When it comes to the operation and maintenance of an air conditioning (AC) system, understanding the role of components like the AC capacitor is essential. Among the common questions that arise is whether a new AC capacitor needs to be charged before it can be fully functional.
The capacitor plays a crucial role in the AC system, providing the initial electrical boost required to start the compressor motor. In this article, we will delve into the concept of charging a new AC capacitor, exploring the reasons behind it, the charging process, and the importance of properly charging the capacitor for optimal system performance.
By understanding the intricacies of capacitor charging, homeowners and HVAC technicians can ensure the efficient operation of AC systems and avoid potential issues down the line.
What Is an AC Capacitor?
An AC capacitor, also known as an air conditioning capacitor, is an essential component of an air conditioning system [1]. It is a small cylindrical device that stores and releases electrical energy. The capacitor plays a crucial role in the operation of the AC unit by providing an extra surge of power to start the motor and helping to maintain a stable flow of electricity throughout the system.
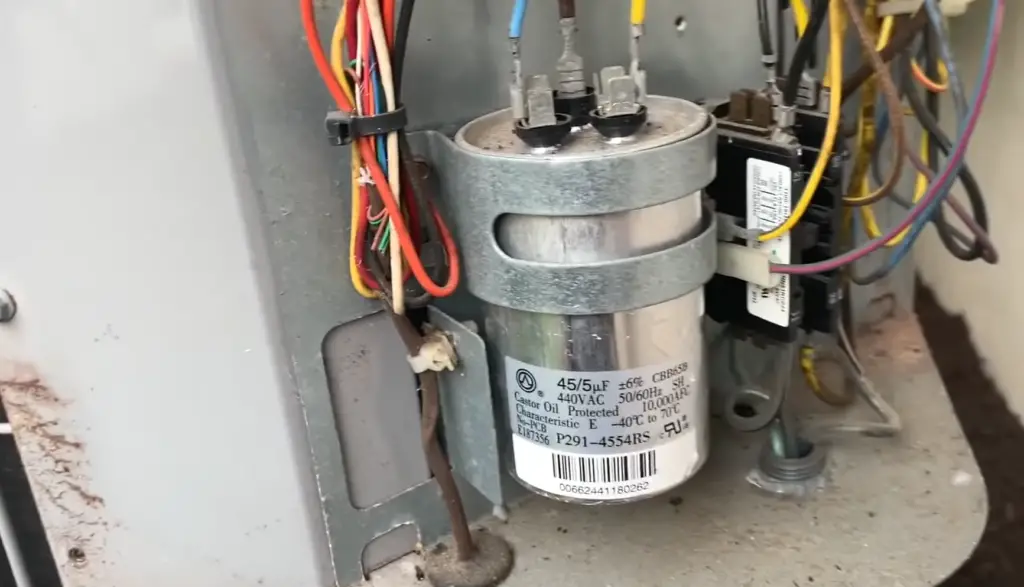

What Does an AC Capacitor Do?
Furthermore, the AC capacitor helps to maintain a continuous flow of electricity by stabilizing the voltage and regulating the current. It stores energy during the electrical cycle and releases it during the cycle’s off periods. This process helps to ensure that the motor runs smoothly and that the system operates efficiently.

Signs Of A Bad AC Capacitor
Like any other component, AC capacitors can wear out or become defective over time. Some common signs of a bad AC capacitor include:
- Failure to start: If your air conditioning system fails to start or experiences difficulty starting, it could be a sign of a faulty capacitor. The capacitor may no longer be providing the necessary power boost to initiate the motor;
- Humming sound: A malfunctioning capacitor may emit a humming or buzzing sound. This noise is often an indication that the capacitor is struggling to function correctly;
- Hot or bulging capacitor: Capacitors should remain relatively cool during normal operation. If you notice that your capacitor feels excessively hot to the touch or appears bulged or swollen, it is likely damaged and needs to be replaced;
- Frequent tripping of circuit breaker: A faulty capacitor can cause the circuit breaker to trip repeatedly. This occurs when the capacitor’s malfunction disrupts the electrical flow, leading to an overload and subsequent tripping of the breaker;
- Poor cooling performance: A failing capacitor may result in reduced cooling capacity or uneven cooling throughout your home. If you notice a decline in your AC system’s performance, the capacitor could be to blame;

What Happens When an AC Capacitor Fails?
When an AC capacitor fails completely, the air conditioning system will cease to function. The motor will not start, and the fan will not circulate air. Without the necessary electrical energy from the capacitor, the system cannot operate efficiently or at all.
In some cases, a failed capacitor may cause additional damage to the compressor or other components of the air conditioning system. Without the initial power surge provided by the capacitor, the motor may strain to start, leading to overheating and potential motor burnout. This can result in costly repairs or the need for a complete system replacement.

How Long Does an AC Capacitor Last?
However, certain circumstances, such as power surges, extreme temperatures, and excessive vibration, can shorten its lifespan.
Regular maintenance and periodic inspections by a professional HVAC technician can help identify any signs of wear or impending failure. It is advisable to replace a capacitor proactively if it shows signs of aging or damage to avoid sudden system breakdowns [2].

Does A New AC Capacitor Need To Charge?
No, a new AC capacitor does not need to charge before installation. Capacitors are passive devices that store electrical energy but do not require a charging process. Once properly installed, the capacitor is ready to function immediately.
However, it is essential to ensure that the replacement capacitor matches the specifications of the original one. Capacitors have specific voltage and capacitance ratings that must be compatible with the air conditioning system. Using an incompatible capacitor can lead to further damage or system malfunctions.

How Long Does It Take an AC Capacitor To Charge?
As mentioned earlier, capacitors do not require charging. Once the air conditioning system is turned on, the capacitor immediately begins storing and releasing electrical energy as needed. Therefore, there is no specific time required for an AC capacitor to charge.

However, it is worth noting that capacitors can retain an electrical charge even after the system is turned off. This stored charge can present a safety hazard if proper precautions are not taken during maintenance or replacement. It is recommended to discharge the capacitor before handling or working on it to prevent the risk of electric shock.
How Long Does It Take For An AC Capacitor To Discharge?
The discharge time of an AC capacitor can vary depending on its capacitance and the specific discharge path. In general, it is advisable to allow at least 5 minutes for a capacitor to discharge fully after the power to the system has been turned off [3].
To discharge the capacitor safely, it is essential to follow specific procedures recommended by HVAC professionals. This typically involves using a specialized discharge tool or shorting the capacitor terminals with an insulated screwdriver to ensure the safe dissipation of any stored electrical charge.

Tips For Prolonging The Life Of Your AC Capacitor:
- Regular maintenance: Schedule regular maintenance visits with a qualified HVAC technician who can inspect and clean the capacitor, as well as other components of the air conditioning system. This can help identify any potential issues before they escalate into major problems;
- Keep the unit clean: Keep the outdoor unit free from debris, such as leaves, dirt, or grass clippings. Regularly clean the unit to prevent blockages and ensure proper airflow;
- Avoid overworking the system: Excessive use of the air conditioning system can put strain on the capacitor and other components. Use programmable thermostats or timers to regulate the system’s operation and avoid unnecessary wear;
- Protect against power surges: Install surge protectors or consider using a whole-house surge protector to safeguard the air conditioning system from voltage spikes that can damage the capacitor;
- Maintain stable power supply: Unstable or fluctuating power supply can be detrimental to the lifespan of the capacitor. If you live in an area with frequent power outages or voltage fluctuations, consider using a voltage stabilizer or installing a power conditioner to regulate the incoming power;
FAQ:
1. How to determine if you have a bad AC capacitor and need a replacement?
To determine if you have a bad AC capacitor and need a replacement, you can look out for the following signs:
- Failure to start: If your air conditioning system does not start or struggles to start, it could indicate a faulty capacitor. The capacitor provides the initial electrical boost to the motor, so if it is not functioning correctly, the system may not start;
- Humming sound: A malfunctioning capacitor may produce a humming or buzzing sound. This noise occurs when the capacitor is struggling to operate effectively;
- Hot or bulging capacitor: A damaged or faulty capacitor may feel excessively hot to the touch or appear bulged or swollen. These physical changes indicate that the capacitor has likely failed and needs to be replaced;
- Frequent circuit breaker tripping: A bad capacitor can cause the circuit breaker to trip repeatedly. The malfunction disrupts the electrical flow, leading to an overload and subsequent tripping of the breaker;
- Poor cooling performance: If you notice reduced cooling capacity or uneven cooling throughout your home, it could be a sign of a failing capacitor. The capacitor helps maintain the proper functioning of the motor, and its failure can impact the system’s cooling performance;
2. How often should you replace an AC capacitor?
The frequency of AC capacitor replacement can vary depending on various factors, including usage patterns, operating conditions, and the quality of the capacitor. On average, a well-maintained capacitor can last between 10 to 20 years [4].
However, it is important to note that capacitors can fail prematurely due to factors such as power surges, extreme temperatures, or excessive vibration. Regular maintenance and inspections by a professional HVAC technician can help identify signs of wear or impending failure. If your capacitor shows signs of aging or damage, it is recommended to replace it proactively to prevent sudden system breakdowns.
3. Can I charge a capacitor with AC?
No, you cannot charge a capacitor with AC directly. Capacitors are passive components and do not charge using AC power directly. They require a DC (direct current) voltage source to charge.
Typically, capacitors are charged by connecting them to a DC power source or by being part of an electrical circuit that converts AC power to DC power, such as a rectifier or power supply.
4. Do you need to discharge the AC capacitor?
Yes, it is essential to discharge the AC capacitor before handling or working on it. Capacitors can retain an electrical charge even after the power to the system is turned off, and this charge can be dangerous if not discharged properly.
To discharge the capacitor safely, it is recommended to follow specific procedures recommended by HVAC professionals. This may involve using a discharge tool designed for capacitors or shorting the capacitor terminals with an insulated screwdriver to ensure the safe dissipation of any stored electrical charge.
5. Will the AC fan run if the capacitor is bad?
No, the AC fan may not run or may run at a reduced speed if the capacitor is bad. The capacitor provides the necessary electrical boost to start the fan motor and keep it running at the desired speed. If the capacitor is faulty, it may not provide the required electrical energy, causing the fan to either fail to start or run inadequately.
6. Do you have to charge a new capacitor?
No, you do not have to charge a new capacitor before installation. Capacitors are passive devices and do not require a charging process. Once a new capacitor is properly installed, it is ready to function immediately.
However, it is crucial to ensure that the replacement capacitor matches the specifications of the original one. Capacitors have specific voltage and capacitance ratings that must be compatible with the air conditioning system. Using an incompatible capacitor can lead to further damage or system malfunctions.
7. How long does an AC capacitor need to charge?
AC capacitors do not require a specific charging time. Once the air conditioning system is turned on, the capacitor immediately starts storing and releasing electrical energy as needed. Therefore, there is no specific duration for an AC capacitor to charge.
However, it is worth mentioning that capacitors can retain an electrical charge even after the system is turned off. It is recommended to allow at least 5 minutes for a capacitor to discharge fully after the power to the system has been turned off before working on or handling it [5].
8. How long does it take for a start capacitor to charge?
The charging time for a start capacitor can vary depending on its capacitance and the specific circuit it is part of. Typically, start capacitors charge rapidly, within a fraction of a second, as they are designed to provide a quick burst of power to start the motor. Once the motor starts, the start capacitor’s function diminishes, and it transitions to its dormant state.
9. How long should I wait to turn the AC on after replacing the capacitor?
After replacing the capacitor, it is generally advisable to wait for at least 24 hours before turning the AC on. This waiting period allows the new capacitor to settle in and stabilize within the system.
However, it is recommended to consult the manufacturer’s guidelines or seek advice from a professional HVAC technician for specific instructions regarding the waiting period after capacitor replacement.
10. Do capacitors stay charged?
Capacitors can retain an electrical charge even after the power source is disconnected. The stored charge in a capacitor can remain for a certain duration depending on various factors such as capacitance, resistance, and the discharge path. However, over time, capacitors will discharge naturally.
To ensure safety, it is important to assume that a capacitor may still hold a charge until it is properly discharged or confirmed to be discharged using appropriate testing equipment.
11. What happens if you charge a capacitor for too long?
Charging a capacitor for too long can cause it to exceed its voltage rating, leading to potential damage or failure. When a capacitor is charged beyond its intended voltage, it can result in the breakdown of the dielectric material inside the capacitor, which can lead to short circuits, leakage, or even an explosion in extreme cases.
It is crucial to adhere to the manufacturer’s specifications and recommended charging procedures to prevent overcharging and potential damage to the capacitor.
12. Is it ok to run AC with a bad capacitor?
Running an AC system with a bad capacitor is not recommended. A faulty capacitor can cause the AC system to operate inefficiently, result in poor cooling performance, or even lead to system breakdown.
Moreover, a bad capacitor may put additional stress on other components of the air conditioning system, such as the compressor, potentially causing further damage.
It is advisable to have a faulty capacitor replaced promptly by a professional HVAC technician to ensure the smooth operation and longevity of the air conditioning system.
13. What is the lifespan of an AC capacitor?
The lifespan of an AC capacitor can vary depending on several factors, including the quality of the capacitor, operating conditions, and usage patterns. On average, a well-maintained capacitor can last between 10 to 20 years.
However, certain factors, such as power surges, extreme temperatures, and excessive vibration, can shorten the lifespan of a capacitor. Regular maintenance and periodic inspections by a professional HVAC technician can help identify signs of wear or impending failure. Proactive replacement of an aging or damaged capacitor can help prevent sudden system breakdowns.
14. Why do AC capacitors fail so often?
AC capacitors can fail more frequently due to various reasons, including:
- Aging: Over time, capacitors can degrade and lose their effectiveness due to constant electrical stress and environmental factors;
- Power surges: Voltage spikes or power surges caused by lightning strikes, utility company issues, or electrical malfunctions can damage capacitors;
- Overheating: Exposure to high temperatures can cause the dielectric material inside capacitors to break down, leading to failure;
- Voltage fluctuations: Unstable or fluctuating voltage levels can put additional strain on capacitors, leading to premature failure;
- Manufacturing defects: Occasionally, capacitors may have manufacturing defects that make them more prone to failure;
- Excessive vibration: Excessive vibrations caused by motor operation or poor installation can impact the internal components of capacitors and contribute to their failure;
15. Can an AC capacitor go bad after 2 years?
Yes, it is possible for an AC capacitor to go bad after 2 years. While capacitors can have a lifespan of 10 to 20 years under normal conditions, certain factors such as power surges, voltage fluctuations, extreme temperatures, or manufacturing defects can lead to premature failure.
16. Why is my AC still not cooling after replacing the capacitor?
If your AC is still not cooling after replacing the capacitor, there could be other underlying issues affecting the system’s performance. It is possible that the initial problem was not solely due to a faulty capacitor.
Some possible reasons for the continued lack of cooling could include:
- Compressor issues: The compressor may be malfunctioning or not operating optimally, impacting the cooling process;
- Refrigerant leak: A refrigerant leak can result in insufficient cooling as the system may not have enough refrigerant to transfer heat effectively;
- Airflow restrictions: Issues such as blocked air filters, clogged ducts, or malfunctioning blower fans can restrict the airflow, reducing cooling efficiency;
- Thermostat problems: A malfunctioning thermostat can cause incorrect temperature readings or improper system operation;
In such cases, it is recommended to contact a professional HVAC technician to diagnose and address the underlying cause of the cooling issue.
17. Can a bad AC capacitor ruin the compressor?
Yes, a bad AC capacitor can potentially damage the compressor. The capacitor provides the initial electrical boost to start the compressor motor, and if the capacitor is faulty, it may not provide the required energy for a proper startup.
In such instances, the compressor may experience a hard start or struggle to start altogether. The repeated stress on the compressor due to improper startup can lead to motor overheating, decreased efficiency, or even compressor failure.
It is important to address a bad capacitor promptly to prevent potential damage to the compressor and other components of the AC system.
18. What are the two typical signs that a capacitor is bad or has failed?
Two typical signs that indicate a bad or failed capacitor are:
- Bulging or swelling: A capacitor that appears bulged or swollen is a clear indication of a failure. This physical deformation often occurs due to the breakdown of the internal components;
- Leakage or electrolyte presence: If you notice any fluid or electrolyte substance leaking from the capacitor, it is a strong indicator of a failure. Leakage suggests that the internal seals of the capacitor have been compromised;
If you observe these signs, it is advisable to have the capacitor replaced by a professional HVAC technician.
19. Can I charge the capacitor without a resistor?
It is not recommended to charge a capacitor without a resistor or a proper charging circuit. Charging a capacitor directly without a resistor or a suitable charging mechanism can result in a sudden surge of current, potentially causing damage to the capacitor or other components of the circuit.
A resistor is commonly used in conjunction with a capacitor to limit the current flow during the charging process, ensuring a gradual and controlled charge.
20. How do you know if a capacitor is holding a charge?
To determine if a capacitor is holding a charge, you can use a multimeter. Follow these steps:
- Set the multimeter to the voltage measurement mode;
- Ensure that the multimeter is set to a voltage range that is higher than the expected voltage of the capacitor;
- Connect the multimeter leads to the terminals of the capacitor, making sure to observe the correct polarity;
- If the multimeter shows a voltage reading, it indicates that the capacitor is holding a charge. If the voltage reading is zero or close to zero, the capacitor is likely discharged;
Remember to exercise caution and follow proper safety procedures when working with capacitors, as they can store electrical energy and pose a risk of electric shock.
21. Does a capacitor charge or discharge immediately?
A capacitor charges and discharges based on the electrical properties of the circuit it is connected to. When a voltage source is connected to a capacitor, it charges by accumulating electrical energy over time. The rate at which a capacitor charges depends on the capacitance, the resistance in the circuit, and the applied voltage.
Similarly, when the voltage source is disconnected or the circuit is opened, a charged capacitor discharges its stored energy. The discharge process also occurs over a period of time, influenced by factors such as the capacitance and the resistance in the discharge path.
22. How do I make sure my capacitor is discharged?
To ensure that a capacitor is discharged before handling or working on it, follow these safety measures:
- Turn off the power supply to the circuit or equipment where the capacitor is installed;
- Use an insulated screwdriver with a shorting tip or a specific discharge tool designed for capacitors;
- Carefully touch the metal part of the screwdriver or the discharge tool to both terminals of the capacitor simultaneously, creating a short circuit between the terminals;
- Hold the shorting connection for a few seconds to allow the stored charge to dissipate;
- Always exercise caution and treat capacitors as if they are charged until properly discharged or confirmed to be discharged using appropriate testing equipment;
23. How do you find out if a capacitor is charged without discharging it?
Determining if a capacitor is charged without discharging it requires specialized equipment, such as a voltmeter or a digital multimeter.
Here’s how you can check if a capacitor is charged without discharging it:
- Set the voltmeter or multimeter to the voltage measurement mode;
- Connect the positive (red) lead of the meter to the positive terminal of the capacitor and the negative (black) lead to the negative terminal;
- Read the voltage displayed on the meter. If the voltage reading is above zero, it indicates that the capacitor is charged;
Keep in mind that working with charged capacitors can be dangerous. Exercise caution, follow safety procedures, and consider seeking professional assistance when working with capacitors.
24. What are three common faults with capacitors?
3 common faults with capacitors are:
- Short circuit: A short circuit occurs when the dielectric material inside the capacitor breaks down, allowing the current to flow freely between the capacitor’s terminals. This fault can lead to excessive current flow, system malfunctions, or damage to other components;
- Open circuit: An open circuit fault refers to a broken or disconnected connection within the capacitor, resulting in a discontinuity in the flow of current. An open circuit fault renders the capacitor unable to perform its intended function;
- Leakage: Leakage occurs when the dielectric material or the seals of the capacitor deteriorate, causing the stored charge to leak out. This fault reduces the capacitor’s effectiveness and can impact the overall performance of the circuit;
Capacitors experiencing any of these faults should be replaced with new ones that meet the required specifications. It is recommended to consult with a professional or an experienced technician for proper diagnosis and replacement.
25. Can capacitors last 40 years?
The lifespan of capacitors can vary significantly depending on various factors, including operating conditions, usage patterns, and quality. While some capacitors can last for 40 years or more under ideal conditions, it is not common.
In many applications, capacitors are designed with an expected lifespan of 10 to 20 years. However, certain factors such as voltage fluctuations, power surges, temperature extremes, and manufacturing defects can impact the lifespan of capacitors, potentially reducing their longevity.
Regular maintenance, periodic inspections, and adherence to manufacturer recommendations can help prolong the lifespan of capacitors and ensure their optimal performance.
26. Do capacitors dry up?
Capacitors do not “dry up” in the same sense as liquid evaporating. However, electrolytic capacitors, a type of capacitor commonly used in electronic devices, contain an electrolyte that can evaporate or dry out over time. The drying of the electrolyte can lead to a decrease in the capacitor’s capacitance or even render it non-functional.
The drying out of electrolytic capacitors can be accelerated by exposure to high temperatures, excessive voltage, or aging. It is one of the reasons why electrolytic capacitors have a limited lifespan and may require replacement after several years of use.
27. Should a capacitor have continuity?
No, a capacitor should not have continuity when tested with a multimeter in the continuity mode. Capacitors are designed to store and release electrical energy rather than allowing a continuous flow of current.
In the continuity mode, if you place the multimeter probes across the terminals of a capacitor, it should not produce a continuous beep or show continuity. Instead, the multimeter should display an open circuit or infinite resistance, indicating that the capacitor is not allowing a direct flow of current.
If a capacitor shows continuity, it suggests a fault or a breakdown in the dielectric insulation, and it should be replaced.
28. How do I know if my capacitor is working without a multimeter?
Without a multimeter, you can perform a visual inspection of the capacitor to check for any visible signs of failure, such as bulging, swelling, or leakage of electrolyte.
Inspect the capacitor for physical damage, such as cracks or broken terminals. Additionally, you can perform a “shake test” by gently shaking the capacitor and listening for any rattling sounds, which could indicate loose internal components.
However, it’s important to note that visual inspection alone may not provide a definitive assessment of the capacitor’s functionality. Using a multimeter or seeking assistance from a professional with proper testing equipment is recommended for a more accurate diagnosis.
29. How do you charge a 1 farad capacitor?
Charging a 1-farad capacitor requires a suitable charging circuit. Here’s a general process for charging a capacitor:
- Connect the positive terminal of the capacitor to the positive terminal of the power supply or charging source;
- Connect the negative terminal of the capacitor to the negative terminal of the power supply or charging source;
- Ensure that the power supply or charging source is set to the appropriate voltage required for charging the capacitor;
- Monitor the charging process, and once the capacitor reaches the desired voltage, disconnect the power supply or charging source;
It is important to use a charging circuit that limits the charging current to a safe level and prevents sudden surges that could damage the capacitor or other components. The specific charging requirements may vary based on the capacitor’s specifications, so referring to the manufacturer’s guidelines is advisable.
30. Can you charge a capacitor with a multimeter?
No, a multimeter is not designed to charge a capacitor. A multimeter is primarily used for measuring electrical properties such as voltage, current, and resistance. It is not equipped with the necessary circuitry or components to charge a capacitor safely and effectively.
Charging a capacitor requires a suitable charging circuit that can control the charging current and voltage. It is recommended to use a proper power supply, charging source, or charging circuit that is specifically designed for charging capacitors.
Useful Video: Diagnosing and Replacing a Run Capacitor
References
- https://homequeries.com/does-a-new-ac-capacitor-need-to-charge/
- https://typeset.io/questions/does-a-new-ac-capacitor-need-time-to-charge-2uevl2ki
- https://www.dekkoi.co/post/ac-capacitors
- https://www.doityourself.com/forum/air-conditioning-cooling-systems/620979-does-c-capacitor-need-recharge.html
- https://dfwairconditioning.com/what-is-an-ac-capacitor-and-can-i-replace-mine/














Leave a Reply