recommendations and guidelines for the proper use of dielectric grease in each application.
Where Should You Not Use Dielectric Grease?
While dielectric grease is a valuable product with numerous advantages for protecting electrical connections and components, there are specific areas and applications where it should not be used. Knowing where not to use dielectric grease is essential to avoid potential issues and ensure the proper functioning of electrical systems.
Here are some situations where you should avoid using dielectric grease:
- Metal-to-Metal Contact Points: Dielectric grease is non-conductive, which means it can inhibit electrical current flow. Therefore, it should not be used on metal-to-metal contact points where electrical conductivity is required for proper functioning. Examples of such areas include electrical contacts inside switches, relays, and connectors. Applying dielectric grease to these contact points may interfere with the flow of electricity, leading to malfunctions or failures;
- Electrical Contacts Requiring Low Resistance: In some applications, low electrical resistance is crucial for efficient operation. For instance, in high-current applications like battery cables or high-power connectors, using dielectric grease can increase resistance and cause voltage drop, reducing the overall performance of the system. In such cases, specialized conductive greases or electrical contact enhancers should be used instead;
- Oxygen Sensors: Dielectric grease should not be used on oxygen sensors in automotive applications. Oxygen sensors require a clean, unobstructed surface to function accurately. Applying dielectric grease to oxygen sensors can interfere with their readings and potentially lead to incorrect fuel mixture calculations, affecting engine performance and emissions;
- ABS Brake Systems: Avoid using dielectric grease on the sensors and connectors of Anti-Lock Braking Systems (ABS) in vehicles. Dielectric grease may interfere with the ABS sensors’ ability to detect wheel speed accurately, potentially compromising the effectiveness of the ABS system;
- Electrical Connection Pins in Sensitive Devices: In sensitive electronic devices, such as smartphones, computers, and other gadgets, avoid applying dielectric grease to the connection pins or circuit boards. The grease may interfere with the precise electrical connections and disrupt the device’s functionality;
- Threads and Fasteners: Dielectric grease is not a suitable lubricant for threads and fasteners. Instead, use appropriate lubricants designed for such applications, as dielectric grease may not provide the necessary characteristics required for securing threaded components properly;
- Rubber and Plastic Components: Dielectric grease may cause some rubber or plastic components to swell or deteriorate over time. Avoid applying the grease to rubber seals, gaskets, or plastic parts, as it could potentially compromise their integrity;
- High-Temperature Environments: While dielectric grease is generally temperature-resistant, it may not be suitable for extremely high-temperature environments. In these situations, use specialized high-temperature greases that can withstand the extreme heat [4];
Always refer to the manufacturer’s guidelines and specifications before applying dielectric grease or any other lubricant or protectant. It’s essential to use the right product for the specific application to ensure optimal performance and reliability of the electrical system or device. When in doubt, consult a professional or an expert in the relevant field to determine the most suitable lubricant or insulating material for your particular needs.
How Do You Clean Dielectric Grease on Connectors?
Cleaning dielectric grease on connectors requires a careful and thorough approach to ensure the removal of excess grease without damaging the electrical components.
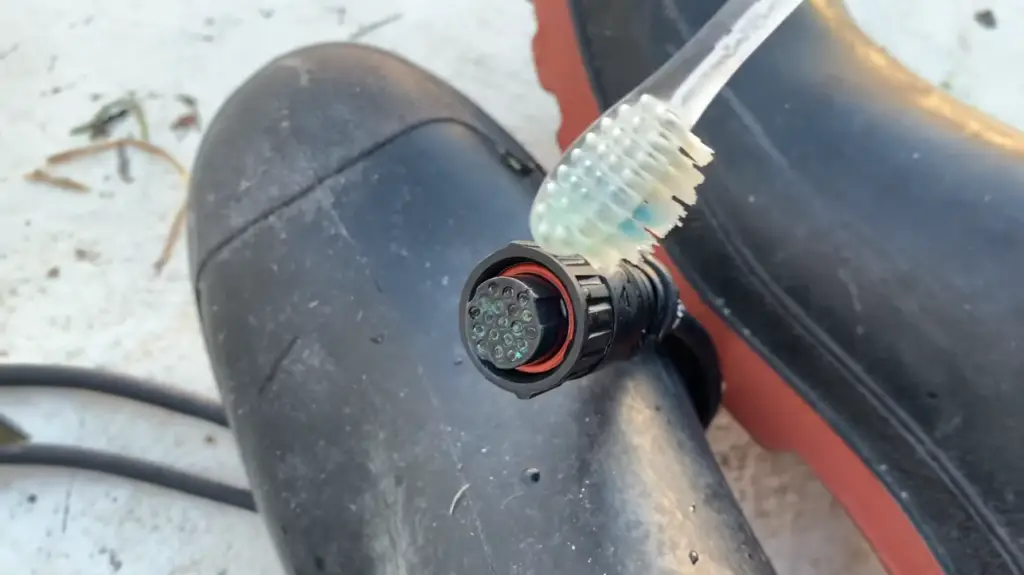

Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to clean dielectric grease on connectors effectively:
Tools and Materials Needed:
- Clean lint-free cloths or paper towels;
- Cotton swabs;
- Isopropyl alcohol (rubbing alcohol) or a suitable solvent;
- Soft-bristled brush (optional);
Step 1: Safety First
Before starting the cleaning process, ensure the power source is disconnected to prevent any electrical accidents. For automotive applications, disconnect the battery or relevant power sources to avoid the risk of electrical shock.
Step 2: Assess the Connectors
Examine the connectors to identify areas where dielectric grease was applied. Focus on spots where the grease is visible or might have been applied in excess.
Step 3: Wipe Away Excess Grease
Use a clean lint-free cloth or paper towel to wipe away visible excess grease from the connectors. Gently dab the cloth on the grease to avoid spreading it further.
Step 4: Use Cotton Swabs
Dampen a cotton swab with isopropyl alcohol (or a suitable solvent if recommended by the manufacturer) and carefully clean the areas where the dielectric grease was applied. Swab the connectors to remove the grease thoroughly.
Step 5: Be Gentle
Handle the connectors with care to avoid bending or damaging the pins or terminals. Be gentle when cleaning, especially if the connectors are delicate or have fine contact points.
Step 6: Brushing (Optional)
If necessary, use a soft-bristled brush to gently scrub the connectors and loosen any grease residue. Ensure the brush is clean and free from debris to prevent contamination.
Step 7: Remove All Residue
Continue using fresh cotton swabs and isopropyl alcohol until all traces of dielectric grease are removed from the connectors. Be patient and thorough to achieve a clean surface.
Step 8: Allow Drying
Allow the connectors to air dry or use a clean, dry lint-free cloth to wipe off any remaining alcohol. Ensure that the connectors are completely dry before reassembly.
Step 9: Reassemble Carefully
Once the connectors are clean and dry, reassemble them carefully. Make sure the connections are secure and seated properly.
Step 10: Dispose of Materials Properly
Dispose of used cleaning materials and excess dielectric grease properly. Check local regulations for guidelines on the disposal of chemical products [5].
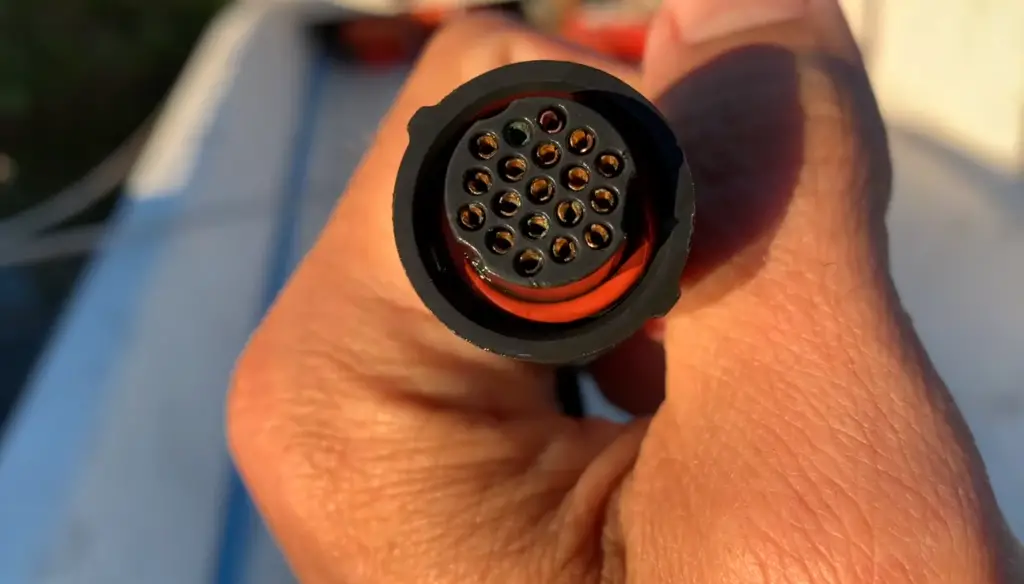

Is Dielectric Grease Oil Soluble?
Dielectric grease is typically not oil-soluble. It is specifically formulated to have low solubility in oil and water, which is one of the reasons it is effective in protecting electrical connections from moisture and other environmental factors.
The non-solubility of dielectric grease allows it to remain in place and form a protective barrier even in the presence of moisture, oil, or other contaminants. When applied to electrical connections and components, it adheres to the surfaces and does not easily wash away or dissolve, providing long-lasting protection against moisture, corrosion, and oxidation.
However, while dielectric grease is not oil-soluble, it is compatible with some types of oils and greases. For example, it can be used in conjunction with some lubricating oils or greases in certain applications to provide both electrical insulation and lubrication. In such cases, it is crucial to ensure that the specific oil or grease used is compatible with the dielectric grease to avoid any adverse reactions.
It is essential to follow the manufacturer’s recommendations and guidelines when using dielectric grease in combination with other lubricants or substances. Always use the appropriate type of grease or lubricant for the specific application to ensure optimal performance and protection of electrical connections and components.
Can You Use Too Much Dielectric Grease After Removing?
Yes, using too much dielectric grease after removing the excess can still be problematic.
While dielectric grease serves as an excellent insulator and protective barrier for electrical connections and components, applying an excessive amount can lead to several issues:
- Messy Appearance: Too much dielectric grease can create a messy appearance on the connectors and surrounding areas. Excess grease may ooze out and attract dirt, dust, and debris, potentially causing more problems in the long run;
- Interference with Electrical Functionality: Dielectric grease, when applied excessively, can get in the way of proper electrical contact between connectors. This may lead to poor conductivity and affect the performance of the electrical system;
- Attracting Contaminants: Excessive grease can attract contaminants, such as dirt and dust, which can lead to clogging and interference with the proper functioning of electrical components;
- Heat Retention: Applying too much grease can lead to heat retention around connectors, particularly in high-temperature environments. This can potentially affect the performance and reliability of sensitive electrical systems;
To avoid these issues, it’s crucial to apply dielectric grease in moderation. A thin and even layer is generally sufficient to provide the necessary insulation and protection for electrical connections. If you have previously removed excess grease, be mindful not to overcompensate by adding too much during reapplication.
What’s the Difference Between Dielectric Grease and Lubricating Grease?
Dielectric grease and lubricating grease are two distinct types of greases, each designed for specific purposes and applications. While both are greases and share some common characteristics, they serve different functions and have different properties.

Here are the key differences between dielectric grease and lubricating grease.
Dielectric Grease:
- Electrical Insulation: The primary purpose of dielectric grease is to provide electrical insulation and protect electrical connections and components from moisture and corrosion. It is non-conductive and prevents current leakage, making it ideal for use on spark plug boots, battery terminals, electrical connectors, and light bulb sockets;
- Non-Conductive: Dielectric grease has high resistance to electrical current flow, which means it does not conduct electricity. This property ensures that it does not interfere with the proper functioning of electrical systems;
- Water and Moisture Resistance: Dielectric grease is effective in repelling water and moisture, protecting electrical connections from rust and corrosion caused by exposure to environmental elements;
- Temperature Stability: It is designed to withstand a wide range of temperatures, ensuring its effectiveness in various conditions;
- Used in Low-Friction Applications: While dielectric grease offers some lubrication properties, it is not intended for heavy-duty lubrication and is not suitable for high-friction mechanical components;
Lubricating Grease:
- Lubrication: The primary purpose of lubricating grease is to provide lubrication and reduce friction between moving parts. It is used in mechanical applications to prevent wear, minimize heat buildup, and ensure smooth operation of various components;
- Various Types: Lubricating greases come in various formulations, each designed for specific applications and environments. Some are designed for high-temperature conditions, while others are formulated for extreme-pressure applications;
- Conductive or Non-Conductive: The electrical conductivity of lubricating grease depends on its specific formulation. Some greases are conductive and should not be used in electrical applications, while others are non-conductive and may be suitable for certain electrical connections;
- Appropriate for Mechanical Components: Lubricating grease is used on bearings, gears, sliding surfaces, hinges, and other mechanical parts that require lubrication to reduce friction and wear;
- Not Suitable for Electrical Insulation: Lubricating grease is not suitable for providing electrical insulation and should not be used on electrical connections where dielectric properties are required;
FAQ:
1. How to apply dielectric grease to a spark plug boot?
To apply dielectric grease to a spark plug boot, follow these steps:
- Ensure the engine is cool and the ignition is off;
- Carefully remove the spark plug boot from the spark plug by gently twisting and pulling it;
- Clean the inside of the boot and the spark plug terminal with a cloth or paper towel to remove any dirt or debris;
- Apply a thin layer of dielectric grease to the inside of the spark plug boot. Use a clean disposable applicator, such as a brush or a cotton swab, to spread the grease evenly;
- Reinsert the spark plug boot onto the spark plug terminal, making sure it is seated securely;
2. Does dielectric grease improve a connection?
Yes, dielectric grease can improve a connection by providing electrical insulation and protecting electrical connections from moisture, corrosion, and oxidation. It helps maintain the integrity and efficiency of the electrical system by preventing current leakage and short circuits.
3. Is Vaseline a dielectric grease?
Vaseline (petroleum jelly) is often used as a substitute for dielectric grease, but it is not the same. While it can provide some level of protection and lubrication, it is not specifically formulated as a dielectric grease and may not offer the same level of electrical insulation and protection.
4. Is dielectric grease necessary?
Dielectric grease is not always necessary for every electrical connection, but it is highly recommended for critical components and areas exposed to moisture or harsh environments. It is particularly useful in automotive applications, marine electronics, outdoor electrical connections, and electrical systems prone to corrosion.
5. Can dielectric grease cause a short?
Dielectric grease is non-conductive, so it will not cause a short circuit in electrical connections. On the contrary, it helps prevent shorts by insulating and protecting the connections from moisture and contaminants.
6. What happens if you use too much dielectric grease?
Using too much dielectric grease can lead to a messy appearance and may attract dirt and debris. Excessive grease may also interfere with electrical contact in certain applications, potentially affecting conductivity.
7. How do you get dielectric grease off your hands?
To remove dielectric grease from your hands, wash them thoroughly with soap and warm water. You may also use a degreasing hand cleaner or rubbing alcohol to help dissolve the grease.
8. What is the solvent for dielectric grease?
Isopropyl alcohol (rubbing alcohol) is a commonly used solvent for removing dielectric grease from surfaces and hands.
9. Does dielectric grease melt?
Dielectric grease is designed to withstand a wide range of temperatures, but it has a relatively high melting point. It will not melt under normal operating conditions but may soften at very high temperatures.
10. Is dielectric grease safe for electronics?
Yes, dielectric grease is safe for electronics. Its non-conductive properties make it suitable for protecting electrical connections and components without interfering with their functionality.
11. What is the best way to remove grease residue?
The best way to remove grease residue is to use a suitable solvent, such as isopropyl alcohol, and gently wipe the surface with a clean cloth or paper towel.
12. How long does dielectric grease last?
Dielectric grease has a long shelf life and can last several years if stored properly. When applied to electrical connections, it can provide protection for an extended period, but it may require reapplication over time, especially in harsh environments.
13. How do you clean grease off?
To clean grease off surfaces, use a suitable solvent or degreaser and wipe the area with a cloth or paper towel. Rinse with water or follow the manufacturer’s instructions if necessary.
14. Is dielectric grease just silicone grease?
Dielectric grease is a type of silicone-based grease. While not all silicone greases are dielectric greases, all-dielectric greases are silicone-based and have non-conductive properties.
15. Is WD40 a dielectric grease?
No, WD-40 is not a dielectric grease. WD-40 is a multi-purpose lubricant and water displacement product, but it is not specifically designed for electrical insulation or protection.
16. Is it ok to put dielectric grease on battery terminals?
Yes, it is okay to apply dielectric grease to battery terminals. It helps prevent corrosion and ensures good electrical conductivity between the battery terminals and the connecting cables.
17. Should you put dielectric grease on plug wires?
Yes, it is common to apply dielectric grease to the inside of spark plug boots or the spark plug wire terminals. It aids in easy installation and removal and protects against moisture and corrosion.
18. Can you put dielectric grease on USB?
Dielectric grease is not typically used on USB connectors. USB connectors are designed to fit snugly, and adding grease may interfere with their proper connection.
19. What is the opposite of dielectric grease?
The opposite of dielectric grease would be a conductive grease that allows electrical current to flow through it.
20. Does rubbing alcohol remove grease?
Yes, rubbing alcohol can be effective in removing grease from surfaces, including hands and tools.
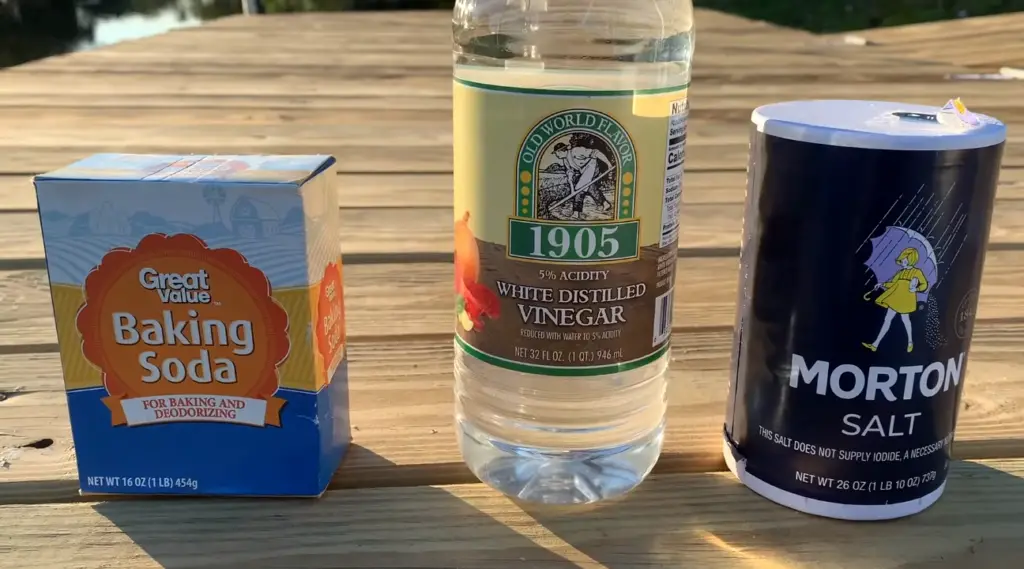
21. Does baking soda remove grease?
Baking soda can help absorb and lift grease stains, making it useful for removing grease from surfaces when combined with water or other cleaning agents.
22. Is lithium grease a dielectric?
Lithium grease is generally not a dielectric grease. Some types of lithium grease may have conductive properties, making them unsuitable for electrical insulation.
23. Can grease be dissolved in water?
No, grease is not soluble in water. Grease is a non-polar substance and does not mix with water. Special degreasers or solvents are needed to dissolve and remove grease effectively.
Useful Video: How Not to use Dielectric grease!
References
- https://www.circuitsgallery.com/how-to-remove-dielectric-grease
- https://www.overclockers.com/forums/threads/any-decent-way-to-remove-dielectric-grease.440586/
- https://holesbaymarine.co.uk/catalog/media/F53DEL3GOJSW4Y3INVQXE2LOMUXW2ZLENFQS6YTNMUXUOQKZIRBVQQSRI5LE6RCDJ5FFUR22J5CUWVCTG5DUKMSBFZYGIZQ
- https://www.thedrive.com/maintenance-repair/39173/dielectric-grease
- https://www.aboutmechanics.com/what-is-dielectric-grease.htm












Leave a Reply