If you’re in the market for a capacitor, you may have come across the terms “radial” and “axial.” But what do these terms mean, and which type of capacitor is right for your needs?
In this guide, we will answer common questions about radial and axial capacitors and help you decide which type is best for your project.
What Are Radial Capacitors?
The leads will be spaced evenly around the circumference of the capacitor and typically have rounded ends for easier connection to a circuit board.
Radial capacitors are generally the most common type of capacitor and can be used in a wide range of applications.
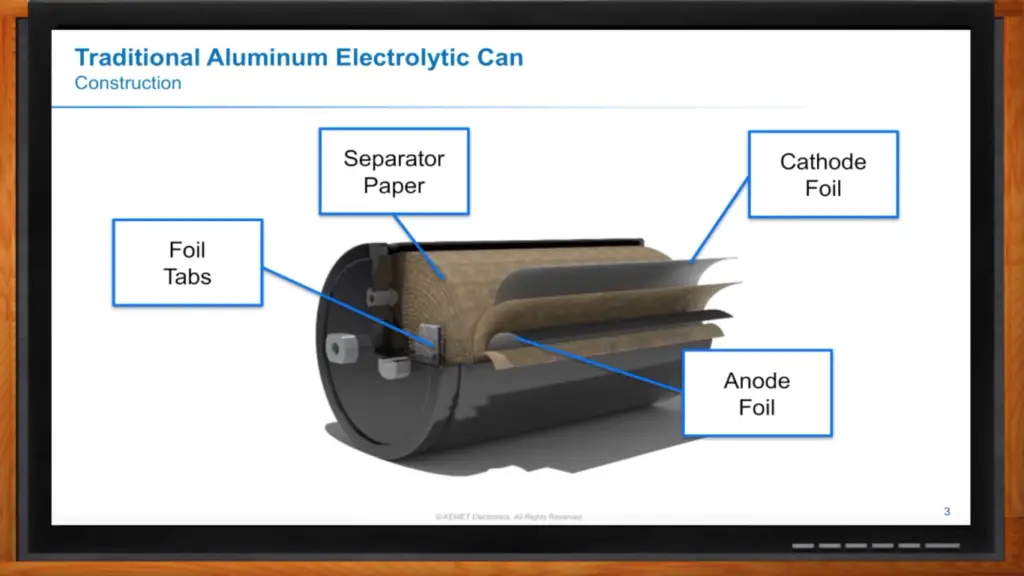
What Are Axial Capacitors?
Axial capacitors are also called leaded capacitors. They have two or more leads that go on opposite sides of the capacitor. The leads will often be sharp so they can go into a circuit board easily.
Axial capacitors are not as common as radial capacitors and they usually cost more money. But sometimes axial capacitors can be better than radial capacitors in certain situations.
Which Type of Capacitor Is Right For You?
When deciding between radial and axial capacitors, you should consider the application. Radial capacitors are generally cheaper and easier to work with than axial capacitors. However, if space is a concern or you need higher precision accuracy, then an axial capacitor may be the better option.
As a result, it’s important to consider your needs and budget before making your decision.
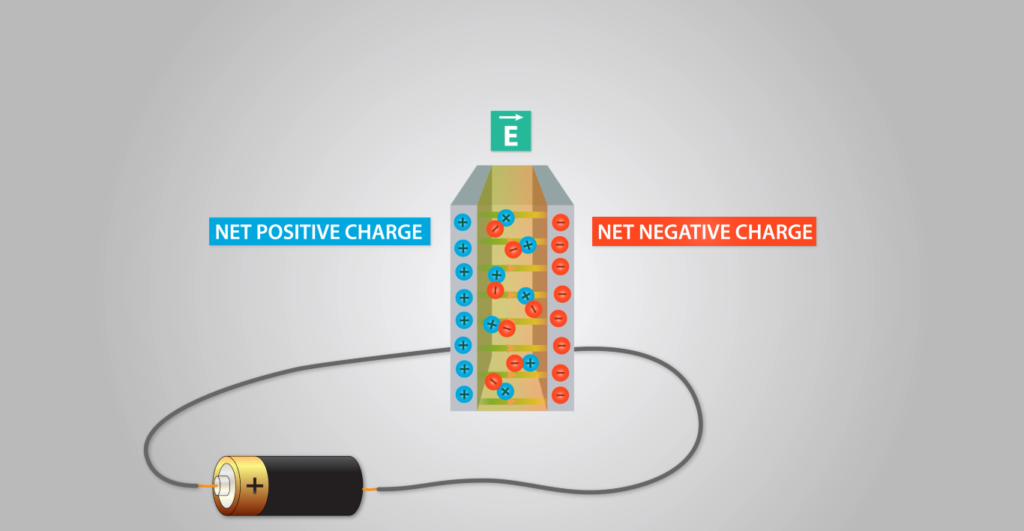
Radial vs. Axial Capacitors
Axial components
Radial capacitors are usually the most common type of capacitor. They are smaller in size, so they can be used in a lot of different applications. Radial capacitors have two or more leads that come out of the same side of the capacitor, and these leads are spaced evenly around the circumference. Axial capacitors, also known as leaded capacitors, have two or more leads that come out of opposite sides of the capacitor. [1]
Radial components
Radial capacitors are usually cheaper and easier to work with than axial capacitors. They have rounded ends, so they can be connected easily to a circuit board. However, radial capacitors may not provide the accuracy or space savings of an axial capacitor in certain applications. [1]
Configuration
When selecting a capacitor for your project, you should consider the configuration of the capacitor. Radial capacitors are easier to work with because they have two or more leads located on the same side of the capacitor body. Axial capacitors can be more difficult to connect due to their sharp leads and opposite-side orientation.
Type of Capacitor
The type of capacitor you choose will also come into play when deciding between radial and axial capacitors.
Equivalent Series Inductance (ESL)
The equivalent series inductance (ESL) of a capacitor is an important factor to consider when selecting a capacitor. The ESL of a capacitor indicates how much inductance it adds to the circuit. Radial capacitors usually have lower ESL than axial components, so they may be a better option in certain applications.
Price
Price can often be a deciding factor when choosing between radial and axial capacitors. Radial capacitors are usually cheaper and easier to work with, while axial components usually cost more money. It’s important to weigh all the factors before making your decision.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Radial vs Axial Capacitors
The major advantage of radial capacitors is their lower cost and easier assembly process compared to axial components. They are also smaller in size, which makes them great for space-constrained projects. Radial capacitors may not provide the accuracy or ESL of an axial capacitor, however.
Axial capacitors have more precision and a lower ESL than radial components. However, they are usually more expensive and harder to work with because of their sharp leads and opposite-side orientation. They are also more susceptible to mechanical stress, so they are not suitable for applications that require a lot of physical movement.
Can I Replace Axial Capacitor with Radial?
Sometimes it is possible to replace an axial capacitor with a radial one. But this should be done carefully, because the shapes and sizes of the capacitors may not be compatible.
It’s also important to consider any differences in ratings and performance between the two components. Before making any changes, always consult a professional or the manufacturer’s specifications.
There are benefits and drawbacks to both radial and axial capacitors. Radial capacitors are usually cheaper and easier to use, but they may not have the accuracy or ESL of an axial capacitor.
Axial capacitors, on the other hand, have more precision and a lower ESL but they are usually more expensive and difficult to use. When selecting a capacitor for your project, make sure to think about all the factors before making your decision! [1]
What Are the 4 Types of Capacitors?
There are four types of capacitors: electrolytic, ceramic, film and tantalum. Each type has different features that make it useful for different applications.
- Electrolytic capacitors often have a large capacity compared to the other types and are used in power supplies, decoupling circuits and filtering applications.
- Ceramic capacitors offer high stability and low cost, making them a popular choice for resonant circuits.
- Film capacitors have low ESL and provide excellent temperature stability, making them great for frequency-dependent applications.
- Finally, tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance per volume and can withstand large temperatures, making them ideal for harsh environments.
No matter what type of capacitor you’re looking for, there is sure to be one that fits your application. Consider all the factors before making your decision!
FAQ
Can I replace the axial capacitor with radial?
Sometimes it is possible to replace an axial capacitor with a radial one. But this should be done carefully, because the shapes and sizes of the capacitors may not be compatible.
It’s also important to consider any differences in ratings and performance between the two components. Before making any changes, always consult a professional or the manufacturer’s specifications.
What is the difference between axial and radial components?
Axial capacitors have more precision and a lower ESL than radial components. However, they are usually more expensive and harder to work with because of their sharp leads and opposite-side orientation.
They are also more susceptible to mechanical stress, so they are not suitable for applications that require a lot of physical movement. Radial capacitors are their lower cost and easier installation.
What is an axial capacitor?
They work by storing energy in an electric field between two metal plates. This makes them good for filtering signals or storing energy.
Axial capacitors are often more precise and have lower ESL than radial components, making them ideal for frequency-dependent applications. However, they are generally more expensive and harder to install.
What is the difference between different types of capacitors?
There are four main types of capacitors: electrolytic, ceramic, film and tantalum. Each type has different features that make it useful for different applications.
- Electrolytic capacitors often have a large capacity compared to the other types and are used in power supplies, decoupling circuits and filtering applications.
- Ceramic capacitors offer high stability and low cost, making them a popular choice for resonant circuits.
- Film capacitors have low ESL and temperature stability, making them good for frequency-dependent applications.
- Tantalum capacitors offer high capacitance per volume and can withstand large temperatures, making them ideal for harsh environments.
When selecting a capacitor type for your project, consider all the factors before making your decision.
Do axial capacitors have polarity?
Axial capacitors have polarity, meaning the current must flow in direction. If it doesn’t, the capacitor might be damaged. The positive and negative leads of the capacitor are usually marked with a “+” and “-” symbol respectively. It is important to connect them according to the manufacturer’s instructions.
How do I choose the right capacitor?
You need to choose the right capacitor for your needs. Think about what type of capacitor you need, its rating, stability and temperature range. Also think about the size and shape of the component so you know if it will fit in your circuit.
Finally, consider cost and any other features that are important to you. Once you have considered all these factors, you can make an informed decision on which capacitor to select.
Does it matter what capacitor you use?
Yes, it is important to choose the right capacitor for your application. Different types of capacitors have different characteristics, such as their size and shape, ratings, temperature range and stability.
It is important to select a capacitor that will fit in your circuit and operate within its rated specifications. If you use the wrong type of capacitor, it may not be able to meet the demands of your application and could cause damage.
It is important to consider any differences in ratings or performance between two components before making changes. Always consult a professional or the manufacturer’s specifications when selecting your capacitor. This will help you make sure that you are making the best decision for your needs.
Which capacitor is more powerful?
The power of a capacitor depends on its capacity (how much it can store), voltage rating (the amount of electricity it can hold) and temperature range (the temperatures it can work in). Generally, if any of these values are higher, the capacitor will have more power.
For example, a capacitor with a large capacitance or high voltage rating will be better able to store energy than one with lower values. Similarly, a capacitor with a wide temperature range is better suited for use in a range of environments.
The size and type of capacitor are also important factors to consider when choosing one. Larger capacitors can store more energy than smaller ones.
Is it OK to oversize a capacitor?
It is OK to choose a capacitor that is larger than what you need. This will allow the capacitor to store more energy and provide better performance in certain applications. However, if you choose too large of a capacitor, it may not fit in your circuit or be too expensive. So it is important to select the right size for your circuit.
What capacitors last the longest?
Generally, ceramic capacitors last longer than other types because they can withstand higher temperatures and are less affected by changes in voltage.
Electrolytic capacitors should also be considered when looking for long-term reliability as they are designed to handle higher voltages and have a higher capacitance.
However, electrolytic capacitors have limited temperature ranges and can be more sensitive to voltage changes, so it is important to choose one with the right specifications for your needs.
Does it matter what capacitor you use?
Yes, it is important to select the right capacitor for your application. Different types of capacitors have different characteristics and ratings, so make sure you select one that meets your needs. Consider the size, shape and rating of the component to ensure it will fit in your circuit.
Additionally, always consult with a professional or read the manufacturer’s specifications before making any changes. This will help you make sure that your capacitor is up to the task and can handle the voltage and current required.
Useful Video: What Does Axial & Radial Compliance Mean?
Conclusion
Radial capacitors have one or more leads coming off of the cylindrical body of the capacitor. Axial capacitors have a lead that runs through the length of the capacitor. Both types are used in electronic circuits, but for different applications.
Radial capacitors are typically used in power supplies, while axial capacitors are often found in RF circuits. Hopefully this article has helped clear up any confusion about radial and axial capacitors. Thanks for reading!
References
- https://www.circuitsgallery.com/radial-vs-axial-capacitors/
- https://www.asourcingelectronics.com/article/industry-news/axial-vs-radial.html













Leave a Reply